Product Description
Product Parameters
| Product Name | Suitable for Daf Truck Engine Belt Tensioner 1406486~8 4898548 4891116 |
| MOQ | 1 pcs |
| OE NO. | As original |
| Size | Same as OE |
| Warranty | 12 Months |
| Specification | OEM Standard |
| Sample | Yes |
| Certification | TS16949 |
Our customer’s satisfaction is our main concern.
1. ONE year warranty be offered.
You have the right to return the good within 1 year,
we will replace any defective part with a new 1 or refund the complete amount within 1 week.
2.100% ensure that products be tested before shipping out.
Welcome to contact us for further information, Click to contact us>>
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, the goods is packed in neutral white boxes or brown cartons.
If you have legally registered patent, the goods can be packed in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of payment?
A: T/T 30% as deposit, and 70% before delivery. The photos of the products and packages will be showed to you before the balance.
Q3.What is your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF, DDU.
Q4. How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take 30 days after receiving advance payment.
The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of the order.
Q5. Can you produce according to the samples?
A: Yes, developing based on your samples or technical drawings is available.
Q6. What is your sample policy?
A: The sample can be supplied if the parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the courier cost.
Q7. Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, 100% test before delivery
Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A:1. Good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them,no matter where they come from.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | One Year After Delivery |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Component: | Cooling Fan |
| Samples: |
US$ 13/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample As Customer′s Request
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
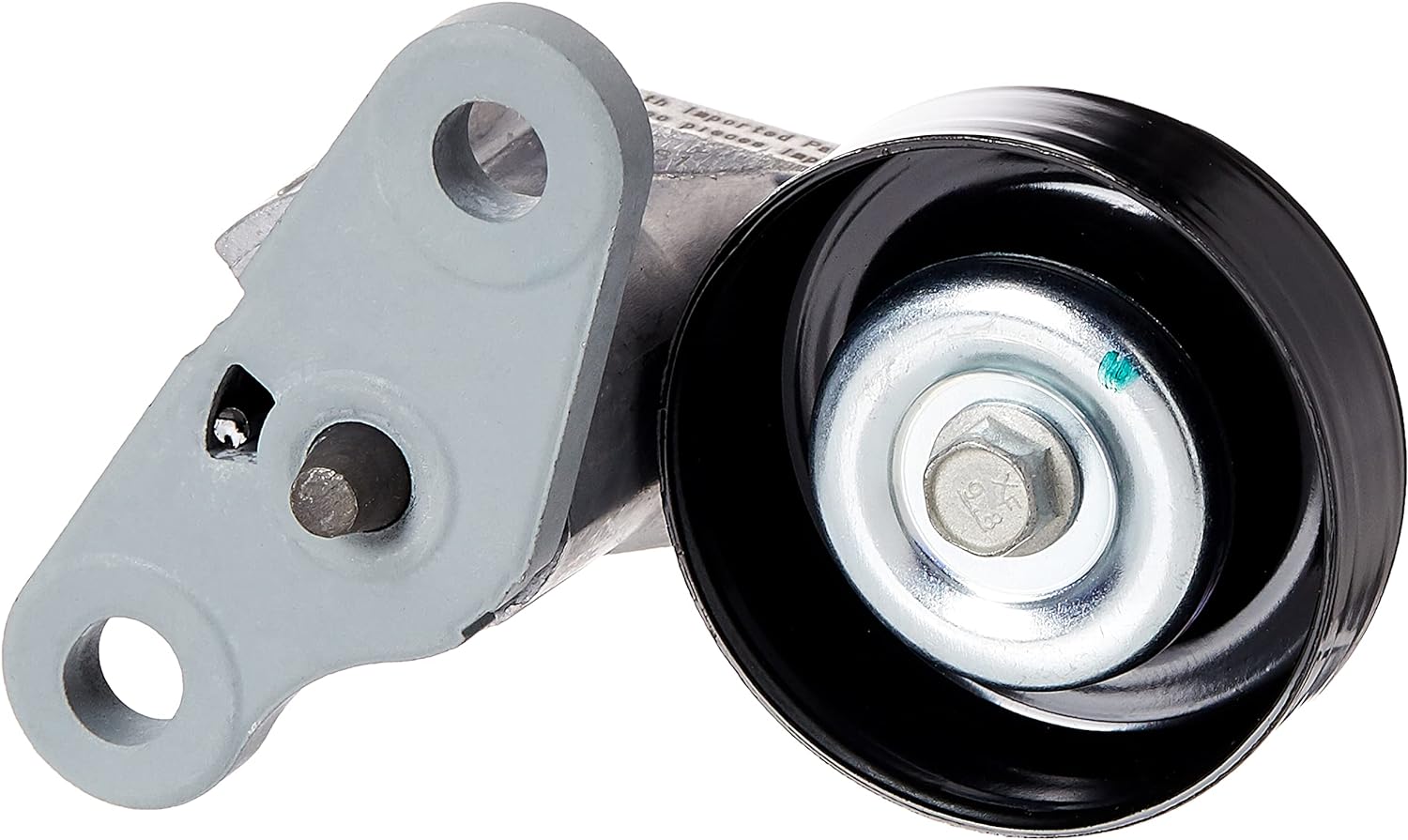

How do drive belt tensioners enhance the overall efficiency and lifespan of drive belts in various automotive and industrial applications?
