Product Description
Product spections :
| Interchange number: | 12568980, 12579981, 12585551, 35719, ALT04013, 49159, |
| Chev |
Description :
1. The tensioner is a belt tensioner used in the automobile transmission system. The tension pulley is mainly composed of a fixed shell, a tension arm, a wheel body, a torsion spring, a rolling bearing and a spring sleeve. It can automatically adjust the tension force according to the different tightness of the belt to make the transmission system stable, safe and reliable.
2. The main function of the tensioner bearing is to support the mechanical rotating body.
3.Reduce the friction coefficient during its movement and ensure its rotation accuracy.
4.Change sliding friction into rolling friction.
| 2017 | Chevrolet | SS | Base Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Chevrolet | SS | Base Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Chevrolet | SS | Base Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Chevrolet | SS | Base Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | 427 Convertible 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Carbon Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2571 | Saturn | Sky | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Saturn | Sky | Red Line Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2009 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2009 | Pontiac | G8 | GT Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Pontiac | G8 | GXP Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Coupe 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Pontiac | Solstice | GXP Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2009 | Pontiac | Solstice | GXP Coupe 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2009 | Saturn | Sky | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Saturn | Sky | Red Line Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2008 | Chevrolet | Corvette | 427 Limited Edition Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Pontiac | G8 | GT Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Pontiac | Solstice | GT Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Pontiac | Solstice | GXP Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2008 | Pontiac | Solstice | SE Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Saturn | Sky | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Saturn | Sky | Red Line Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2007 | Cadillac | CTS | V Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Pontiac | Solstice | GT Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Pontiac | Solstice | GXP Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2007 | Pontiac | Solstice | SE Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Saturn | Sky | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Saturn | Sky | Red Line Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2006 | Cadillac | CTS | V Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Pontiac | Solstice | GT Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Pontiac | Solstice | SE Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Cadillac | CTS | V Sedan 4-Door | 5.7L 346Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2004 | Cadillac | CTS | V Sedan 4-Door | 5.7L 346Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Tensioner Bearing |
|---|---|
| Material: | Aluminum |
| Certification: | TS16949 |
| Car Make: | Toyota |
| Transport Package: | Standard Stronger Export Carton |
| Origin: | China |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do drive belt tensioners enhance the overall efficiency and lifespan of drive belts in various automotive and industrial applications?
Drive belt tensioners play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency and lifespan of drive belts in various automotive and industrial applications. They ensure proper tensioning of the belts, which is essential for optimal power transmission, reduced slippage, and prolonged belt life. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive belt tensioners enhance efficiency and lifespan:
- Optimal Tension:
- Reduced Slippage:
- Prevention of Belt Misalignment:
- Improved Belt Life:
- Reduced Maintenance:
Drive belt tensioners maintain the proper tension in the belts, which is crucial for efficient power transmission. Tensioners apply the correct amount of force to keep the belt tightly engaged with the pulleys or sprockets. This optimal tension minimizes belt slippage, ensuring efficient power transfer from the driving pulley to the driven components. By maintaining the correct tension, tensioners maximize the efficiency of the belt-driven system, enabling the components to operate at their designed speeds and deliver the intended performance.
Slippage between the belt and the pulleys can lead to energy losses and reduced efficiency in automotive and industrial applications. Drive belt tensioners help minimize belt slippage by ensuring proper tension throughout the operating range. The tensioner’s role is to keep the belt under sufficient tension, preventing it from slipping or losing contact with the pulleys during operation. By reducing slippage, tensioners optimize power transmission efficiency, allowing the system to operate with minimal energy losses and improved overall efficiency.
Belt misalignment can cause uneven loading, increased wear, and reduced belt life. Drive belt tensioners help prevent belt misalignment by maintaining consistent tension and keeping the belt properly aligned with the pulleys or sprockets. Tensioners with alignment features, such as guide rollers or pulley systems, guide the belt and ensure it remains in the correct position. By preventing belt misalignment, tensioners contribute to the even distribution of load and reduce the risk of premature wear or failure of the belt.
Proper tensioning provided by drive belt tensioners significantly extends the lifespan of drive belts. When belts are undercorrect tension, excessive stress or slack can lead to accelerated wear, stretching, and premature failure. Tensioners help maintain the optimal tension that allows the belt to operate within its designed parameters, reducing the risk of wear and elongation. By promoting the correct tension, tensioners contribute to prolonged belt life, reducing the frequency of belt replacements and associated maintenance costs.
Efficient and reliable drive belt tensioners minimize the need for frequent maintenance or adjustments. Tensioners designed for durability and longevity can operate for extended periods without requiring significant maintenance interventions. By ensuring consistent tension and reducing belt wear, tensioners minimize the likelihood of unexpected belt failures or the need for frequent re-tensioning. This results in reduced maintenance requirements, increased system uptime, and improved overall productivity in automotive and industrial applications.
In summary, drive belt tensioners enhance the overall efficiency and lifespan of drive belts in automotive and industrial applications by maintaining optimal tension, reducing slippage, preventing belt misalignment, improving belt life, and reducing maintenance requirements. By providing the necessary tension and ensuring proper belt operation, tensioners optimize power transmission efficiency, minimize wear, and contribute to the reliable and long-lasting performance of drive belts in a wide range of applications.

How do innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology impact their use?
Innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology have a significant impact on their use, improving performance, reliability, and overall efficiency. These advancements drive the evolution of tensioners, allowing them to meet the changing needs of automotive and industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology impact their use:
- Enhanced Tensioning Mechanisms:
- Improved Belt Life and Performance:
- Quieter Operation:
- Increased Versatility:
- Diagnostic Capabilities:
Advancements in tensioner technology have led to the development of enhanced tensioning mechanisms. Traditional tensioners relied on mechanical springs or fixed pulleys to maintain belt tension. However, modern tensioners incorporate innovative mechanisms such as hydraulic or automatic tensioners. Hydraulic tensioners use hydraulic pressure to automatically adjust the tension, providing more precise and consistent tension control. Automatic tensioners utilize a combination of mechanical and spring-loaded systems to automatically adapt to changes in belt length or tension. These enhanced tensioning mechanisms ensure optimal tension under varying conditions, improving the overall performance and lifespan of the belt-driven system.
Advancements in tensioner technology have resulted in improved belt life and performance. Tensioners with advanced designs and materials can better distribute the tension across the belt, reducing stress concentrations and minimizing belt wear. Additionally, innovations in tensioner coatings and materials have improved their resistance to environmental factors, such as heat, moisture, and contaminants. These advancements help prolong the life of the belt, reduce maintenance requirements, and enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of the belt-driven system.
Modern drive belt tensioners are designed to provide a quieter operation compared to their predecessors. Advancements in tensioner technology have allowed for better dampening of vibrations and noise generated during belt operation. Tensioners with built-in dampers or improved bearing systems can effectively reduce noise and vibrations, resulting in a quieter and more comfortable operating environment. This is particularly beneficial in automotive applications, where noise reduction contributes to the overall driving experience.
Innovations in drive belt tensioner technology have increased their versatility, allowing them to be used in a wide range of applications. Tensioners can now accommodate different belt widths, pulley sizes, and mounting configurations. They can also be customized or adjusted to suit specific requirements, making them compatible with various automotive and industrial systems. This versatility simplifies the selection and installation process, providing flexibility and adaptability in different applications.
Some modern drive belt tensioners incorporate diagnostic capabilities to monitor the tension and condition of the belt. These tensioners may be equipped with sensors that provide real-time feedback on belt tension, allowing for proactive maintenance and early detection of potential issues. By monitoring the tension, operators can identify and address problems promptly, minimizing downtime and preventing costly failures. Diagnostic capabilities improve the overall reliability and efficiency of the belt-driven system.
In summary, innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology have a significant impact on their use. Enhanced tensioning mechanisms, improved belt life and performance, quieter operation, increased versatility, and diagnostic capabilities are some of the key benefits. These advancements contribute to the overall reliability, efficiency, and longevity of belt-driven systems, making them more robust and suitable for a wide range of automotive and industrial applications.

What is a drive belt tensioner, and how does it function in automotive and industrial applications?
A drive belt tensioner is a mechanical component used in automotive and industrial applications to maintain proper tension in the drive belt system. It is designed to ensure that the belt remains tight and properly engaged with the pulleys, allowing for efficient power transmission. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive belt tensioner is and how it functions:
- Definition and Components:
- Function in Automotive Applications:
- Function in Industrial Applications:
- Functioning Mechanism:
- Benefits and Importance:
A drive belt tensioner, also known as a belt tensioner or a serpentine belt tensioner, is typically a spring-loaded or hydraulic mechanism that exerts constant tension on the drive belt. It consists of several components, including a tensioner pulley, an arm or bracket, a spring or hydraulic cylinder, and a pivot point. The tensioner pulley is responsible for applying tension to the belt, while the arm or bracket holds the pulley in place. The spring or hydraulic cylinder provides the force necessary to maintain tension, and the pivot point allows for movement and adjustment.
In automotive applications, drive belt tensioners are commonly used in the serpentine belt system. The serpentine belt is a single, long belt that drives various engine accessories, such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. The tensioner ensures that the serpentine belt remains properly tensioned, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power transfer to these accessories. It compensates for belt stretch, wear, and load variations, maintaining consistent tension and optimizing the performance of the engine accessories.
In industrial applications, drive belt tensioners are employed in various belt drive systems. These systems may include multiple belts, such as V-belts or timing belts, driving different components in machinery or equipment. The tensioner’s role is to maintain proper tension in each belt, ensuring reliable power transmission and preventing slippage. It adapts to load variations, compensates for belt stretch and wear, and helps distribute the load evenly among the belts. By maintaining optimal tension, drive belt tensioners enhance the overall efficiency, reliability, and lifespan of the belt drive systems in industrial applications.
The functioning of a drive belt tensioner depends on its specific design, which can vary depending on the application and the type of tensioner used. In general, tensioners utilize the force generated by a spring or hydraulic cylinder to exert tension on the belt. The tensioner is typically mounted on an adjustable arm or bracket, allowing for movement and adjustment to maintain the desired tension. As the belt stretches or wears over time, the tensioner compensates by applying additional tension to keep the belt properly engaged with the pulleys. Some tensioners incorporate automatic self-adjustment mechanisms, while others may require manual adjustment or periodic inspection to ensure proper tension.
Drive belt tensioners offer several benefits and play a crucial role in automotive and industrial applications. They prevent slippage, optimize power transmission, and maintain consistent tension in the belt drive systems. By compensating for belt stretch, wear, and load variations, tensioners ensure reliable and efficient operation of the driven components. They reduce the risk of belt failure, minimize wear and fatigue, and extend the lifespan of the belts. Proper tensioning provided by drive belt tensioners enhances overall system performance, reduces maintenance requirements, and increases the reliability and longevity of the belt drive systems.
In summary, a drive belt tensioner is a mechanical component that maintains proper tension in the drive belt system. It functions by applying tension to the belt using a pulley, spring, or hydraulic cylinder. In automotive applications, tensioners optimize power transmission in the serpentine belt system, while in industrial applications, they ensure reliable power transfer in various belt drive systems. By compensating for belt stretch, wear, and load variations, drive belt tensioners enhance efficiency, reduce wear, and extend the lifespan of the belts, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of automotive and industrial machinery.


