Product Description
-Tensioner pulley, tensioner lever, v-ribbed belt set, belt tensioner OE number For CITROEN, FIAT, LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A, PEUGEOT
DESCRIPTION & FITMENT
| OEM NO. | 5751A7 1318336 30650927 30684427 96505424 4M5Q6A228FD 4M5Q6A228FC |
| REF.NO. | INA DAYCO APV1114 GATES T38477 SKF VKM33320 FEBI 37266 |
LINKED VEHICLES
Ford Focus II Kombi 2.0 TDCi DA_ 07.2004-01.2008 1997 ccm, 98 KW, 133 PS
Ford Focus II 2.0 TDCi DA_ 07.2004-01.2008 1997 ccm, 98 KW, 133 PS
Ford Focus C-Max 2.0 TDCi — 10.2003-03.2007 1997 ccm, 98 KW, 133 PS
Ford C-Max 2.0 TDCi DM2 02.2007-09.2571 1997 ccm, 98 KW, 133 PS
Ford Focus C-Max 2.0 TDCi — 10.2003-03.2007 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 307 2.0 HDi 135 3A/C 10.2003-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 407 2.0 HDi 135 6D_ 05.2004-12.2571 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Volvo S40 II 2.0 D MS 01.2004-12.2571 1998 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Volvo V50 2.0 D CZPT 04.2004-12.2571 1998 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 307 Break 2.0 HDi 135 3E 02.2004-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 307 SW 2.0 HDi 135 3H 02.2004-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 407 SW 2.0 HDi 135 6E_ 05.2004-12.2571 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën C4 I 2.0 HDi LC_ 11.2004-07.2011 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën C4 Coupe 2.0 HDi LA_ 11.2004-12.2571 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford Focus II 2.0 TDCi DA_ 07.2004-09.2012 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën C5 2.0 HDi RC_ 09.2004-12.2571 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën C5 Break 2.0 HDi RE_ 09.2004-12.2571 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford Focus II Kombi 2.0 TDCi DA_ 07.2004-09.2012 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 307 CC 2.0 HDi 135 3B 06.2005-12.2008 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford Focus II Stufenheck 2.0 TDCi DA_ 04.2005-09.2012 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 607 2.0 HDi 9D, 9U 09.2005-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford Focus II Cabriolet 2.0 TDCi — 10.2006-07.2011 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Lancia Phedra 2.0 JTD 179 06.2006-11.2571 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Citroën C4 Picasso I 2.0 HDi 138 UD_ 10.2006-08.2013 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 807 2.0 HDi E 06.2006-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Volvo C30 2.0 D — 10.2006-12.2012 1998 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën Jumpy 2.0 HDi 120 — 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Citroën Jumpy 2.0 HDi 140 — 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën Jumpy Kasten 2.0 HDi 120 — 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Citroën Jumpy Kasten 2.0 HDi 140 — 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot Expert Tepee 2.0 HDi 120 VF3V_ 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Peugeot Expert Tepee 2.0 HDi 140 VF3V_ 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot Expert Kasten 2.0 HDi 120 VF3A_, VF3U_, VF3X_ 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Peugeot Expert Kasten 2.0 HDi 140 VF3A_, VF3U_, VF3X_ 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot Expert Pritsche/Fahrgestell 2.0 HDi 120 — 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Peugeot Expert Pritsche/Fahrgestell 2.0 HDi 140 — 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Fiat Scudo 2.0 D Multijet 270_ 01.2007-12.2016 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Fiat Scudo 2.0 D Multijet 270_ 01.2007-12.2016 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Fiat Scudo Kasten 2.0 D Multijet 270_ 01.2007-12.2016 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Fiat Scudo Kasten 2.0 D Multijet 270_ 01.2007-12.2016 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Fiat Scudo Pritsche/Fahrgestell 2.0 D Multijet 270_ 01.2007-12.2016 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Fiat Scudo Pritsche/Fahrgestell 2.0 D Multijet 270_ 01.2007-12.2016 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën C4 Grand Picasso 2.0 HDi 138 UA_ 10.2006-12.2013 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford C-Max 2.0 TDCi DM2 02.2007-09.2571 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën C8 2.0 HDi EA_, EB_ 07.2006-12.2014 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Fiat Ulysse 2.0 D Multijet 179AX 05.2006-06.2011 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Fiat Ulysse 2.0 D Multijet 179AX 05.2006-06.2011 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Lancia Phedra 2.0 D Multijet 179 07.2006-11.2571 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 308 2.0 HDi 4A_, 4C_ 09.2007-12.2013 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford S-Max 2.0 TDCi WA6 11.2007-12.2014 1997 ccm, 85 KW, 115 PS