editor by CX 2024-04-10
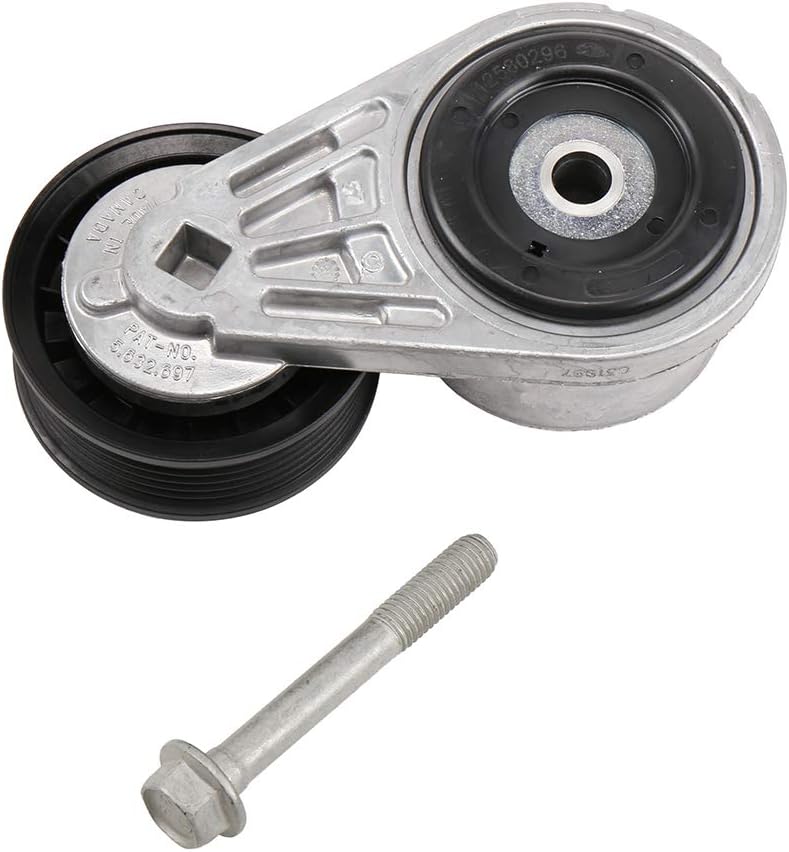
China high quality Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner for Mitsubishigalant Fortis Saloon (CY/Z_A) 1345A059 1345A060 1345A061 as thru axle
Product Description
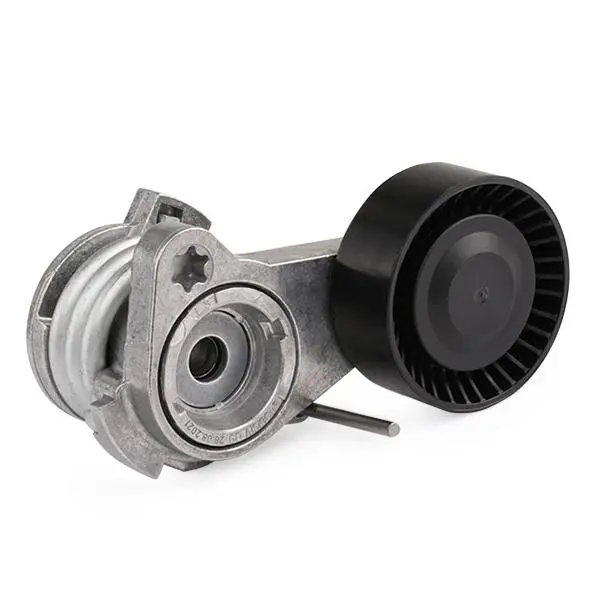
Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner for MITSUBISHIGALANT FORTIS SALOON(CY/Z_A) 1345A059 1345A060 1345A061
Product Description
|
Product Name |
Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner for MITSUBISHIGALANT FORTIS SALOON(CY/Z_A) 1345A059 1345A060 1345A061 |
| Certification | ISO/TS16949:2009 |
|
OE Number |
1345A059 1345A060 1345A061 |
| Car Fitment | MITSUBISHI |
|
Quality guarantee |
12 months |
|
Leading time |
30 days |
|
MOQ |
50pcs |
Why Choose Us
1.Reply your enquiry in 24 working hours,any time you can contact me.
2.OEM, buyer design, buyer label services provided.
3.Exclusive and unique solution can be provide to our customer by our welltrained
and professional engineers and staffs.
4.we can provide free sample for your check
5.we have the certification of ISO 9001
6.Special discount and protection of sales area provided to our distributor.
7.timely delivery
8.Good after-sale service
9.Small MOQ is acceptable
Our Service
1.Your inquiry related to our products or prices will be replied in 24 hours.
2.Protection of your sales area, ideas of design and all your private information.
3.Best quality and competitive price.
Packaging & Delivery
1.Packaging Details:Can be customized
2. Delivery Detail:About 3-5 days and based on your requirements.
FAQ
Q1.Are you a Manufacturer or a Trading Company?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in filters for several years.
Factory belong to us,100% industrial corporation,not cooperating partner.It would be our big honor,if you can come to visit us.
Q2.What products can you supply?
A: As a manufacturer, Gpaiplus Company with more than 10 years experience.
We produce a complete range of oil filters, air filters, cabin air filters and fuel filters.If you have your own brand or willing to start one, we would be happy to do OEM for you.
Q3: How is the quality of the filters?How do you guarantee the after-sale service?
A: Strict control before shipment.
If any problems caused by the product itself, we will supply you the new replaced ones ASAP.
Q4. Can I get some samples? How could I pay the sample charge?
A: It depents on the sample costs, but the freight might be bared by our customers.
We accept the sample payment via Western Union,Money Gram or T/T.
Q5. What is the payment terms?
A: Our paymnet terms: 30% deposit before production, 70%balance before shipment.
Q6. How long is your Delivery Time ?
A: If there is stock, the delivery time is about 3-5 working days after getting the payment.
If no stock,30-45 working days according to the order.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Type: | Tensioner Bearing |
| Material: | Iron, Steel |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Condition: | New |
| Application Brand: | Mitsubishi |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What role do materials and coatings play in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners?
Materials and coatings play a crucial role in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners. The selection of appropriate materials and the use of specialized coatings can significantly impact the tensioner’s durability, resistance to wear, and overall functionality. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role materials and coatings play in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners:
- Strength and Stiffness:
- Wear Resistance:
- Corrosion and Rust Protection:
- Friction Reduction:
- Heat Resistance:
The materials used in drive belt tensioners should exhibit sufficient strength and stiffness to withstand the forces and stresses exerted on them during operation. High-quality materials, such as hardened steel or alloyed metals, are commonly employed in tensioner components like brackets, pulleys, and arms. These materials provide the necessary strength and rigidity to maintain the tensioner’s structural integrity and prevent deformation or failure under load. By using robust materials, tensioners can effectively withstand the demands of the belt drive system, ensuring long-term performance and longevity.
Tensioners are subjected to continuous contact with the belt and other moving components, which can lead to wear over time. The choice of materials with excellent wear resistance properties can significantly extend the tensioner’s lifespan. Hardened steel, cast iron, or materials with specialized surface treatments, such as nitriding or hard chrome plating, are commonly used to enhance wear resistance. These materials and coatings reduce friction, minimize surface degradation, and prevent premature wear of critical tensioner components. By improving wear resistance, tensioners can maintain consistent tension and performance over an extended period.
Drive belt tensioners are often exposed to harsh environments, including high humidity, temperature variations, and chemical contaminants. Corrosion and rust can compromise the performance and longevity of tensioners, leading to premature failure. To mitigate these issues, manufacturers employ materials and coatings that provide corrosion and rust protection. Stainless steel, galvanized steel, or materials with corrosion-resistant coatings, such as zinc or powder coatings, are commonly used. These protective measures prevent the degradation of tensioner components, ensuring their functionality and prolonging their lifespan even in challenging operating conditions.
Reducing friction is essential for optimizing the performance and efficiency of drive belt tensioners. Excessive friction can lead to energy losses, increased wear, and decreased belt life. Materials and coatings that possess low friction characteristics are employed in tensioner components to minimize frictional forces between the belt and the tensioner. For example, self-lubricating materials or coatings with low friction coefficients, such as Teflon or molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), can be utilized. By reducing friction, tensioners operate more efficiently, generate less heat, and experience reduced wear, resulting in improved performance and longevity.
Drive belt tensioners are exposed to elevated temperatures generated by the operating belt drive system. Materials and coatings with excellent heat resistance properties are necessary to ensure the tensioner’s performance and longevity. High-temperature alloys, heat-resistant plastics, or coatings designed to withstand thermal stresses are utilized to prevent deformation, softening, or degradation of tensioner components at elevated temperatures. By using heat-resistant materials and coatings, tensioners can operate reliably and maintain consistent tension without compromising their structural integrity.
In summary, materials and coatings play a vital role in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners. The selection of appropriate materials and the application of specialized coatings help ensure the tensioner’s strength, stiffness, wear resistance, corrosion protection, friction reduction, and heat resistance. By utilizing high-quality materials and employing suitable coatings, tensioners can withstand the demands of the belt drive system, resist wear and corrosion, operate efficiently, and maintain consistent tension over an extended period, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of the belt-driven system.

How do innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology impact their use?
Innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology have a significant impact on their use, improving performance, reliability, and overall efficiency. These advancements drive the evolution of tensioners, allowing them to meet the changing needs of automotive and industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology impact their use:
- Enhanced Tensioning Mechanisms:
- Improved Belt Life and Performance:
- Quieter Operation:
- Increased Versatility:
- Diagnostic Capabilities:
Advancements in tensioner technology have led to the development of enhanced tensioning mechanisms. Traditional tensioners relied on mechanical springs or fixed pulleys to maintain belt tension. However, modern tensioners incorporate innovative mechanisms such as hydraulic or automatic tensioners. Hydraulic tensioners use hydraulic pressure to automatically adjust the tension, providing more precise and consistent tension control. Automatic tensioners utilize a combination of mechanical and spring-loaded systems to automatically adapt to changes in belt length or tension. These enhanced tensioning mechanisms ensure optimal tension under varying conditions, improving the overall performance and lifespan of the belt-driven system.
Advancements in tensioner technology have resulted in improved belt life and performance. Tensioners with advanced designs and materials can better distribute the tension across the belt, reducing stress concentrations and minimizing belt wear. Additionally, innovations in tensioner coatings and materials have improved their resistance to environmental factors, such as heat, moisture, and contaminants. These advancements help prolong the life of the belt, reduce maintenance requirements, and enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of the belt-driven system.
Modern drive belt tensioners are designed to provide a quieter operation compared to their predecessors. Advancements in tensioner technology have allowed for better dampening of vibrations and noise generated during belt operation. Tensioners with built-in dampers or improved bearing systems can effectively reduce noise and vibrations, resulting in a quieter and more comfortable operating environment. This is particularly beneficial in automotive applications, where noise reduction contributes to the overall driving experience.
Innovations in drive belt tensioner technology have increased their versatility, allowing them to be used in a wide range of applications. Tensioners can now accommodate different belt widths, pulley sizes, and mounting configurations. They can also be customized or adjusted to suit specific requirements, making them compatible with various automotive and industrial systems. This versatility simplifies the selection and installation process, providing flexibility and adaptability in different applications.
Some modern drive belt tensioners incorporate diagnostic capabilities to monitor the tension and condition of the belt. These tensioners may be equipped with sensors that provide real-time feedback on belt tension, allowing for proactive maintenance and early detection of potential issues. By monitoring the tension, operators can identify and address problems promptly, minimizing downtime and preventing costly failures. Diagnostic capabilities improve the overall reliability and efficiency of the belt-driven system.
In summary, innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology have a significant impact on their use. Enhanced tensioning mechanisms, improved belt life and performance, quieter operation, increased versatility, and diagnostic capabilities are some of the key benefits. These advancements contribute to the overall reliability, efficiency, and longevity of belt-driven systems, making them more robust and suitable for a wide range of automotive and industrial applications.

In what industries and machinery are drive belt tensioners commonly used for optimal belt performance?
Drive belt tensioners are commonly used in various industries and machinery to ensure optimal belt performance. They play a crucial role in maintaining the proper tension of drive belts, optimizing power transmission, and preventing belt slippage. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries and machinery where drive belt tensioners are commonly employed:
- Automotive Industry:
- Industrial Machinery:
- HVAC Systems:
- Power Generation:
- Printing and Packaging:
- Textile Industry:
Drive belt tensioners are extensively used in the automotive industry. They are a critical component of serpentine belt systems found in vehicles. Serpentine belts are long, continuous belts that drive multiple engine accessories, such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. Drive belt tensioners in automotive applications ensure that the serpentine belt remains properly tensioned, allowing efficient power transmission to these accessories. They help maintain the performance and reliability of the vehicle’s electrical and mechanical systems.
Drive belt tensioners are widely employed in various industrial machinery and equipment. They are used in belt drive systems that power different components and processes in industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, and agriculture. In industrial applications, drive belts can be V-belts, timing belts, or other types depending on the specific requirements. Drive belt tensioners ensure proper tension of these belts, allowing reliable power transmission and preventing belt slippage. They are commonly found in equipment like conveyors, pumps, compressors, generators, mills, and agricultural machinery.
Drive belt tensioners are crucial components in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. HVAC systems utilize belt-driven blowers, fans, and pumps to circulate air and control temperatures in buildings, vehicles, and industrial settings. Drive belt tensioners in HVAC systems ensure that the belts driving these components remain properly tensioned. This helps maintain efficient operation, reliable performance, and optimal energy consumption in HVAC systems.
In the power generation industry, drive belt tensioners are utilized in various applications. They can be found in power plants, where belt-driven generators, turbines, and auxiliary equipment are used. Drive belt tensioners help maintain the tension of these belts, ensuring efficient power transmission, preventing slippage, and optimizing the performance of power generation systems.
The printing and packaging industry relies on drive belt tensioners to ensure precise and reliable operation of printing presses, packaging machines, and other related equipment. Belt-driven systems play a vital role in moving paper, labels, or packaging materials through the machines. Drive belt tensioners help maintain the tension of these belts, ensuring accurate registration, consistent printing quality, and smooth material handling.
In the textile industry, drive belt tensioners are commonly used in various textile machines, such as spinning machines, weaving machines, and knitting machines. These machines utilize drive belts to control the movement of yarn or fabric through the production process. Drive belt tensioners help maintain the tension of these belts, ensuring precise yarn or fabric control, accurate weaving or knitting patterns, and consistent product quality.
In summary, drive belt tensioners are commonly used in industries such as automotive, industrial machinery, HVAC, power generation, printing and packaging, and textile. They ensure optimal belt performance by maintaining the proper tension of drive belts, enabling efficient power transmission, preventing slippage, and maximizing the performance and reliability of machinery and equipment in these industries.


editor by CX 2024-03-29
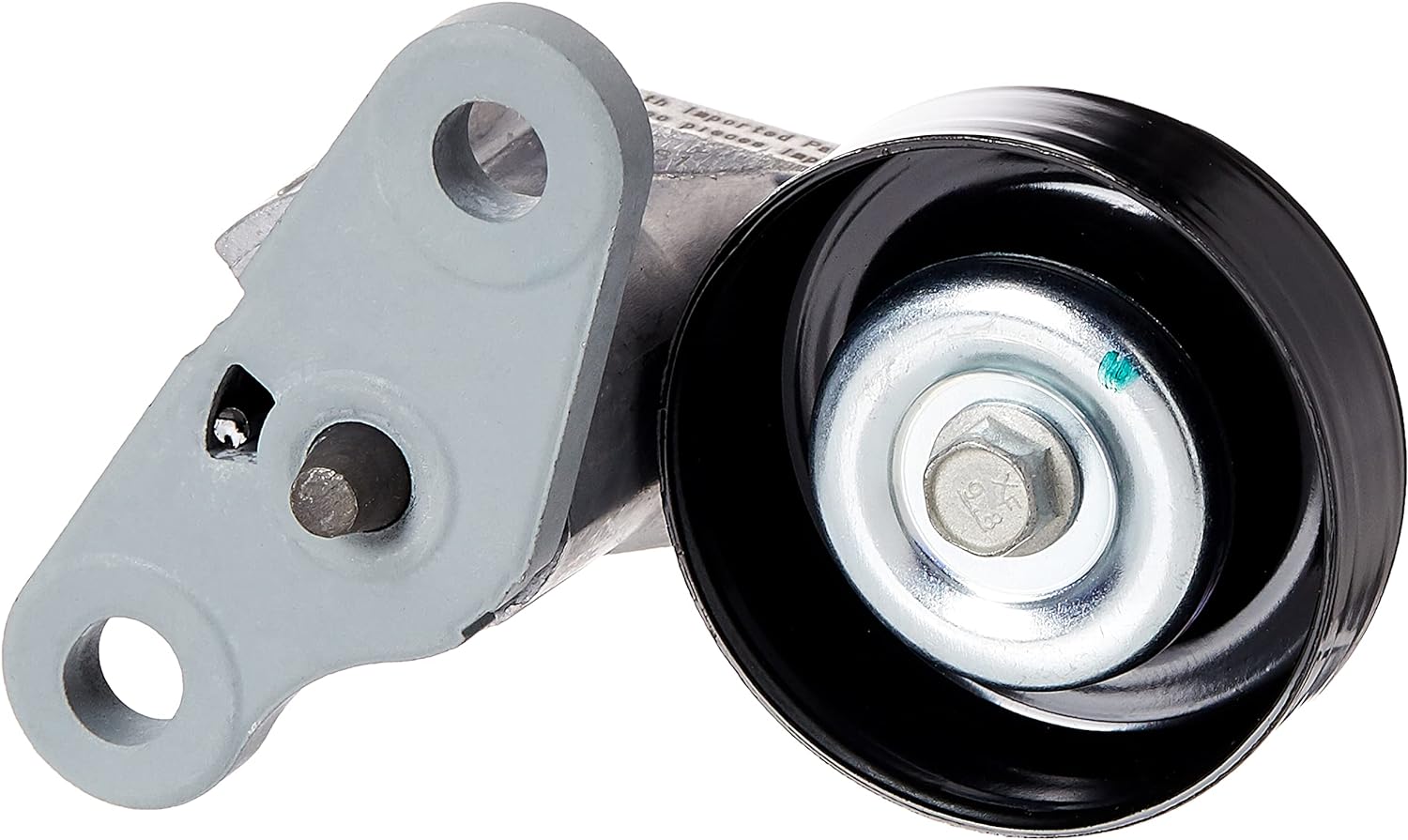
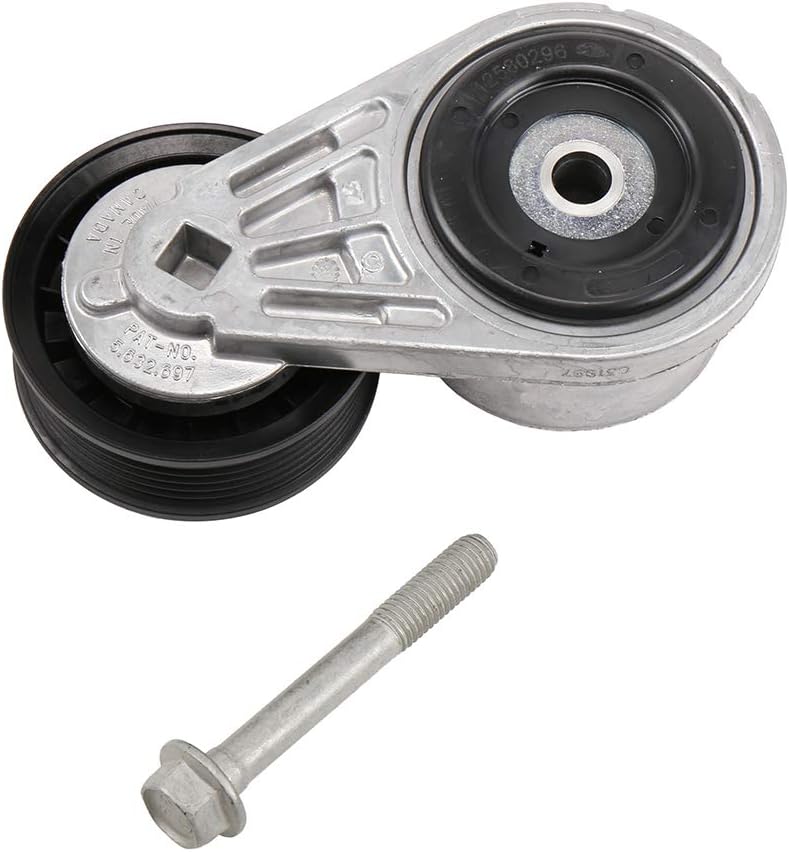
China manufacturer Alternator Tensioner 12568980, 12579981, 12585551, 305339, Alt04013, 49159, 900259A, for Cadillac Chevy Chevrolet, Drive Belt Assembly Tensor De Tiempo / Tensor axle and wheels
Product Description
Product spections :
| Interchange number: | 12568980, 12579981, 12585551, 35719, ALT04013, 49159, |
| Chev |
Description :
1. The tensioner is a belt tensioner used in the automobile transmission system. The tension pulley is mainly composed of a fixed shell, a tension arm, a wheel body, a torsion spring, a rolling bearing and a spring sleeve. It can automatically adjust the tension force according to the different tightness of the belt to make the transmission system stable, safe and reliable.
2. The main function of the tensioner bearing is to support the mechanical rotating body.
3.Reduce the friction coefficient during its movement and ensure its rotation accuracy.
4.Change sliding friction into rolling friction.
| 2017 | Chevrolet | SS | Base Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2016 | Chevrolet | SS | Base Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2015 | Chevrolet | SS | Base Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2014 | Chevrolet | SS | Base Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | 427 Convertible 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2013 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2012 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Caprice | PPV Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 FLEX OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Carbon Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2011 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Grand Sport Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2571 | Saturn | Sky | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2571 | Saturn | Sky | Red Line Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2009 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Chevrolet | Corvette | ZR1 Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Supercharged |
| 2009 | Pontiac | G8 | GT Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Pontiac | G8 | GXP Sedan 4-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Coupe 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Pontiac | Solstice | GXP Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2009 | Pontiac | Solstice | GXP Coupe 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2009 | Saturn | Sky | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2009 | Saturn | Sky | Red Line Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2008 | Chevrolet | Corvette | 427 Limited Edition Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.2L 6162CC 376Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Pontiac | G8 | GT Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Pontiac | Solstice | GT Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Pontiac | Solstice | GXP Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2008 | Pontiac | Solstice | SE Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Saturn | Sky | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2008 | Saturn | Sky | Red Line Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2007 | Cadillac | CTS | V Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Pontiac | Solstice | GT Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Pontiac | Solstice | GXP Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2007 | Pontiac | Solstice | SE Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Saturn | Sky | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2007 | Saturn | Sky | Red Line Convertible 2-Door | 2.0L 1998CC 122Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Turbocharged |
| 2006 | Cadillac | CTS | V Sedan 4-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Z06 Hatchback 2-Door | 7.0L 7011CC 427Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Pontiac | Solstice | Base Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Pontiac | Solstice | GT Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2006 | Pontiac | Solstice | SE Convertible 2-Door | 2.4L 2384CC 145Cu. In. l4 GAS DOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Cadillac | CTS | V Sedan 4-Door | 5.7L 346Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Convertible 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2005 | Chevrolet | Corvette | Base Hatchback 2-Door | 6.0L 5967CC 364Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| 2004 | Cadillac | CTS | V Sedan 4-Door | 5.7L 346Cu. In. V8 GAS OHV Naturally Aspirated |
| Type: | Tensioner Bearing |
|---|---|
| Material: | Aluminum |
| Certification: | TS16949 |
| Car Make: | Toyota |
| Transport Package: | Standard Stronger Export Carton |
| Origin: | China |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What role do materials and coatings play in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners?
Materials and coatings play a crucial role in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners. The selection of appropriate materials and the use of specialized coatings can significantly impact the tensioner’s durability, resistance to wear, and overall functionality. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role materials and coatings play in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners:
- Strength and Stiffness:
- Wear Resistance:
- Corrosion and Rust Protection:
- Friction Reduction:
- Heat Resistance:
The materials used in drive belt tensioners should exhibit sufficient strength and stiffness to withstand the forces and stresses exerted on them during operation. High-quality materials, such as hardened steel or alloyed metals, are commonly employed in tensioner components like brackets, pulleys, and arms. These materials provide the necessary strength and rigidity to maintain the tensioner’s structural integrity and prevent deformation or failure under load. By using robust materials, tensioners can effectively withstand the demands of the belt drive system, ensuring long-term performance and longevity.
Tensioners are subjected to continuous contact with the belt and other moving components, which can lead to wear over time. The choice of materials with excellent wear resistance properties can significantly extend the tensioner’s lifespan. Hardened steel, cast iron, or materials with specialized surface treatments, such as nitriding or hard chrome plating, are commonly used to enhance wear resistance. These materials and coatings reduce friction, minimize surface degradation, and prevent premature wear of critical tensioner components. By improving wear resistance, tensioners can maintain consistent tension and performance over an extended period.
Drive belt tensioners are often exposed to harsh environments, including high humidity, temperature variations, and chemical contaminants. Corrosion and rust can compromise the performance and longevity of tensioners, leading to premature failure. To mitigate these issues, manufacturers employ materials and coatings that provide corrosion and rust protection. Stainless steel, galvanized steel, or materials with corrosion-resistant coatings, such as zinc or powder coatings, are commonly used. These protective measures prevent the degradation of tensioner components, ensuring their functionality and prolonging their lifespan even in challenging operating conditions.
Reducing friction is essential for optimizing the performance and efficiency of drive belt tensioners. Excessive friction can lead to energy losses, increased wear, and decreased belt life. Materials and coatings that possess low friction characteristics are employed in tensioner components to minimize frictional forces between the belt and the tensioner. For example, self-lubricating materials or coatings with low friction coefficients, such as Teflon or molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), can be utilized. By reducing friction, tensioners operate more efficiently, generate less heat, and experience reduced wear, resulting in improved performance and longevity.
Drive belt tensioners are exposed to elevated temperatures generated by the operating belt drive system. Materials and coatings with excellent heat resistance properties are necessary to ensure the tensioner’s performance and longevity. High-temperature alloys, heat-resistant plastics, or coatings designed to withstand thermal stresses are utilized to prevent deformation, softening, or degradation of tensioner components at elevated temperatures. By using heat-resistant materials and coatings, tensioners can operate reliably and maintain consistent tension without compromising their structural integrity.
In summary, materials and coatings play a vital role in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners. The selection of appropriate materials and the application of specialized coatings help ensure the tensioner’s strength, stiffness, wear resistance, corrosion protection, friction reduction, and heat resistance. By utilizing high-quality materials and employing suitable coatings, tensioners can withstand the demands of the belt drive system, resist wear and corrosion, operate efficiently, and maintain consistent tension over an extended period, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of the belt-driven system.

How do drive belt tensioners contribute to reducing wear and increasing the efficiency of power transmission?
Drive belt tensioners play a vital role in reducing wear and increasing the efficiency of power transmission in various applications. These tensioners help maintain the proper tension of drive belts, which in turn has several key contributions:
- Preventing Belt Slippage:
- Optimizing Contact and Engagement:
- Reducing Vibration and Noise:
- Preventing Premature Wear:
- Maximizing Power Transfer:
Drive belt tensioners ensure that the belts remain properly tensioned, minimizing the risk of belt slippage. When a belt slips, it loses its grip on the pulleys, resulting in inefficient power transmission and increased wear. Belt slippage can occur under heavy loads, sudden changes in speed or direction, or when belts are not properly tensioned. Drive belt tensioners apply the necessary force to maintain the optimal tension, preventing slippage and ensuring consistent power transfer. By minimizing belt slippage, drive belt tensioners reduce wear on the belt’s surface and the pulleys, increasing the overall efficiency of power transmission.
Proper tensioning by drive belt tensioners optimizes the contact and engagement between the belt and the pulleys. When a belt is under-tensioned, it may not make sufficient contact with the pulleys, leading to reduced power transmission efficiency. On the other hand, over-tensioning can cause excessive friction and wear. Drive belt tensioners maintain the ideal tension, ensuring that the belt remains in proper contact with the pulleys, allowing for efficient power transfer. By optimizing contact and engagement, drive belt tensioners minimize energy losses, reduce wear on the belt and pulleys, and increase the efficiency of power transmission.
Proper tensioning by drive belt tensioners helps reduce vibration and noise associated with power transmission. When a belt is not properly tensioned, it may vibrate or produce excessive noise during operation. This can be caused by belt slippage, misalignment, or inadequate tension. Drive belt tensioners ensure the correct tension, promoting stability and minimizing vibrations. By reducing vibration and noise, drive belt tensioners contribute to a smoother and quieter operation of the belt system, improving overall efficiency and user comfort.
Drive belt tensioners help prevent premature wear of the belts and associated components. When a belt is under-tensioned, it may experience excessive stretching, accelerated wear, and premature failure. Conversely, over-tensioning can lead to increased stress on the belt, causing it to wear out more quickly. Drive belt tensioners maintain the optimal tension, ensuring that the belt operates within its designed parameters, minimizing wear and extending its lifespan. By preventing premature wear, drive belt tensioners enhance the longevity and durability of the belt system, reducing maintenance needs and improving overall efficiency.
By maintaining the proper tension, drive belt tensioners maximize the efficiency of power transfer. When a belt is properly tensioned, it efficiently transfers power from the driving pulley to the driven pulley. This ensures that the driven components, such as alternators, pumps, or compressors, receive the necessary power for optimal operation. By maximizing power transfer, drive belt tensioners contribute to the overall efficiency of the system, minimizing energy losses and improving the performance of the driven components.
In summary, drive belt tensioners contribute to reducing wear and increasing the efficiency of power transmission by preventing belt slippage, optimizing contact and engagement between the belt and pulleys, reducing vibration and noise, preventing premature wear, and maximizing power transfer. These contributions enhance the overall performance, reliability, and lifespan of drive belt systems in various applications.

Can you explain the importance of proper tensioning for drive belts in various machinery and vehicles?
Proper tensioning of drive belts is of utmost importance in various machinery and vehicles. Maintaining the right level of tension ensures optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the belt drive system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the importance of proper tensioning for drive belts:
- Efficient Power Transmission:
- Preventing Belt Slippage:
- Reducing Wear and Fatigue:
- Optimizing Belt Life and Performance:
- Adapting to Load Variations:
- Enhancing System Reliability:
Proper tensioning is crucial for efficient power transmission in machinery and vehicles. When a drive belt is under-tensioned, it can slip on the pulleys, resulting in power loss and reduced performance. Insufficient tension leads to inadequate friction between the belt and the pulleys, compromising the transfer of power from the driving pulley to the driven pulley. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts remain properly engaged with the pulleys, ensuring maximum power transfer and efficient operation of the machinery or vehicle.
Correct tensioning helps prevent belt slippage, which is a common issue in belt drive systems. Slippage occurs when the belt loses its grip on the pulleys, leading to power loss, decreased efficiency, and potential damage to the belt and pulleys. Proper tension ensures that the belt remains securely in place, creating sufficient friction to prevent slippage even under high loads or sudden changes in speed or torque. By preventing belt slippage, proper tensioning maintains reliable power transmission and protects the integrity of the belt drive system.
Improper tensioning can cause excessive wear and fatigue on drive belts. If a belt is over-tensioned, it experiences increased stress, leading to accelerated wear and potential premature failure. On the other hand, under-tensioning can cause the belt to flex excessively, leading to fatigue and eventual belt failure. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts operate within their design limits, minimizing wear and fatigue. Proper tensioning extends the lifespan of the belts, reducing maintenance costs and downtime associated with belt replacements.
Proper tensioning plays a vital role in optimizing the life and performance of drive belts. When belts are correctly tensioned, they operate in their intended range, minimizing stress and strain. This optimal operating condition reduces the risk of belt damage, such as cracking, stretching, or delamination. Additionally, proper tensioning ensures that the belts track properly on the pulleys, preventing misalignment and excessive side loads. By optimizing belt life and performance, proper tensioning contributes to increased reliability, reduced maintenance, and improved overall efficiency of machinery and vehicles.
Drive belts in machinery and vehicles often experience load variations during operation. Proper tensioning allows the belts to adapt to these load changes effectively. When the load increases, the tensioner compensates by applying additional tension to prevent slippage. Conversely, when the load decreases, the tensioner releases some tension to avoid excessive stress on the belt and pulleys. This adaptability ensures that the belts maintain the optimal tension regardless of the varying load conditions, allowing for consistent power transmission and reliable performance.
The proper tensioning of drive belts enhances the overall reliability of machinery and vehicles. By maintaining optimal tension, belts operate within their designed parameters, reducing the risk of unexpected belt failure and associated downtime. Reliable power transmission ensures that machinery operates as intended, minimizing the chances of equipment damage, production delays, and costly repairs. The use of proper tensioning techniques adds a layer of control and stability to the belt drive system, enhancing its overall reliability and ensuring smooth operation.
In summary, proper tensioning of drive belts is essential for efficient power transmission, preventing belt slippage, reducing wear and fatigue, optimizing belt life and performance, adapting to load variations, and enhancing system reliability in various machinery and vehicles. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts operate effectively, ensuring reliable performance, extended lifespan, and minimized downtime.