Citroën C5 2.0 HDi RD_ 02.2008-12.2571 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën C5 Break 2.0 HDi TD_ 02.2008-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford C-Max 2.0 TDCi DM2 02.2008-09.2571 1997 ccm, 81 KW, 110 PS
Peugeot 308 SW 2.0 HDi — 09.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 407 Coupe 2.0 HDi 6C_ 10.2005-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 807 2.0 HDi E 02.2006-12.2017 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Peugeot 407 2.0 HDi 6D_ 08.2008-12.2017 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Peugeot 407 SW 2.0 HDi 6E_ 08.2008-12.2017 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Volvo C70 II Cabriolet 2.0 D — 01.2008-10.2009 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 308 CC 2.0 HDi — 04.2009-12.2017 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Citroën C4 I 2.0 HDi LC_ 07.2008-07.2011 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Citroën C4 Coupe 2.0 HDi LA_ 07.2008-07.2011 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Ford Focus II 2.0 TDCi DA_ 02.2008-07.2011 1997 ccm, 81 KW, 110 PS
Ford Focus II Stufenheck 2.0 TDCi DA_ 02.2008-07.2011 1997 ccm, 81 KW, 110 PS
Ford Focus II Kombi 2.0 TDCi DA_ 02.2008-07.2011 1997 ccm, 81 KW, 110 PS
Peugeot 308 SW 2.0 HDi — 09.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Citroën C5 2.0 HDi 140 RD_ 04.2009-12.2571 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Citroën C5 Break 2.0 HDi 140 TD_ 04.2009-12.2571 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Peugeot 308 CC 2.0 HDi — 04.2009-12.2017 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Peugeot 308 2.0 HDi 4A_, 4C_ 07.2571-12.2017 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Peugeot Expert Tepee 2.0 HDi 120 4×4 VF3V_ 01.2007-12.2017 1997 ccm, 88 KW, 120 PS
Peugeot 508 2.0 HDi — 11.2571-12.2017 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Peugeot 508 SW 2.0 HDi — 11.2571-12.2017 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Ford Galaxy 2.0 TDCi WA6 05.2006-06.2015 1997 ccm, 96 KW, 130 PS
Ford Galaxy 2.0 TDCi WA6 05.2006-06.2015 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Ford S-Max 2.0 TDCi WA6 05.2006-12.2014 1997 ccm, 96 KW, 130 PS
Ford S-Max 2.0 TDCi WA6 05.2006-12.2014 1997 ccm, 103 KW, 140 PS
Ford Galaxy 2.0 TDCi WA6 11.2007-06.2015 1997 ccm, 85 KW, 115 PS
Ford Kuga I 2.0 TDCi — 03.2008-11.2012 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford Kuga I 2.0 TDCi 4×4 — 03.2008-11.2012 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford Galaxy 2.0 TDCi WA6 05.2006-06.2015 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Ford S-Max 2.0 TDCi WA6 05.2006-12.2014 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Citroën C8 2.0 HDi 135 EA_, EB_ 03.2006-12.2009 1997 ccm, 100 KW, 136 PS
Company Details:
HangZhou CZPT Auto Parts Industry Co., Ltd is a family owned company, established in 2005.
As a real, direct and professional manufacture in China, CZPT has grown to become 1 of greatest manfacturer and exporter in Performance parts, include intake system, exhaust system, cooling system, interior&exterior parts etc.
We own a factory located in HangZhou, HangZhou, which has 8000 square meter, tens of machine, 150 workers, 15 person sales team, 5 R&D department. Our customers cover North American, South American, Asia, Middle east and Europe. We export the millions of USD per year. Looking forward to have a nice cooperation with you
Why Choose YiBai?
It’s simple. The YiBai Company is built on delivering more Quality, Reliability, and Value than any other manufacturer. Whether supplying the world’s automakers with reliable OE parts, or developing aftermarket replacement parts at or above spec, YiBai’s line of products are built to deliver superior all-around performance every day.
Aftermarket Parts Built At or Above Specification
The quality of YiBai parts is guaranteed because every component that leaves a YiBai factory has been designed with precision, manufactured to the strictest OE standards or above, and subjected to rigorous safety and performance tests. In the end, it all comes down to quality – that’s what the YiBai name stands for.