editor by CX 2023-12-11
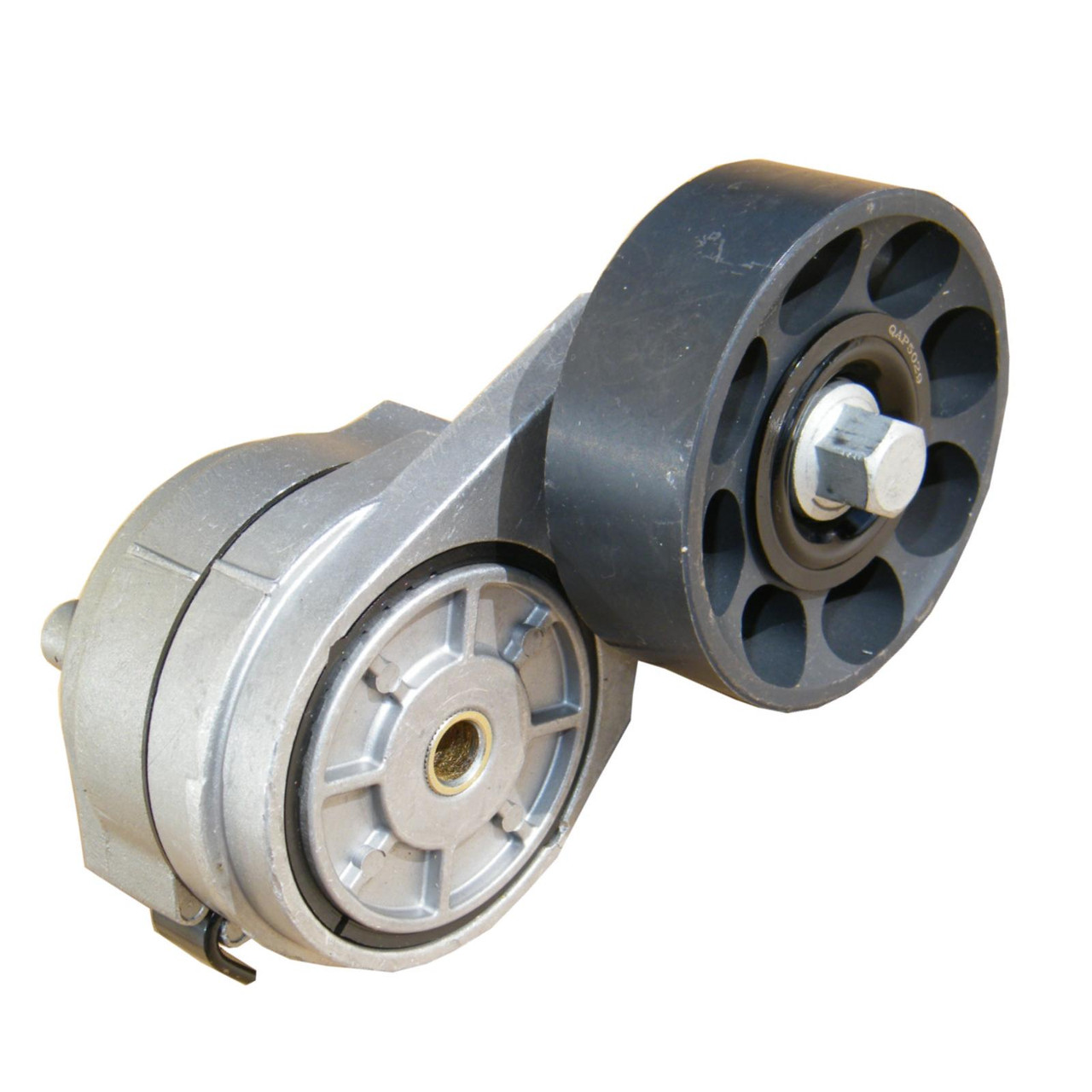
China manufacturer Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner for Mitsubishigalant Fortis Saloon (CY/Z_A) 1345A059 1345A060 1345A061 wholesaler
Product Description
Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner for MITSUBISHIGALANT FORTIS SALOON(CY/Z_A) 1345A059 1345A060 1345A061
Product Description
|
Product Name |
Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner for MITSUBISHIGALANT FORTIS SALOON(CY/Z_A) 1345A059 1345A060 1345A061 |
| Certification | ISO/TS16949:2009 |
|
OE Number |
1345A059 1345A060 1345A061 |
| Car Fitment | MITSUBISHI |
|
Quality guarantee |
12 months |
|
Leading time |
30 days |
|
MOQ |
50pcs |
Why Choose Us
1.Reply your enquiry in 24 working hours,any time you can contact me.
2.OEM, buyer design, buyer label services provided.
3.Exclusive and unique solution can be provide to our customer by our welltrained
and professional engineers and staffs.
4.we can provide free sample for your check
5.we have the certification of ISO 9001
6.Special discount and protection of sales area provided to our distributor.
7.timely delivery
8.Good after-sale service
9.Small MOQ is acceptable
Our Service
1.Your inquiry related to our products or prices will be replied in 24 hours.
2.Protection of your sales area, ideas of design and all your private information.
3.Best quality and competitive price.
Packaging & Delivery
1.Packaging Details:Can be customized
2.Delivery Detail:About 3-5 days and based on your requirements.
FAQ
Q1.Are you a Manufacturer or a Trading Company?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in filters for several years.
Factory belong to us,100% industrial corporation,not cooperating partner.It would be our big honor,if you can come to visit us.
Q2.What products can you supply?
A: As a manufacturer, Gpaiplus Company with more than 10 years experience.
We produce a complete range of oil filters, air filters, cabin air filters and fuel filters.If you have your own brand or willing to start one, we would be happy to do OEM for you.
Q3: How is the quality of the filters?How do you guarantee the after-sale service?
A: Strict control before shipment.
If any problems caused by the product itself, we will supply you the new replaced ones ASAP.
Q4. Can I get some samples? How could I pay the sample charge?
A: It depents on the sample costs, but the freight might be bared by our customers.
We accept the sample payment via Western Union,Money Gram or T/T.
Q5. What is the payment terms?
A: Our paymnet terms: 30% deposit before production, 70%balance before shipment.
Q6. How long is your Delivery Time ?
A: If there is stock, the delivery time is about 3-5 working days after getting the payment.
If no stock,30-45 working days according to the order.
| After-sales Service: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Type: | Tensioner Bearing |
| Material: | Iron, Steel |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Condition: | New |
| Application Brand: | Mitsubishi |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can you describe the various mounting options and installations for drive belt tensioners in different settings?
When installing drive belt tensioners, various mounting options and configurations are available to accommodate different settings and applications. The choice of mounting option depends on factors such as space constraints, belt path, alignment requirements, and the specific design of the tensioner. Here’s a detailed description of the various mounting options and installations for drive belt tensioners:
- Fixed Mounting:
- Adjustable Mounting:
- Spring-Loaded or Automatic Mounting:
- Hydraulic or Pneumatic Mounting:
- Combination Mounting:
The most common mounting option for drive belt tensioners is the fixed mounting configuration. In this setup, the tensioner is securely bolted or fastened to a stationary component or mounting bracket within the system. The fixed mounting option provides stability and ensures that the tensioner remains in a fixed position relative to the belt path. It is suitable for applications where there is sufficient space and where the belt path does not require any adjustment or movement of the tensioner.
Adjustable mounting configurations allow for fine-tuning of the tensioner position and belt tension. These setups typically feature slotted mounting holes or adjustable arms that enable movement and positioning of the tensioner. By loosening the mounting bolts, the tensioner can be adjusted vertically or horizontally to achieve the desired belt tension or alignment. Adjustable mounting options are beneficial when precise tension adjustment or alignment is required, especially in applications with varying belt lengths or when pulley positions need to be optimized.
Some tensioners employ a spring-loaded or automatic mounting mechanism, which automatically adjusts the tension based on the belt’s requirements. These tensioners incorporate a built-in spring mechanism that applies a constant force to maintain the desired tension. The mounting configuration for such tensioners typically involves a pivot point and a spring-loaded arm that keeps the tensioner in contact with the belt. Spring-loaded or automatic mounting options are particularly useful in applications where frequent belt length changes occur or when consistent tension needs to be maintained dynamically.
In certain industrial applications, hydraulic or pneumatic mounting options are utilized for drive belt tensioners. These tensioners use hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders to apply and control the tension. Hydraulic or pneumatic mounting configurations provide precise tension control and can accommodate larger belt drives or heavy-duty applications. They are often found in industrial machinery or equipment where adjustable tension and dynamic tension control are critical.
In some cases, a combination of mounting options may be employed to achieve the desired tensioning setup. For example, a tensioner may have a fixed mounting base with an adjustable arm or pulley attached to it. This combination allows for both stability and fine-tuning of the tensioner position. Combination mounting options are useful in applications where a balance between stability and adjustability is required.
In summary, drive belt tensioners can be mounted using various configurations depending on the specific requirements of the application. Fixed mounting provides stability and is suitable when the tensioner’s position does not need adjustment. Adjustable mounting options allow for precise tension adjustment and alignment. Spring-loaded or automatic mounting options automatically adjust the tension based on the belt’s requirements. Hydraulic or pneumatic mounting configurations provide precise tension control in heavy-duty applications. Combination mounting options offer a balance between stability and adjustability. Choosing the appropriate mounting option ensures proper tensioning and optimal performance of the belt-driven system.

Can drive belt tensioners be customized or modified to suit specific automotive or industrial needs?
Drive belt tensioners can be customized or modified to suit specific automotive or industrial needs. Manufacturers of tensioners offer various options and configurations to accommodate different applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive belt tensioners can be customized or modified:
- Tensioner Design:
- Tensioner Size and Mounting:
- Tensioner Load Capacity:
- Additional Features:
Drive belt tensioners come in different designs to meet specific needs. Manufacturers offer a range of tensioner designs, such as spring-loaded tensioners, hydraulic tensioners, and automatic tensioners. These designs can be customized based on the specific requirements of the automotive or industrial application. For example, some applications may require tensioners with higher load-bearing capacity or increased resistance to environmental factors like dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures. Manufacturers can modify the tensioner design to incorporate features that enhance durability, performance, and reliability in these challenging conditions.
Drive belt tensioners are available in various sizes to accommodate different belt widths and pulley configurations. Manufacturers provide tensioners in different dimensions, allowing customization based on the specific dimensions of the belt and pulley system. Additionally, tensioners can be modified to suit different mounting requirements. Some applications may require tensioners with specific mounting brackets or orientations to fit within the available space or align with other components. Manufacturers can customize the tensioner’s size, shape, and mounting features to ensure compatibility and ease of installation in the target application.
The load capacity of a drive belt tensioner is an essential consideration for certain applications. Industrial or heavy-duty automotive applications may require tensioners with higher load capacity to withstand increased belt tensions or accommodate larger belt-driven systems. Manufacturers can customize tensioners to meet these requirements by using stronger materials, incorporating reinforced components, or optimizing the tensioner’s internal structure to handle higher loads. By customizing the tensioner’s load capacity, it can reliably handle the specific demands of the application and ensure long-term performance.
Drive belt tensioners can be customized with additional features to enhance their functionality or address specific needs. For example, manufacturers may offer tensioners with built-in dampers to reduce vibrations or noise in certain applications. Some tensioners may have adjustable arms or pulleys to provide fine-tuning of the belt tension. Manufacturers can also customize tensioners to incorporate special coatings or materials that improve resistance to corrosion, abrasion, or other environmental factors. These additional features can be tailored to suit the specific automotive or industrial needs, providing enhanced performance and longevity.
In summary, drive belt tensioners can be customized or modified to suit specific automotive or industrial needs. Manufacturers offer various options for tensioner design, size, mounting, load capacity, and additional features. By customizing tensioners, they can be optimized to meet the requirements of different applications, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and enhanced performance. When selecting or modifying drive belt tensioners, it is essential to consider the specific needs of the application and consult with manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable customization options.

Can you explain the importance of proper tensioning for drive belts in various machinery and vehicles?
Proper tensioning of drive belts is of utmost importance in various machinery and vehicles. Maintaining the right level of tension ensures optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the belt drive system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the importance of proper tensioning for drive belts:
- Efficient Power Transmission:
- Preventing Belt Slippage:
- Reducing Wear and Fatigue:
- Optimizing Belt Life and Performance:
- Adapting to Load Variations:
- Enhancing System Reliability:
Proper tensioning is crucial for efficient power transmission in machinery and vehicles. When a drive belt is under-tensioned, it can slip on the pulleys, resulting in power loss and reduced performance. Insufficient tension leads to inadequate friction between the belt and the pulleys, compromising the transfer of power from the driving pulley to the driven pulley. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts remain properly engaged with the pulleys, ensuring maximum power transfer and efficient operation of the machinery or vehicle.
Correct tensioning helps prevent belt slippage, which is a common issue in belt drive systems. Slippage occurs when the belt loses its grip on the pulleys, leading to power loss, decreased efficiency, and potential damage to the belt and pulleys. Proper tension ensures that the belt remains securely in place, creating sufficient friction to prevent slippage even under high loads or sudden changes in speed or torque. By preventing belt slippage, proper tensioning maintains reliable power transmission and protects the integrity of the belt drive system.
Improper tensioning can cause excessive wear and fatigue on drive belts. If a belt is over-tensioned, it experiences increased stress, leading to accelerated wear and potential premature failure. On the other hand, under-tensioning can cause the belt to flex excessively, leading to fatigue and eventual belt failure. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts operate within their design limits, minimizing wear and fatigue. Proper tensioning extends the lifespan of the belts, reducing maintenance costs and downtime associated with belt replacements.
Proper tensioning plays a vital role in optimizing the life and performance of drive belts. When belts are correctly tensioned, they operate in their intended range, minimizing stress and strain. This optimal operating condition reduces the risk of belt damage, such as cracking, stretching, or delamination. Additionally, proper tensioning ensures that the belts track properly on the pulleys, preventing misalignment and excessive side loads. By optimizing belt life and performance, proper tensioning contributes to increased reliability, reduced maintenance, and improved overall efficiency of machinery and vehicles.
Drive belts in machinery and vehicles often experience load variations during operation. Proper tensioning allows the belts to adapt to these load changes effectively. When the load increases, the tensioner compensates by applying additional tension to prevent slippage. Conversely, when the load decreases, the tensioner releases some tension to avoid excessive stress on the belt and pulleys. This adaptability ensures that the belts maintain the optimal tension regardless of the varying load conditions, allowing for consistent power transmission and reliable performance.
The proper tensioning of drive belts enhances the overall reliability of machinery and vehicles. By maintaining optimal tension, belts operate within their designed parameters, reducing the risk of unexpected belt failure and associated downtime. Reliable power transmission ensures that machinery operates as intended, minimizing the chances of equipment damage, production delays, and costly repairs. The use of proper tensioning techniques adds a layer of control and stability to the belt drive system, enhancing its overall reliability and ensuring smooth operation.
In summary, proper tensioning of drive belts is essential for efficient power transmission, preventing belt slippage, reducing wear and fatigue, optimizing belt life and performance, adapting to load variations, and enhancing system reliability in various machinery and vehicles. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts operate effectively, ensuring reliable performance, extended lifespan, and minimized downtime.


editor by CX 2023-11-30
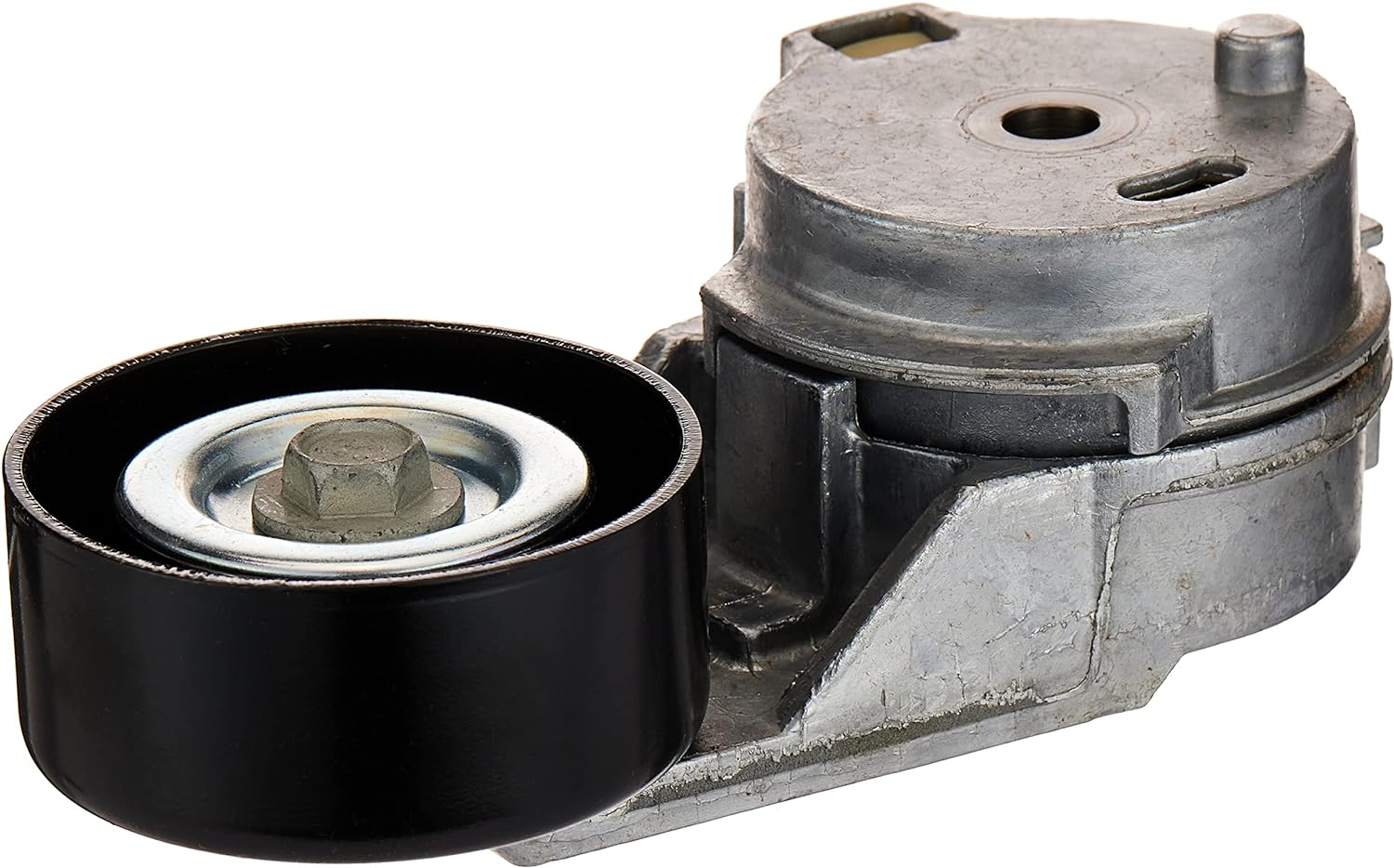
China Professional Alternator Tensioner for CZPT Mondeo V-Ribbed Belt Drive Tensioner Timing Adjuster OEM No.: 1371224, 534012820, 1s7q-6A228-AC, 1226638 CZPT Escaple 2.3L axle cap
Product Description
FAQ
•Is your company’s trader or factory?
•We are the trade department under the joint venture of the factory
•
•Does your company participate in the exhibition? What are the specific exhibitions?
•Yes ,we are participate Frankfurt fairs worldwide
•
•Where is your company? Can I come and visit?
•Welcome to visit us !
•
•Do your products support third-party testing, such as SGS?
•Yes
•
•How about your company’s quality control?
•All products are 100% inspected before packaging , and there are also random inspections for life testing.
•
•
•Does your company provide after-sales service? What kind of after-sales service is provided?
•If it is confirmed that the verification is our problem, we will refund the purchase price 100% or replace 1 by 1 .
•
•
•Do your products support customization? Can I put my logo on the product?
•Yes , we support customization .
•
•What is the packaging of the product?
•Customized brand box or white blank box .
•
•What certificate does the product have?
•ISO9001 , ISO/TS16949 , ETC ….
•
•What information do I need to provide for a quotation?
•You can provide your requirement list with model and quantity,we will make an offer during 24 hours .
•
• How long is the lead time generally?
•30-60days .
Product spections :
| Interchange number: | 1S7Q-6A228-AC |
| FORD ESCAPLE 2.3L MONDEO 1.8L |
Description :
1. The tensioner is a belt tensioner used in the automobile transmission system. The tension pulley is mainly composed of a fixed shell, a tension arm, a wheel body, a torsion spring, a rolling bearing and a spring sleeve. It can automatically adjust the tension force according to the different tightness of the belt to make the transmission system stable, safe and reliable.
2. The main function of the tensioner bearing is to support the mechanical rotating body.
3.Reduce the friction coefficient during its movement and ensure its rotation accuracy.
4.Change sliding friction into rolling friction.
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year Guarantee |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year Guarantee |
| Type: | Tensioner Bearing |
| Material: | Aluminum |
| Certification: | TS16949 |
| Car Make: | Ford |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can you describe the various mounting options and installations for drive belt tensioners in different settings?
When installing drive belt tensioners, various mounting options and configurations are available to accommodate different settings and applications. The choice of mounting option depends on factors such as space constraints, belt path, alignment requirements, and the specific design of the tensioner. Here’s a detailed description of the various mounting options and installations for drive belt tensioners:
- Fixed Mounting:
- Adjustable Mounting:
- Spring-Loaded or Automatic Mounting:
- Hydraulic or Pneumatic Mounting:
- Combination Mounting:
The most common mounting option for drive belt tensioners is the fixed mounting configuration. In this setup, the tensioner is securely bolted or fastened to a stationary component or mounting bracket within the system. The fixed mounting option provides stability and ensures that the tensioner remains in a fixed position relative to the belt path. It is suitable for applications where there is sufficient space and where the belt path does not require any adjustment or movement of the tensioner.
Adjustable mounting configurations allow for fine-tuning of the tensioner position and belt tension. These setups typically feature slotted mounting holes or adjustable arms that enable movement and positioning of the tensioner. By loosening the mounting bolts, the tensioner can be adjusted vertically or horizontally to achieve the desired belt tension or alignment. Adjustable mounting options are beneficial when precise tension adjustment or alignment is required, especially in applications with varying belt lengths or when pulley positions need to be optimized.
Some tensioners employ a spring-loaded or automatic mounting mechanism, which automatically adjusts the tension based on the belt’s requirements. These tensioners incorporate a built-in spring mechanism that applies a constant force to maintain the desired tension. The mounting configuration for such tensioners typically involves a pivot point and a spring-loaded arm that keeps the tensioner in contact with the belt. Spring-loaded or automatic mounting options are particularly useful in applications where frequent belt length changes occur or when consistent tension needs to be maintained dynamically.
In certain industrial applications, hydraulic or pneumatic mounting options are utilized for drive belt tensioners. These tensioners use hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders to apply and control the tension. Hydraulic or pneumatic mounting configurations provide precise tension control and can accommodate larger belt drives or heavy-duty applications. They are often found in industrial machinery or equipment where adjustable tension and dynamic tension control are critical.
In some cases, a combination of mounting options may be employed to achieve the desired tensioning setup. For example, a tensioner may have a fixed mounting base with an adjustable arm or pulley attached to it. This combination allows for both stability and fine-tuning of the tensioner position. Combination mounting options are useful in applications where a balance between stability and adjustability is required.
In summary, drive belt tensioners can be mounted using various configurations depending on the specific requirements of the application. Fixed mounting provides stability and is suitable when the tensioner’s position does not need adjustment. Adjustable mounting options allow for precise tension adjustment and alignment. Spring-loaded or automatic mounting options automatically adjust the tension based on the belt’s requirements. Hydraulic or pneumatic mounting configurations provide precise tension control in heavy-duty applications. Combination mounting options offer a balance between stability and adjustability. Choosing the appropriate mounting option ensures proper tensioning and optimal performance of the belt-driven system.

How do innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology impact their use?
Innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology have a significant impact on their use, improving performance, reliability, and overall efficiency. These advancements drive the evolution of tensioners, allowing them to meet the changing needs of automotive and industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology impact their use:
- Enhanced Tensioning Mechanisms:
- Improved Belt Life and Performance:
- Quieter Operation:
- Increased Versatility:
- Diagnostic Capabilities:
Advancements in tensioner technology have led to the development of enhanced tensioning mechanisms. Traditional tensioners relied on mechanical springs or fixed pulleys to maintain belt tension. However, modern tensioners incorporate innovative mechanisms such as hydraulic or automatic tensioners. Hydraulic tensioners use hydraulic pressure to automatically adjust the tension, providing more precise and consistent tension control. Automatic tensioners utilize a combination of mechanical and spring-loaded systems to automatically adapt to changes in belt length or tension. These enhanced tensioning mechanisms ensure optimal tension under varying conditions, improving the overall performance and lifespan of the belt-driven system.
Advancements in tensioner technology have resulted in improved belt life and performance. Tensioners with advanced designs and materials can better distribute the tension across the belt, reducing stress concentrations and minimizing belt wear. Additionally, innovations in tensioner coatings and materials have improved their resistance to environmental factors, such as heat, moisture, and contaminants. These advancements help prolong the life of the belt, reduce maintenance requirements, and enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of the belt-driven system.
Modern drive belt tensioners are designed to provide a quieter operation compared to their predecessors. Advancements in tensioner technology have allowed for better dampening of vibrations and noise generated during belt operation. Tensioners with built-in dampers or improved bearing systems can effectively reduce noise and vibrations, resulting in a quieter and more comfortable operating environment. This is particularly beneficial in automotive applications, where noise reduction contributes to the overall driving experience.
Innovations in drive belt tensioner technology have increased their versatility, allowing them to be used in a wide range of applications. Tensioners can now accommodate different belt widths, pulley sizes, and mounting configurations. They can also be customized or adjusted to suit specific requirements, making them compatible with various automotive and industrial systems. This versatility simplifies the selection and installation process, providing flexibility and adaptability in different applications.
Some modern drive belt tensioners incorporate diagnostic capabilities to monitor the tension and condition of the belt. These tensioners may be equipped with sensors that provide real-time feedback on belt tension, allowing for proactive maintenance and early detection of potential issues. By monitoring the tension, operators can identify and address problems promptly, minimizing downtime and preventing costly failures. Diagnostic capabilities improve the overall reliability and efficiency of the belt-driven system.
In summary, innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology have a significant impact on their use. Enhanced tensioning mechanisms, improved belt life and performance, quieter operation, increased versatility, and diagnostic capabilities are some of the key benefits. These advancements contribute to the overall reliability, efficiency, and longevity of belt-driven systems, making them more robust and suitable for a wide range of automotive and industrial applications.

Can you explain the importance of proper tensioning for drive belts in various machinery and vehicles?
Proper tensioning of drive belts is of utmost importance in various machinery and vehicles. Maintaining the right level of tension ensures optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the belt drive system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the importance of proper tensioning for drive belts:
- Efficient Power Transmission:
- Preventing Belt Slippage:
- Reducing Wear and Fatigue:
- Optimizing Belt Life and Performance:
- Adapting to Load Variations:
- Enhancing System Reliability:
Proper tensioning is crucial for efficient power transmission in machinery and vehicles. When a drive belt is under-tensioned, it can slip on the pulleys, resulting in power loss and reduced performance. Insufficient tension leads to inadequate friction between the belt and the pulleys, compromising the transfer of power from the driving pulley to the driven pulley. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts remain properly engaged with the pulleys, ensuring maximum power transfer and efficient operation of the machinery or vehicle.
Correct tensioning helps prevent belt slippage, which is a common issue in belt drive systems. Slippage occurs when the belt loses its grip on the pulleys, leading to power loss, decreased efficiency, and potential damage to the belt and pulleys. Proper tension ensures that the belt remains securely in place, creating sufficient friction to prevent slippage even under high loads or sudden changes in speed or torque. By preventing belt slippage, proper tensioning maintains reliable power transmission and protects the integrity of the belt drive system.
Improper tensioning can cause excessive wear and fatigue on drive belts. If a belt is over-tensioned, it experiences increased stress, leading to accelerated wear and potential premature failure. On the other hand, under-tensioning can cause the belt to flex excessively, leading to fatigue and eventual belt failure. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts operate within their design limits, minimizing wear and fatigue. Proper tensioning extends the lifespan of the belts, reducing maintenance costs and downtime associated with belt replacements.
Proper tensioning plays a vital role in optimizing the life and performance of drive belts. When belts are correctly tensioned, they operate in their intended range, minimizing stress and strain. This optimal operating condition reduces the risk of belt damage, such as cracking, stretching, or delamination. Additionally, proper tensioning ensures that the belts track properly on the pulleys, preventing misalignment and excessive side loads. By optimizing belt life and performance, proper tensioning contributes to increased reliability, reduced maintenance, and improved overall efficiency of machinery and vehicles.
Drive belts in machinery and vehicles often experience load variations during operation. Proper tensioning allows the belts to adapt to these load changes effectively. When the load increases, the tensioner compensates by applying additional tension to prevent slippage. Conversely, when the load decreases, the tensioner releases some tension to avoid excessive stress on the belt and pulleys. This adaptability ensures that the belts maintain the optimal tension regardless of the varying load conditions, allowing for consistent power transmission and reliable performance.
The proper tensioning of drive belts enhances the overall reliability of machinery and vehicles. By maintaining optimal tension, belts operate within their designed parameters, reducing the risk of unexpected belt failure and associated downtime. Reliable power transmission ensures that machinery operates as intended, minimizing the chances of equipment damage, production delays, and costly repairs. The use of proper tensioning techniques adds a layer of control and stability to the belt drive system, enhancing its overall reliability and ensuring smooth operation.
In summary, proper tensioning of drive belts is essential for efficient power transmission, preventing belt slippage, reducing wear and fatigue, optimizing belt life and performance, adapting to load variations, and enhancing system reliability in various machinery and vehicles. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts operate effectively, ensuring reliable performance, extended lifespan, and minimized downtime.