Measure Everything for a First Time Fit
Our First Time Fit philosophy attracts attention throughout the automotive world, while our commitment to pushing technology into the future and continually sets us apart around the globe.First Time Fit is a promise that YiBai makes to the aftermarket, by providing products that are OE grade or better – and fits the first time.
Our Service
1. OEM Manufacturing welcome: Product, Package…
2. Sample order
3. We will reply you for your inquiry in 24 hours.
4. After sending, we will track the products for you once every 2 days, until you get the products. When you got the goods, test them, and give me a feedback.If you have any questions about the problem, contact with us, we will offer the solve way for you.
FAQ
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, we pack our goods in neutral white boxes and brown cartons. If you have legally registered patent, we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB CIF, DDU.
Q3. How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take 15 to 20 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q4. What is your sample policy?
A: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the sample cost and the courier cost.
What Is a V-Belt?
A v-belt is a type of belt that provides a continuous motion to the vehicle’s wheels. This type of belt is made of several different components. They usually have a trapezium-shaped cross-section because of its elastomer core. Elastomers are often made of polyurethane or a synthetic rubber with good shock resistance. Sometimes, a v-belt will have 2 sections – cushion rubber and compression rubber.
Link-type V-belt
A laminated link-type V-belt is 1 embodiment of the present invention. The belt comprises individual lamina sections connected longitudinally by studs and tubes, each of which has at least 1 connecting means. The slots in the links allow for a full share of the load to be transferred through the belt, and they also reduce substantially all internal mechanical stresses. The belt is preferably designed to extend substantially the entire width of the machine being driven.
Conventional link-type V-belts are installed between 2 pulleys on the tight side of the V-drive. A wide end of a link moves in the direction of rotation, while the stud of a second, smaller link pulls the nose end of the third link forward. The shank of the stud pivots on a solid fabric located in hole 2 of the third link below. The bottom link, however, curls over the stud and the belt is assembled.
The present invention offers an improved method of forming a link-type V-belt. The belt is manufactured using links and does not have to be fitted as tightly as conventional link-type V-belts. This belt is flexible and strong enough to handle normal tension loads in a well-designed drive. In addition, the belts made using the present invention will have a longer life, thereby extending the drive’s load-carrying capacity.
Classical V-belt
A classical trapezoidal belt profile makes the VB Classical V-belt ideal for various industrial applications. Available in small sizes from 5mm to 3mm, these belts are available with cogged or raw edges. Their highly engineered construction makes them ideal for a variety of uses. These belts are commonly used in motors, compressors, milling machines, mixers, and other mechanical devices. To determine the right belt for your application, consider the following factors.
The classic v-belt is the most common and economically-priced type of v-belt. They are manufactured using special formulated rubber reinforced with polyester cords. These belts can span from 16 inches to 400 inches in length. The classic V-belt is also very easy to replace. The belt’s outer diameter and pitch can be measured. The length is typically standardized by the Association for Rubber Product Manufacturers.
Typically, classical V-belts are used in single-belt drives. Because they don’t require lubrication or maintenance, these belts are often available in sizes A and B. However, larger belt sizes are rarely used for single-belt drives. In such cases, multiple A or B belts are an economical alternative to single-belt C. In addition, narrower-profile V-belts provide higher power ratings than conventional V-belts because of their higher depth-to-width ratio. These belts are ideal for heavy-duty applications.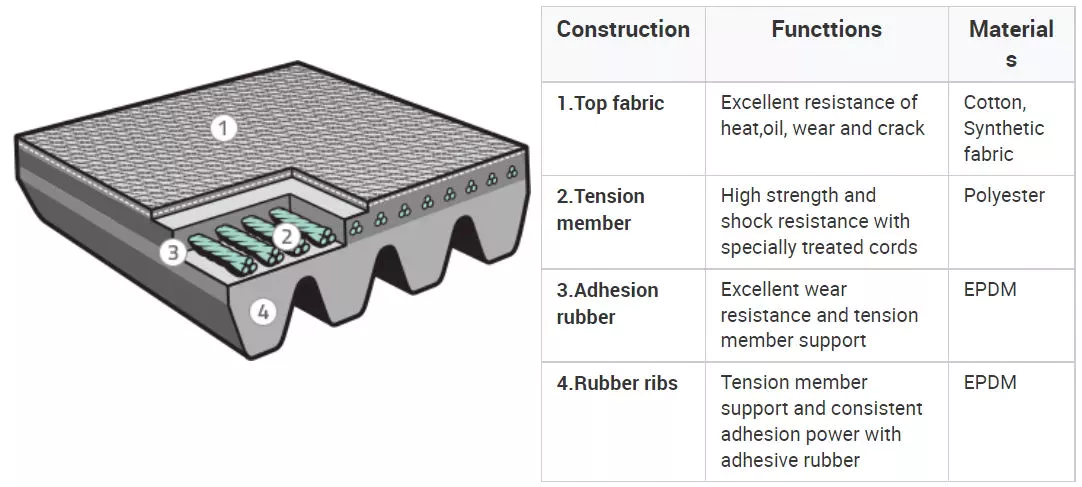
Narrow V-belt
The narrow v-belt is the same as a conventional v-belt, but it has a smaller top and bottom width. This makes it suitable for higher horsepower applications, and it is used in high-end sports cars. Narrow v-belts are generally characterized by a letter “v” on the top side and a length of outside dimensions of 1.6:1.