editor by CX 2023-11-17
China Belt Tensioner Pulley for Land Rover Discovery I 89-98 etc8552 pulley alternator
Item Description
| Item Name | belt tensioner pulley for Land Rover DISCOVERY I 89-ninety eight |
| OEM Number | ETC8552 ERR2530 |
| Diameter | 37mm |
| Top | 31mm |
| Bodyweight | .8kg |
| MOQ | 100pcs |
| Warranty | twelve months |
|
US $5-25 / Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Type: | Belt Tensioner Pulley |
|---|---|
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Tolerance: | P2 |
| Certification: | ISO9001 |
| ABS: | Without ABS |
| Car Make: | for Land Rover |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Item Name | belt tensioner pulley for Land Rover DISCOVERY I 89-98 |
| OEM Number | ETC8552 ERR2530 |
| Diameter | 37mm |
| Height | 31mm |
| Weight | 0.8kg |
| MOQ | 100pcs |
| Warranty | 12 months |
|
US $5-25 / Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Type: | Belt Tensioner Pulley |
|---|---|
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Tolerance: | P2 |
| Certification: | ISO9001 |
| ABS: | Without ABS |
| Car Make: | for Land Rover |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Item Name | belt tensioner pulley for Land Rover DISCOVERY I 89-98 |
| OEM Number | ETC8552 ERR2530 |
| Diameter | 37mm |
| Height | 31mm |
| Weight | 0.8kg |
| MOQ | 100pcs |
| Warranty | 12 months |
What is a pulley?
Pulleys are shafts or wheels on a shaft that support the movement and change of direction of a taut cable. The pulley also transfers power from the shaft to the cable. A simple pulley is used to raise the school flag. Read on to learn about the basic types of pulleys. We also covered the use of pulleys in everyday life. Read on to learn more about this important mechanical part.
composite pulley
A composite pulley is a mechanical system where two or more pulleys and ropes are connected together. It reduces the force required to lift the load because the force is divided by the distance of each pulley. Distance is equal to the mass of the object. Composite pulleys are a common mechanical system on sailboats. Composite pulleys can be used to lift heavy equipment such as sails.
The compound pulley unit consists of two pulleys, one fixed and the other movable. The fixed pulley is fixed overhead, while the movable pulley is connected to the load by a chain. The lift applies force to the other end of the rope. Anchor points are attached to fixed joists, ceiling joists or sturdy branches. The chain should be long enough to support the load during lifting.
Composite pulleys can be made from a variety of materials. Some are fixed and remain fixed. Others are detachable. The composite pulley combines the advantages of both types, making it a versatile tool. In the table below, these three types of pulleys are compared. It’s easy to see which one is best for your needs. The right choice depends on your specific needs and budget.
The compound pulley system consists of two fixed pulleys and one movable pulley. The compound pulley system multiplies the force by a factor of 2. The compound pulley system is particularly suitable for heavy loads and is ideal for construction sites. Workers apply less than half the load force on the composite pulley, significantly reducing the force required. This is a major benefit for many people.
Fixed pulley
Fixed pulleys are fixed gears of fixed length that are mounted on solid objects. There are many different types of pulley systems. Some cooperate with each other, but not “fixed”.
Fixed pulleys can be used for a variety of purposes. One application is to lift small objects. They have a one-to-one mechanical advantage. Often, a single pulley can lift small loads. The force required to lift a single fixed pulley remains the same. They are usually used to lift lighter objects. They can even be attached to buckets used to draw water from wells.
While single fixed pulleys have desirable mechanical advantages, they are not suitable for force multipliers. Because their mechanical advantage diminishes over time, they are not effective force multipliers. They are used to redirect work so that it can be applied in the most convenient direction. This mechanical advantage is the main advantage of fixed pulleys and the most common way of moving objects. They have several benefits, including the ability to increase the speed of moving objects.
Another application for fixed pulleys is lifting supplies. A scaffold can weigh more than one and can be directly hoisted. In order to facilitate the transportation of materials, fixed pulleys are usually installed on the top of the scaffolding on construction sites. Then thread the rope through the edge of the groove that holds the pulley. The fixed pulley exerts the same force on the pull side as on the push side. The same is true for moving objects with fixed pulleys.
moving pulley
A movable pulley is a device whose part is fixed to another object, usually a rod or beam. The movable part moves with the load, making the load feel lighter. This is a useful tool for those who need to carry heavy items such as large bags. The advantages of moving pulleys are many. Here are some of them. Read on to learn more about them.
One of the most common uses of movable pulley systems is climbing high objects. Climbers act as pulley loads and pull ropes to lift objects. Eventually, when the traction stops, the climber descends. However, it is still a useful tool in other situations. The movable pulley system can help you climb the tallest objects or lift them to level surfaces.
Another example of movable pulleys is in industry. Depending on the load, movable pulleys make handling and moving loads easier. You can use them in a variety of applications in manufacturing and industry, including cleaning. For example, the American flag is raised and lowered every day. Removable pulleys are a handy tool when buildings need cleaning.
If you’re not sure whether a task requires a pulley, a zipline might be a good option. Connect the two ends of the rope and the pulley will move along the rope, then attach the rope to the metal cable. The load is the person holding the pulley, and the force comes from the attachment on the other end of the rope. There are two types of live pulleys: simple pulleys with just one wheel and live pulleys with many ropes attached.
School flag raised with simple pulleys
How is the school flag raised? It is pulled up by a rope attached to a pulley at the top of the pole. When the rope is pulled, the pulley turns, raising the flag. A pulley is a simple mechanism that helps people move heavier objects with ease. The rope must be securely attached to the pulley to keep the flag stable.
A simple pulley is a spinning wheel with grooves on one side and ropes on the other. The rope can be any length and the wheels can be any size. The rope has to go through the groove and the load is attached to the other end of the rope. Simple pulleys are pulleys with fixed shafts. An example is the wheel on a school flagpole.
A simple pulley system consists of a primary pole, a secondary pole and an outer member. The primary flagpole is connected to the track by a detour, while the secondary flagpole is connected to the track by a pipe. There is a groove on one side of the track, which passes through the inner cavity of the flagpole. An open track at the upper end of the track connects the two parts of the pulley.
A simple pulley can be used for many purposes. This is a useful machine that can be used to raise the flag. Among other things, it can be used in clothing lines, bird feeders, and even roofers. And, of course, you can use the pulley to raise the flag. Its versatility makes it an essential part of school decor.
cast iron pulley
If you are looking for pulleys for your machine, you may come across cast iron pulleys. They are usually cheap and available in a variety of sizes. The rim is held in place by a mesh attached to a central boss. The arms and spokes can be straight or curved, but most are oval. There are many uses for this type of pulley.
You might wonder why the arms of cast iron pulleys are so curved. Bent arms tend to yield rather than break. Cast iron pulleys are usually round with a slight bump on the rim, which helps keep the belt centered on the rim as it moves. On a 300mm diameter pulley, the bumps may be as small as 9mm.


editor by czh 2022-12-19
China high quality Auto Drive Belt Tensioner OEM 11288604266 Alternator Pulley for BMW wholesaler
Product Description
Auto Drive Belt Tensioner OEM Alternator Pulley For BMW
Product Specification:
| OEM | 11288604266 |
| Apply To |
For car |
| Brand | FENGMING |
| Condition | Brand New |
| Stock Availability | Yes |
| Minimum Order QTY | 2PCS |
| OEM Order Acceptability | Yes |
| Small order Lead Time | 3-7 days |
| Large Order Lead Time | 15-30 days |
| Quality Warranty | 12 months |
| PACKAGING | As neutral or as customer’s request, FENG MING PACKING |
| Payment Methods | Paypal, Western Union, Bank T/T, L/C |
| Shipment Methods | DHL, UPS, TNT, FedEx, Aramex, EMS, Air Cargo, Sea Cargo |
Company Profile
Replacing a Failing Drive Belt Tensioner
A failing drive belt tensioner can be extremely costly. Here’s what to look for and what to do if you suspect yours is bad. In addition, you’ll learn how to identify Idler pulleys and repair it yourself. If the tensioner is failing, you should replace the belt, as well as the Idler pulleys and shaft bearings. But what if the tensioner isn’t faulty?
Symptoms of a bad or failing drive belt tensioner
If your car’s drive belt is not moving smoothly, the pulley may be at fault. Ideally, the tensioner pulley should move away from the engine when the car starts. However, if it stays put or starts to move toward the engine, it’s time to replace the tensioner. The belt may also start to exhibit different wear patterns, such as the uneven wear of the sprockets, bearings, and springs.
If the serpentine belt begins to look loose and the engine loses its luster, the problem is most likely the bad drive belt tensioner. This issue will result in engine vibration. A faulty drive belt tensioner may also lead to a faulty spark plug, which prevents fuel from burning in the combustion chamber. This issue will likely require an engine diagnostic tool, such as an OBD2 scanner, to determine the cause of the check engine light.
Another sign that your drive belt tensioner is failing is a chirping noise. This noise can occur intermittently or constantly, and it may signal a problem with the pulley. In some cases, a faulty pulley may even cause your engine to misfire. Additionally, you may notice that the engine won’t start, even if you engage the starter motor.
In addition to the noise that may come from a failing tensioner, the bad belt tensioner may cause your serpentine to fail. In addition to the noise, this can also lead to overheating of the engine, which can result in costly damages. In addition to causing engine damage, a bad belt tensioner won’t reserve the minimum tension it needs to do its job and may even exceed it, causing the belt to wear out much faster.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it may be time to replace the drive belt tensioner. You can find a replacement OEM part online at a discounted price, as they’re available in wholesale quantities. A Mazda engine typically has no other parts blocking the serpentine belt path, so you can easily find the part you need. After replacing the drive belt tensioner, you’ll need to replace the serpentine belt as well.
Cost to replace a drive belt tensioner
Depending on the location and type of vehicle, replacing a drive belt tensioner can cost between $235 and $267. Some repairs may require other parts, such as a serpentine belt or tensioner housing. RepairPal’s Fair Price Estimator can help you get an accurate estimate for your particular vehicle. You can also contact HomeX, a virtual repair shop that can fix simple issues like loose drive belt tension.
It’s a relatively simple DIY job for most cars. An experienced mechanic will be able to replace the belt in a half hour or less, depending on the type of car and how many parts are affected. Depending on the complexity of the repair, the labor to replace the drive belt tensioner could cost anywhere from $50 to $170. The labor to replace the drive belt tensioner is typically included in the quoted price, but some auto shops may charge more to replace other car parts as well.
Replacing the drive belt tensioner is a relatively easy task. While the process might take an hour or more, it will be worthwhile in the long run. Regular inspections can prevent costly repairs by identifying problems before they cause major damage. A car’s belt is essential to the operation of the engine and can’t be operated without it. Changing it can save you money, as it will save you from spending extra on unnecessary parts.
Thankfully, there are plenty of tools available to help you replace your drive belt. While it may not be the easiest repair, it will still cost less than a mechanic’s service call. It is better to replace the belt early than to wait for the vehicle to break down, as this will prevent more expensive parts from breaking. You may also consider investing in a premium belt, which will give you twice as much mileage as a cheaper one.
While a drive belt tensioner is generally considered a wear-and-tear item, it is a part that should last the entire life of the vehicle. You can expect to replace the drive belt tensioner no earlier than 125,000 miles, but it is better to do it early if your car isn’t that old. And it doesn’t hurt to check the owner’s manual for directions on how to replace the drive belt tensioner.
Idler pulleys
Idler pulleys may seem like a minor part of your car, but their important job is to keep various components in good working order. Fortunately, they are inexpensive and don’t need much maintenance. If 1 pulley fails, it is best to replace all of them. However, it is not always easy to check idler pulleys yourself. It’s recommended that you visit a professional auto repair shop that is ASE-certified to inspect and replace the idler pulley.
Depending on the size and type of idler pulleys you need, you’ll have to purchase 2 or 3 pieces. You’ll need to purchase a pair of pliers for this part, as well as a tensioner pulley wrench. The cost of a replacement idler pulley will vary by make and model, but you can expect to pay between $40 and $200. These prices don’t include taxes or fees. Because they are so essential to drive belts, it’s worth investing in 1 or two.
Idler pulleys are a vital part of a car’s engine. They’re found underneath the hood and are usually 2 to 4 inches in diameter. They run over a roller that’s used to tension the belt. The belt is wrapped around a series of engine parts, and the idler pulleys are a complement to each other. You may not need an idler pulley on your car, but your mechanic will install it for you if you don’t.
The idler pulleys for a belt tensioner are crucial parts of your car’s engine. If they are worn down, the belt is likely to move loosely over them. Corrosion may also make the idler pulley move less freely. If the idler pulley is slipping, the belt may jump over the pulley, and the squealing noises will indicate a serious problem.
The idler pulley is a pivotal part of the engine’s power train. It redirects the path of the serpentine and timing belts, so that they can make optimal contact. The larger the contact patch, the more power the belt will transfer. The idler pulley can also improve the vehicle’s performance. It is a vital part of the engine, so make sure you check it frequently and install it correctly.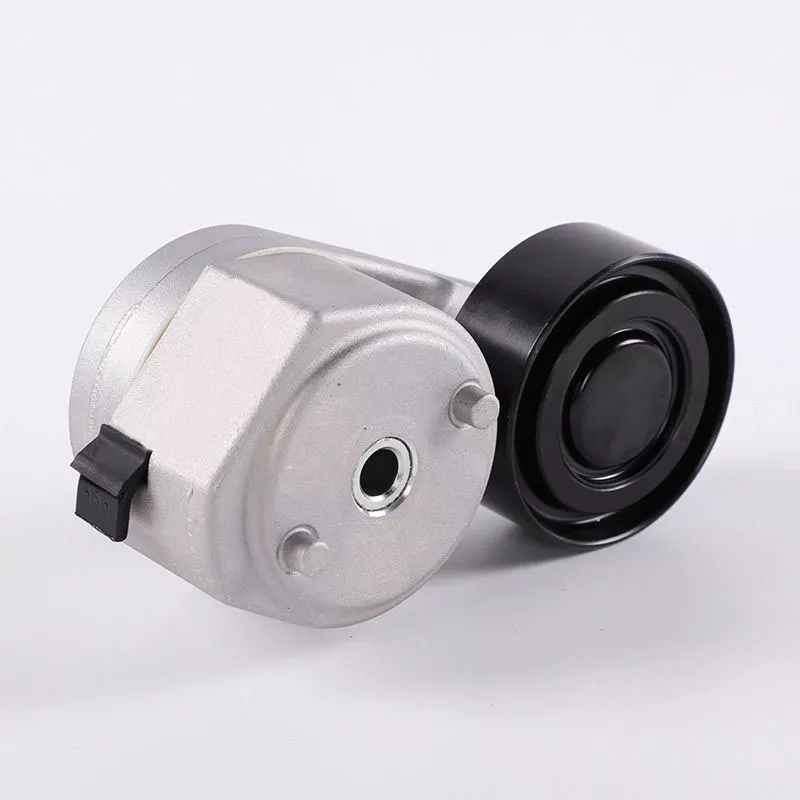
Repairing a drive belt tensioner
Replacing a drive belt tensioner is relatively simple. While your belt may need to be replaced, other parts of your engine may also need to be fixed. Typically, the tensioner will be replaced along with the pulley, as both parts are prone to malfunction. Replacing the drive belt tensioner is a fairly straightforward job, and it should only take about an hour or two. By following these simple steps, you can save yourself a lot of money and time.
You can detect the problem by observing the belt glazing. Typically, it occurs when the tensioner does not have enough spring tension. Another sign of a failed component bearing is excessive arm oscillation. Excessive chattering and oscillation indicate that the damper has worn out. If you notice excessive oscillation, you should replace the tensioner pulley. Otherwise, you might be dealing with a defective bearing.
A damaged or out-of-adjusted drive belt will make a squealing noise. This is due to the belt slipping on the pulleys. It is most noticeable when the car is first started in the morning. A damaged drive belt will also be hard to manipulate. The new belt should be the same length and width as the old one. You can check the tensioner by pulling the belt and compressing it.
A worn-out drive belt tensioner will result in unusual noise, excessive wear, and a loose belt. This is especially affecting if the car is equipped with a serpentine belt. The drive belt tensioner has a roller bearing that can wear out, which will cause a squealing noise or even cause the belt to roll off entirely. Because of its important role in engine operation, it is vital to check the condition of the drive belt tensioner on a regular basis.
While replacing a drive belt tensioner may seem like a simple DIY project, you should consult a mechanic before undertaking the work. The parts and labor costs of a drive belt tensioner repair can range from $140 to $400, and you should allow an hour for this repair. If you are not comfortable performing the repair yourself, you can always hire a mechanic to do it for you. In most cases, a drive belt tensioner replacement will cost approximately $70 to $80 and take about an hour.


China factory Alternator Belt Pulley FIAT Doblo 2010 1, 3mtj Tensioner with Hot selling
Product Description
Alternator belt pulley Fiat Doblo 2571 1,3MTJ tensioner
Alternator belt pulley Fiat Doblo 2571 1,3MTJ tensioner
| Compatible with OEM number | 55244469 |
| Weight | 0,65 kg |
FIAT
FIAT Doblo 05/2001 – 10/2005 1,3 MTJD
FIAT Fiorino 2016 – 1,3 MJTD
FIAT Doblo 01/2015 – 1,3 MJTD
FIAT Doblo 02/2571 – 12/2014 1,3 MJTD
FIAT Fiorino 2007 – 2016 1,3 MJTD
FIAT Doblo 11/2005 – 01/2571 1,3 MJTD
CITROEN
CITROEN Nemo 2007 – 2016 1,3 HDI
PEUGEOT
PEUGEOT Bipper 2007 – 2016 1,3 HDI
Company Details:
HangZhou CZPT Auto Parts Industry Co., Ltd is a family owned company, established in 2005.
As a real, direct and professional manufacture in China, CZPT has grown to become 1 of greatest manfacturer and exporter in Performance parts, include intake system, exhaust system, cooling system, interior&exterior parts etc.
We own a factory located in HangZhou, HangZhou, which has 8000 square meter, tens of machine, 150 workers, 15 person sales team, 5 R&D department. Our customers cover North American, South American, Asia, Middle east and Europe. We export the millions of USD per year. Looking forward to have a nice cooperation with you
Why Choose YiBai?
It’s simple. The YiBai Company is built on delivering more Quality, Reliability, and Value than any other manufacturer. Whether supplying the world’s automakers with reliable OE parts, or developing aftermarket replacement parts at or above spec, YiBai’s line of products are built to deliver superior all-around performance every day.
Aftermarket Parts Built At or Above Specification
The quality of YiBai parts is guaranteed because every component that leaves a YiBai factory has been designed with precision, manufactured to the strictest OE standards or above, and subjected to rigorous safety and performance tests. In the end, it all comes down to quality – that’s what the YiBai name stands for.
Measure Everything for a First Time Fit
Our First Time Fit philosophy attracts attention throughout the automotive world, while our commitment to pushing technology into the future and continually sets us apart around the globe.First Time Fit is a promise that YiBai makes to the aftermarket, by providing products that are OE grade or better – and fits the first time.
Our Service
1. OEM Manufacturing welcome: Product, Package…
2. Sample order
3. We will reply you for your inquiry in 24 hours.
4. After sending, we will track the products for you once every 2 days, until you get the products. When you got the goods, test them, and give me a feedback.If you have any questions about the problem, contact with us, we will offer the solve way for you.
FAQ
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, we pack our goods in neutral white boxes and brown cartons. If you have legally registered patent, we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB CIF, DDU.
Q3. How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take 15 to 20 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q4. What is your sample policy?
A: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the sample cost and the courier cost.
What Is a V-Belt?
A v-belt is a type of belt that provides a continuous motion to the vehicle’s wheels. This type of belt is made of several different components. They usually have a trapezium-shaped cross-section because of its elastomer core. Elastomers are often made of polyurethane or a synthetic rubber with good shock resistance. Sometimes, a v-belt will have 2 sections – cushion rubber and compression rubber.
Link-type V-belt
A laminated link-type V-belt is 1 embodiment of the present invention. The belt comprises individual lamina sections connected longitudinally by studs and tubes, each of which has at least 1 connecting means. The slots in the links allow for a full share of the load to be transferred through the belt, and they also reduce substantially all internal mechanical stresses. The belt is preferably designed to extend substantially the entire width of the machine being driven.
Conventional link-type V-belts are installed between 2 pulleys on the tight side of the V-drive. A wide end of a link moves in the direction of rotation, while the stud of a second, smaller link pulls the nose end of the third link forward. The shank of the stud pivots on a solid fabric located in hole 2 of the third link below. The bottom link, however, curls over the stud and the belt is assembled.
The present invention offers an improved method of forming a link-type V-belt. The belt is manufactured using links and does not have to be fitted as tightly as conventional link-type V-belts. This belt is flexible and strong enough to handle normal tension loads in a well-designed drive. In addition, the belts made using the present invention will have a longer life, thereby extending the drive’s load-carrying capacity.
Classical V-belt
A classical trapezoidal belt profile makes the VB Classical V-belt ideal for various industrial applications. Available in small sizes from 5mm to 3mm, these belts are available with cogged or raw edges. Their highly engineered construction makes them ideal for a variety of uses. These belts are commonly used in motors, compressors, milling machines, mixers, and other mechanical devices. To determine the right belt for your application, consider the following factors.
The classic v-belt is the most common and economically-priced type of v-belt. They are manufactured using special formulated rubber reinforced with polyester cords. These belts can span from 16 inches to 400 inches in length. The classic V-belt is also very easy to replace. The belt’s outer diameter and pitch can be measured. The length is typically standardized by the Association for Rubber Product Manufacturers.
Typically, classical V-belts are used in single-belt drives. Because they don’t require lubrication or maintenance, these belts are often available in sizes A and B. However, larger belt sizes are rarely used for single-belt drives. In such cases, multiple A or B belts are an economical alternative to single-belt C. In addition, narrower-profile V-belts provide higher power ratings than conventional V-belts because of their higher depth-to-width ratio. These belts are ideal for heavy-duty applications.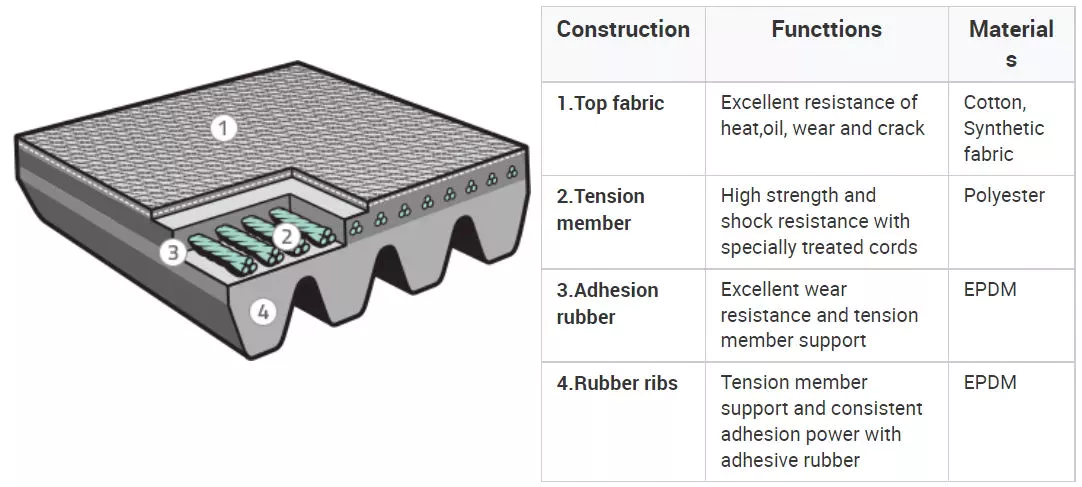
Narrow V-belt
The narrow v-belt is the same as a conventional v-belt, but it has a smaller top and bottom width. This makes it suitable for higher horsepower applications, and it is used in high-end sports cars. Narrow v-belts are generally characterized by a letter “v” on the top side and a length of outside dimensions of 1.6:1.
The steel wires that comprise the core of the v-belt are endless and are free of joints. This provides the strength required for torque transmission. A base rubber compound is placed around the steel wire and acts as a medium of compression and shock absorption during power transmission. A plastic layer acts as a protective cover, and provides the rubber with a degree of temperature tolerance. While choosing a narrow v-belt, it is important to keep in mind that there are some disadvantages to a narrow V-belt.
For example, a narrow V-belt is suitable for high-power applications, and may be used in a small assembly space. Its narrow profile also allows it to be space-saving in layout and allows high-speed drives without additional belts. Furthermore, it reduces operating and maintenance costs. It is ideal for applications where space is limited, and a high torque is required. The benefits of a narrow V-belt are plentiful.
Banded belt
Identifying a banded v-belt can be tricky, but there are a few signs that can indicate a possible problem. Cracked belts can be difficult to spot, but they can be an early indicator of a more serious problem. Look for cracked underside edges, worn covers, and misplaced slack. If 1 or more of these factors applies to your belt, you may want to seek a replacement.
Banded v-belts are made with an elastomer core. The main component of this belt is the elastomer, which is used for the band’s flexural strength and shock resistance. It’s sometimes separated into 2 sections, with each section connected to the other by a tension cord. This gives the belt its trapezium cross-section, which increases tensile strength.
The 2 main types of banded v-belts are wrapped or raw edge. Wrapped v-belts have a fiber-covered body while raw edge belts are uncovered. Banded v-belts are often classified by their cross-section, and include: standard v-belt, wedge v-belt, narrow versus double v-belt, cogged v-belt, and double t-belt.
Banded v-belts are popular with commercial applications. Whether you’re looking for a 2V-belt or a large 8V-belt, V-Belt Guys has what you need. We also stock a wide variety of different banded v-belts and can help you find 1 that fits your needs and budget. Take a look at our selection today!
Traditional V-belt
Although a traditional V-belt may be a glorified rubber band, modern variations reflect advances in engineering. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for trouble-free service. When you are replacing a traditional V-belt, be sure to follow these simple steps to ensure its longevity. Read on to learn more. Listed below are the features of each type of V-belt. Identify the type of belt you need by measuring its top width, circumference, and dimensions.
TEC Traditional V-belts have an exceptionally low slip rate and are resistant to high operating temperatures. These types of belts do not experience early belt aging. They are also highly resistant to poor operating conditions. However, the maintenance is more extensive than other types of belts. A typical V-belt part number is B50, which is the cross-section size of a 50-inch belt. The belt’s lifespan is greatly increased because of this feature.
A ribbed V-belt is another option. It has a deeper V than a traditional V-belt. The ribs in this type are narrower and more flexible. These ribs are smaller than the classic V-belt, but they can transmit 3 times as much horsepower. Because they are thinner, these belts are more flexible than traditional V-belts. The thickness of the ribs is less critical.
Metric V-belt
Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.Metric V-belts are made to a more precise standard than their American counterparts. These belts are manufactured to meet ARPM tolerances, making them suitable for industrial, machine, and food processing applications. This metric system is also more convenient than converting between the 2 units. Listed below are the most common uses for a Metric V-belt. If you’re in the market for a new belt, consider ordering a metric one.
Metric V-belts are generally more durable than their equivalents made of standard American-sized belts. Metric V-belts are available in many different sizes to fit different machineries. In addition to offering superior load-carrying capacity, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are known for their exceptional flex and stretch characteristics. For optimum performance in textile mills, food processing, and machine tool applications, Metric Power(tm) V-belts are manufactured using a proprietary construction that combines a higher load-carrying capacity with superior flex and stretch.
Metric belts can generate 50% to 100% more horsepower than conventional and classic sectioned belts. This is achieved through improved construction and placement of the cord line. These belts also have unique wedge designs that help them support the cord in motion. However, you must ensure the proper tension when buying a Metric V-belt, because improper tension may damage the belt. They are compatible with both U.S. and international standards.