The steel wires that comprise the core of the v-belt are endless and are free of joints. This provides the strength required for torque transmission. A base rubber compound is placed around the steel wire and acts as a medium of compression and shock absorption during power transmission. A plastic layer acts as a protective cover, and provides the rubber with a degree of temperature tolerance. While choosing a narrow v-belt, it is important to keep in mind that there are some disadvantages to a narrow V-belt.
For example, a narrow V-belt is suitable for high-power applications, and may be used in a small assembly space. Its narrow profile also allows it to be space-saving in layout and allows high-speed drives without additional belts. Furthermore, it reduces operating and maintenance costs. It is ideal for applications where space is limited, and a high torque is required. The benefits of a narrow V-belt are plentiful.
Banded belt
Identifying a banded v-belt can be tricky, but there are a few signs that can indicate a possible problem. Cracked belts can be difficult to spot, but they can be an early indicator of a more serious problem. Look for cracked underside edges, worn covers, and misplaced slack. If 1 or more of these factors applies to your belt, you may want to seek a replacement.
Banded v-belts are made with an elastomer core. The main component of this belt is the elastomer, which is used for the band’s flexural strength and shock resistance. It’s sometimes separated into 2 sections, with each section connected to the other by a tension cord. This gives the belt its trapezium cross-section, which increases tensile strength.
The 2 main types of banded v-belts are wrapped or raw edge. Wrapped v-belts have a fiber-covered body while raw edge belts are uncovered. Banded v-belts are often classified by their cross-section, and include: standard v-belt, wedge v-belt, narrow versus double v-belt, cogged v-belt, and double t-belt.
Banded v-belts are popular with commercial applications. Whether you’re looking for a 2V-belt or a large 8V-belt, V-Belt Guys has what you need. We also stock a wide variety of different banded v-belts and can help you find 1 that fits your needs and budget. Take a look at our selection today!
Traditional V-belt
Although a traditional V-belt may be a glorified rubber band, modern variations reflect advances in engineering. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for trouble-free service. When you are replacing a traditional V-belt, be sure to follow these simple steps to ensure its longevity. Read on to learn more. Listed below are the features of each type of V-belt. Identify the type of belt you need by measuring its top width, circumference, and dimensions.
TEC Traditional V-belts have an exceptionally low slip rate and are resistant to high operating temperatures. These types of belts do not experience early belt aging. They are also highly resistant to poor operating conditions. However, the maintenance is more extensive than other types of belts. A typical V-belt part number is B50, which is the cross-section size of a 50-inch belt. The belt’s lifespan is greatly increased because of this feature.
A ribbed V-belt is another option. It has a deeper V than a traditional V-belt. The ribs in this type are narrower and more flexible. These ribs are smaller than the classic V-belt, but they can transmit 3 times as much horsepower. Because they are thinner, these belts are more flexible than traditional V-belts. The thickness of the ribs is less critical.
Metric V-belt
Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.
Metric V-belts are generally more durable than their equivalents made of standard American-sized belts. Metric V-belts are available in many different sizes to fit different machineries. In addition to offering superior load-carrying capacity, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are known for their exceptional flex and stretch characteristics. For optimum performance in textile mills, food processing, and machine tool applications, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are manufactured using a proprietary construction that combines a higher load-carrying capacity with superior flex and stretch.
Metric belts can generate 50% to 100% more horsepower than conventional and classic sectioned belts. This is achieved through improved construction and placement of the cord line. These belts also have unique wedge designs that help them support the cord in motion. However, you must ensure the proper tension when buying a Metric V-belt, because improper tension may damage the belt. They are compatible with both U.S. and international standards.