China best Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner for Outlander 1345A090 near me factory
Product Description
We have All Spare Parts for CZPT and Japanese Pickups, and also series parts for different cars.
High quality products Original, Made in ZheJiang , Made in China Mainland, 4000+ square meters warehouse, many parts in stock.
Please feel free to contact and know more.
|
1.Item Name: |
Alternator drive belt auto tensioner For Outlander 1345A090 |
|
MR580154 |
1345A090 |
|
3.Suitable for: |
For Outlander 1345A090 |
|
4. Delivery Time: |
Normally Within 1-50 days after deposit or as customers’ requirement, depend on stock |
|
7.Advantages: |
Our Advantages: |
FAQ:
Q1: How many years are your company in the autoparts industry?
A: The company has been founded for 15 years till now.
Q2: What are your major products?
A: Our main products are all kinds of sensor&switch and blower motor for passenger car,truck and excavator.
Q3: Where are your company?
A: We are located in HangZhou, China.
Q4: Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are factory with export licenses.
Q5: What is the MOQ?
A: Normaly, our MOQ is 100pcs ,but different product may have the different MOQ.
Q6:How about the quality of your sensors?
A: Our products meet the QC/T 824-2009 and have got the ISO9001 Certification. OEM Standard is also welcome and could be
fulfilled. Every item will be tested before shipment. You are very welcome to visit our factory at your convenience.
Q7:How about the warrenty of your sensors?
A: All of our sensors are with warrenty of 1 year, for some sensors the warrenty could be extented to 3 years.
Q8: What is the payment terms?
A: 30% deposit before production,70% balance before shipment.
Q9: Can your company customize sensors?
A: YES! You are very welcome to customize sensors, but it is strongly recommended to provide samples.
How to Tell If Your Timing Belt is Worn Out
The timing belt is a component of your engine that consists of special materials that coordinate the rotational movement of your camshaft and crankshaft. This synchronization is vital for sustainable combustion. In addition to being vital for the proper operation of your engine, the belt is also responsible for setting the pace at which it will turn. Timing belts must be extremely strong and resilient, able to maintain a high degree of synchronicity, and operate effectively even in the most severe conditions.
Problems caused by a worn-out timing belt
A worn-out timing belt can cause misfiring. Because the belt controls the movement of the pistons in the engine, it’s critical that it’s functioning properly. Misfires can cause serious engine damage and should be fixed as soon as possible. But how do you know if your timing belt is worn out? Here are 3 of the most common symptoms of a worn-out belt.
A car engine will misfire if the timing belt is broken, which could lead to severe damage. A broken belt may also cause excessive smoke to be produced by the exhaust system. If these symptoms are present, it’s time to take the car in for a timing belt replacement. A worn-out belt will affect the performance of your car. It will also affect the engine’s starting speed. When it’s time to replace it, you should do it now to avoid future problems.
Misfiring and premature cylinder closing are 2 of the most common symptoms of a worn-out timing belt. A worn-out belt can cause permanent engine damage. Because the timing belt contains teeth that grip the gears, it can slip. If the timing belt slips, the teeth can fall into the gears, causing the engine to misfire. Worn-out timing belts can also cause the engine to stall.
Engine ticking is another common sign of a worn-out timing belt. It can also be caused by low oil pressure. When oil pressure drops, the timing belt will become loose and cause a ticking sound. You should replace the timing belt as soon as it’s damaged. But it’s not enough if you don’t notice any of these signs right away. If the ticking sound continues, you’ll probably have an engine-related problem.
Types of timing belts
Timing belts are made of special materials that help the engine synchronize the crankshaft’s rotation with the camshaft’s. This precision is vital for the combustion process, as it ensures the proper opening and closing of the valves within the combustion chamber. The belts control the engine’s pace, which is why they must be strong enough to maintain synchronicity and operate at high speeds. However, timing belts do not come cheap, so there are several factors that you should be aware of before buying one.
First, timing belts come in different pitch sizes. A typical metric pitch is 5 millimeters, but some manufacturers use a higher or lower pitch. The pitch determines how much tension the belt will be able to carry and whether or not it will wear out prematurely. Other pitch sizes are more common. Timing belts come in 3 different widths, and they all have different tooth profiles. To find the right 1 for your engine, you need to know the pitch.
Modified curvilinear belts are made of 2 different types of materials. They combine the strengths of trapezoidal and curvilinear belts. The outer surface of these belts has a steeper angle than the belt’s teeth, which means that the power transmitted by the motor is much higher. Consequently, they are the primary choice for high-performance industrial applications. A synchronous timing belt is ideal for applications where precise synchronization of the driven and driver shafts is important.
Spliced and welded timing belts are used in many general applications. These belts typically have no joints or weak points and are more durable. These types of timing belts are also made with a smooth back and sealed edges. If you need a custom length or shape, these can also be manufactured. Then, you can order them for your exact measurements. When you need a new timing belt, you can simply ask for a quote and order 1 online.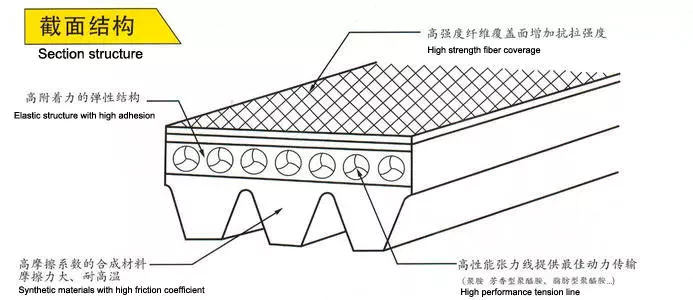
Common problems
Timing belts are a crucial part of your car’s drive system, and improper installation can cause a whole host of issues. It is also susceptible to crimping and premature wear. In either case, it is vital to take action early to prevent excessive engine wear and extend the life of the timing belt. Here are some common problems with timing belts. You may be surprised to learn that these problems are often caused by common car maintenance practices.
Regardless of the cause of the problem, a worn or faulty timing belt will affect the engine’s timing. This may result in misfires or excessive exhaust release. Engine misfiring is a serious sign that something is amiss. Depending on the extent of the problem, it could even lead to engine damage. If you experience erratic performance or excessive smoke, it’s likely the timing belt is faulty. Here are some common problems with timing belts and their causes.
Engine misfire is a common warning sign that your timing belt is wearing. This occurs when the timing belt slips off the gears or camshaft, causing the cylinder to open too early. If you notice this problem, take immediate action by visiting your mechanic immediately. Moreover, timing belt failures can cause a large amount of damage to your car’s engine, so it is essential to have your timing belt replaced in time.
Improperly adjusting the tension of your timing belt can also lead to serious problems. This can cause excessive wear on your engine’s pistons and valves, and damage the engine. Ultimately, a damaged timing belt may result in an expensive engine rebuild. While this might seem like a good option, it is not always the most practical solution. Ultimately, your car’s timing belt will wear down if you don’t fix these problems immediately.
Symptoms of a worn-out timing belt
If your car’s engine makes a high-pitched squeal when you start or run it, you may be experiencing a worn-out timing belt. You can check the belt by opening the hood and listening closely to the noise. You may also notice uneven RPM counts. The squealing sound can be caused by a number of factors, such as low oil pressure, engine lubrication problems, or even the timing belt.
If your car is exhibiting these symptoms, then it’s time for a replacement. A timing belt breaks down while your engine is running, and this can cause major engine damage. The timing belt is connected to the crankshaft and camshaft by a belt that keeps the 2 parts in sync rotation. When the timing belt wears out, it may cause a jump in the belt’s tooth, causing cylinders to open and close randomly, resulting in blow-by.
A timing belt is crucial to the functioning of your car’s engine. It synchronizes the engine rotation system and opens and closes the valves at the right time. Because it is subject to great forces inside the engine, the belt must be replaced at some point. Every vehicle needs a new timing belt at least once in its lifecycle. But what are the symptoms of a worn-out timing belt?
The timing belt is crucial to your car’s performance, so if you notice any of these signs in your vehicle, you should make an appointment with a qualified mechanic. The best way to tell if your timing belt needs to be replaced is to visually inspect the belt. You can visually inspect the belt while the engine is off, and if you notice it’s sagging, you should replace it.
When to replace a timing belt
A timing belt is an essential part of your vehicle’s engine and is responsible for synchronizing the rotation system, allowing the valves to open and close at the correct time. Due to its constant use and great forces inside the engine, timing belts must be replaced at some point. The recommended interval for timing belt replacement is anywhere from 60,000 to 150,000 miles. In most cases, timing belt replacement is recommended for vehicles between 6 and 10 years old.
Costs for a timing belt replacement can vary widely depending on the make and model of your vehicle. The labour and parts used for timing belt replacement are relatively inexpensive, but you’ll have to remove several parts of your engine to access them. Timing belt replacement also involves replacing the water pump, which is driven by the timing belt. These other parts will be replaced with new ones, but the overall cost of the repair depends on the type of car you drive.
A timing belt is a thin, rubber piece that runs along the front of the engine. It’s responsible for synchronizing the valves and camshafts and is an important component of an engine. The belt’s custom teeth make it easy to see when it’s time to replace your car’s timing belt. Oftentimes, car manufacturers recommend timing belt replacement every 2 to 4 years or 50,000 miles, and they’re not the only ones who recommend it.
A professional mechanic can replace the timing belt and water pump in 1 service, saving you both time and money. Timing belt replacement is an intricate task and can last anywhere between 4 and 8 hours, depending on the make and model of your car. However, it is worth it if you can get your vehicle into a garage or repair shop sooner rather than later. You can save a lot of money on labor costs by replacing your timing belt and water pump yourself.


China Hot selling Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner for CZPT Outlander Lancer Asx 1345A079 1345A060 1345A008 with Hot selling
Product Description
We have All Spare Parts for CZPT and Japanese Pickups, and also series parts for different cars.
High quality products Original, Made in ZheJiang , Made in China Mainland, 4000+ square meters warehouse, many parts in stock.
Please feel free to contact and know more.
|
1.Item Name: |
Alternator Drive Belt Auto Tensioner |
|
2.OE NO.: |
1345A079 1345A060 1345A008 |
|
3.Suitable for: |
For CZPT Outlander Lancer ASX |
|
4. Delivery Time: |
Normally Within 1-50 days after deposit or as customers’ requirement, depend on stock |
|
7.Advantages: |
Our Advantages: |
FAQ:
Q1: How many years are your company in the autoparts industry?
A: The company has been founded for 15 years till now.
Q2: What are your major products?
A: Our main products are all kinds of sensor&switch and blower motor for passenger car,truck and excavator.
Q3: Where are your company?
A: We are located in HangZhou, China.
Q4: Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are factory with export licenses.
Q5: What is the MOQ?
A: Normaly, our MOQ is 100pcs ,but different product may have the different MOQ.
Q6:How about the quality of your sensors?
A: Our products meet the QC/T 824-2009 and have got the ISO9001 Certification. OEM Standard is also welcome and could be
fulfilled. Every item will be tested before shipment. You are very welcome to visit our factory at your convenience.
Q7:How about the warrenty of your sensors?
A: All of our sensors are with warrenty of 1 year, for some sensors the warrenty could be extented to 3 years.
Q8: What is the payment terms?
A: 30% deposit before production,70% balance before shipment.
Q9: Can your company customize sensors?
A: YES! You are very welcome to customize sensors, but it is strongly recommended to provide samples.
Choosing a V-Belt
When choosing a v-belt, you should understand the characteristics of each type and how they affect the performance of your machine. Listed below are the characteristics of Cogged, Narrow profile, and wide v-belts. Learn about the advantages and disadvantages of each. Choose the right v-belt for your machine to maximize its performance. Learn about the different materials used to make v-belts and how they influence the performance of your machine.
Narrow v-belts
While the flat belts are the most common type of v-belt, narrow v-belts are also a common option for industrial applications. These belts are similar to wedge belts in that they transmit heavier loads, but in a smaller form. Narrow v-belts are typically designated as 3V, 5V, and 8V and are denoted by their top width, multiplied by an eighth of an inch. Narrow v-belt sections conform to a wedge belt profile and are usually standardized by manufacturers. For example, section 3V corresponds to a wedge-type profile, while section 5V corresponds to SPB.
Both narrow and conventional v-belts are made of rubber stocks, which are generally composed of polymer or synthetic rubber. Fabric materials may be used to cover the stock material, adding a layer of reinforcement and protection. Narrow v-belts have a higher power rating than traditional V-belts. This is due to their greater depth-to-width ratio, which puts more of the reinforcing cord beneath the sheave.
The Wedge TLP ™ Narrow V-belt from Continental features a homogeneous one-piece design for maximum strength and long-term performance. These belts feature a high-denier cord and can handle significant horsepower increases. These belts are ideal for industrial applications. However, they are not as durable as their wider counterparts. The Wedge TLP is also an excellent choice for heavy-duty industrial applications.
Cogged v-belts
A key benefit of cogged v-belts is their ability to increase power output without sacrificing reliability. These belts are designed with precision-engineered cogs, which allow them to fit into smaller pulleys without reducing power output. Their raw-edge sidewalls and specially formulated EPDM rubber compound also help provide grip power. Cogged v-belts are manufactured by Carlisle(r) and offer several advantages over conventional belts.
The performance benefits of Cogged V-Belts are widely acknowledged. The company uses added-strength EPDM compounds in their belts to help reduce downtime and energy consumption. They are ideal for demanding applications such as power transmission. These belts are available in a variety of sizes and cross-sections. The section number of Cogged v-belts is H3V, H4V, and H5V.
The main difference between cogged v-belts and wedge belts is in the contact angle. While wedge and cogged v-belts have the same contact angle, the design and construction differs. Cogged v-belts typically include top and bottom layers of rubber, dampening rubber, tension cords, and top and bottom metal rings. Polychloroprene and polyester cords are common materials for the top and bottom layers, while aramid fibers are used for punishing applications.
Cogged v-belts are more flexible than traditional v-belts. Because of the slots on the belt surface, they reduce bending resistance. They are compatible with the same pulleys as standard v-belts, and run cooler and longer. They are also more efficient than standard V-belts. If you are considering a cogged V-belt for your application, it may be worth it to investigate the benefits of this belt type.
Wide v-belts
Variable-speed v-belts are wider in cross section than classical v-belts. The design of variable-speed v-belts varies depending on the manufacturer, but generally features a parallel top and bottom surface. This type of v-belt wedges tightly into its pulley’s grooves, reducing power loss and slippage. This type of v-belt is best suited to applications where speed changes frequently.
High-performance Wide V-belts feature a fibre-reinforced EPDM rubber base. The resulting supercharged EPDM mix is better suited for applications where the belts are subject to higher temperatures. This type of drive belt can also replace existing drives with ease and efficiency. CZPT offers a wide range of drive belts for all applications. For applications where slack is an issue, wrapped V-belts are a smart choice.
Narrow-V-belts, on the other hand, have a more favorable height-to-width ratio. This means that a narrow-V belt can be smaller while still providing the same power transmission. These belts also have a lower mass, which reduces centrifugal forces and enables higher speeds. However, narrow-V-belts are prone to wear, but are still a popular choice in many applications.
In addition to being more durable, wrapped-V-belts have fabric-coated edges for better heat resistance. The material covering wrapped-V-belts also protects them from damage from friction and external contaminants. Unlike their rigid counterparts, these wide-V-belts have an improved lifespan and require less maintenance and downtime. These are excellent alternatives to conventional v-belts. So, what are the benefits of Wide-V-belts?
Narrow profile v-belts
When it comes to choosing the best V-belt for your needs, it is important to understand the differences between narrow profile and classical. Narrow profile V-belts are generally narrower in cross-section than classical v-belts. This makes them ideal for high-speed compact drives and light-duty applications. The following section details the differences between narrow and classical v-belts.
The tensile cords, or “cords,” are embedded into the rubber compound. These cords are the main power-transmitting component of a narrow profile v-belt. The tension cords are located at the pitch diameter of the belt cross-section and increase the tensile strength. They are typically made of steel, aramid fibers, or polyester. The core is usually made of polyurethane, but other materials can be used.
When measuring the v-belt’s width, it is important to understand the various sign-codes. Some v-belts have the wrong sign-coding schema. For example, a classical profile belt should be read as Lw = 3522 mm, while a narrow profile belt should be read as La=3553mm. A narrow profile v-belt has a steeper side-wall, which increases the wedging action. Moreover, the narrow profile v-belt has higher load capacity.
Despite their name, narrow profile v-belts are the most widely used and versatile type of v-belts. They are also the easiest to install. Their general size is similar to that of a wedge, and their number is derived from their numerical prefix. A narrow profile v-belt with a 3L300 part number is 3/8″ wide and 300.0 inches long.
Wide profile v-belts
Wide profile v-belts are designed for heavy-duty applications where extreme performance is required. They are ideal for such applications due to their high-flexural strength and shock-resistance. They also come with many benefits, including good noise-reduction, increased sturdiness, and easy maintenance. This article explores the features of wide profile v-belts and how they can benefit your business.
Classical v-belts have an internal dimensional metric marking called the “CZPT.” This identifies each specific belt. Generally, this number is a combination of the normal profile size designation letter and the internal length in inches. The inside length of the v-belt is indicated on the index of the v-belt. To begin installing the v-belt, mark the floor where it will be hung. Tape the end stop marker to the first stick.
Narrow v-belts are narrower than standard wide v-belts. They are also available in raw-edge cogged profiles and are intended for light-duty applications. Narrow V-belts are also available in 4 sizes. Compared to standard wide profile v-belts, narrow v-belts are most appropriate for high-speed, compact drives. However, wide profile v-belts are generally longer than narrow V-belts.
A v-belt is composed of different types of rubber and reinforcements. It undergoes tensile and compressive stresses on both sides. The top side of a v-belt experiences longitudinal tensile force, while the bottom side is subjected to compression against a pulley. Moreover, the included angle of a v-belt section is 40 deg. Various types of v-belts are available according to their cross-sections and performance specifications.
Standard v-belts
If you are installing v-belts, you must know the right way to measure them. Many v-belts are mislabelled as classic or SPA. If you are unsure of which 1 to choose, you can refer to the standard v-belts index. The basic way to measure v-belts is by using a measuring tape or a cable tie. Using the right technique will ensure you get the right length.
A well-engineered V-belt is made from an elastomer core, which is a material that is resistant to abrasion. The elastomer core is usually composed of polyurethane, which has excellent flexural strength and shock resistance. In addition to the elastomer core, a fabric cover protects the core from wear and environmental forces. Its fabric cover is treated to form a chemical bond with the belt core, which increases the fabric’s resistance to constant bending.
The cross-section of a standard V-belt is commonly described as a trapezium, with its top and bottom sides parallel. Knowing the cross-section of a standard V-belt is essential in matching it with a pulley. It is also important to know how the v-belt is positioned on a pulley and how to select the right belt for the job.