Drive belt tensioners play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency and lifespan of drive belts in various automotive and industrial applications. They ensure proper tensioning of the belts, which is essential for optimal power transmission, reduced slippage, and prolonged belt life. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive belt tensioners enhance efficiency and lifespan:
- Optimal Tension:
- Reduced Slippage:
- Prevention of Belt Misalignment:
- Improved Belt Life:
- Reduced Maintenance:
Drive belt tensioners maintain the proper tension in the belts, which is crucial for efficient power transmission. Tensioners apply the correct amount of force to keep the belt tightly engaged with the pulleys or sprockets. This optimal tension minimizes belt slippage, ensuring efficient power transfer from the driving pulley to the driven components. By maintaining the correct tension, tensioners maximize the efficiency of the belt-driven system, enabling the components to operate at their designed speeds and deliver the intended performance.
Slippage between the belt and the pulleys can lead to energy losses and reduced efficiency in automotive and industrial applications. Drive belt tensioners help minimize belt slippage by ensuring proper tension throughout the operating range. The tensioner’s role is to keep the belt under sufficient tension, preventing it from slipping or losing contact with the pulleys during operation. By reducing slippage, tensioners optimize power transmission efficiency, allowing the system to operate with minimal energy losses and improved overall efficiency.
Belt misalignment can cause uneven loading, increased wear, and reduced belt life. Drive belt tensioners help prevent belt misalignment by maintaining consistent tension and keeping the belt properly aligned with the pulleys or sprockets. Tensioners with alignment features, such as guide rollers or pulley systems, guide the belt and ensure it remains in the correct position. By preventing belt misalignment, tensioners contribute to the even distribution of load and reduce the risk of premature wear or failure of the belt.
Proper tensioning provided by drive belt tensioners significantly extends the lifespan of drive belts. When belts are undercorrect tension, excessive stress or slack can lead to accelerated wear, stretching, and premature failure. Tensioners help maintain the optimal tension that allows the belt to operate within its designed parameters, reducing the risk of wear and elongation. By promoting the correct tension, tensioners contribute to prolonged belt life, reducing the frequency of belt replacements and associated maintenance costs.
Efficient and reliable drive belt tensioners minimize the need for frequent maintenance or adjustments. Tensioners designed for durability and longevity can operate for extended periods without requiring significant maintenance interventions. By ensuring consistent tension and reducing belt wear, tensioners minimize the likelihood of unexpected belt failures or the need for frequent re-tensioning. This results in reduced maintenance requirements, increased system uptime, and improved overall productivity in automotive and industrial applications.
In summary, drive belt tensioners enhance the overall efficiency and lifespan of drive belts in automotive and industrial applications by maintaining optimal tension, reducing slippage, preventing belt misalignment, improving belt life, and reducing maintenance requirements. By providing the necessary tension and ensuring proper belt operation, tensioners optimize power transmission efficiency, minimize wear, and contribute to the reliable and long-lasting performance of drive belts in a wide range of applications.

Can you provide examples of vehicles or machinery that rely on drive belt tensioners for efficient operation?
There are numerous vehicles and machinery across various industries that rely on drive belt tensioners for efficient operation. These tensioners play a critical role in maintaining the proper tension of drive belts, ensuring optimal power transmission, preventing belt slippage, and maximizing the performance of the following examples:
- Automobiles:
- Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
- Industrial Machinery:
- HVAC Systems:
- Power Generation Equipment:
- Printing and Packaging Machinery:
Drive belt tensioners are essential components in automobiles. They are commonly found in serpentine belt systems that power various engine accessories. Automobiles rely on drive belt tensioners for efficient operation of components such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, water pump, and more. By maintaining the proper tension of the serpentine belt, drive belt tensioners ensure that these accessories receive the necessary power and operate optimally, contributing to the overall performance and functionality of the vehicle.
Trucks and commercial vehicles also rely on drive belt tensioners for efficient operation. Similar to automobiles, these vehicles utilize serpentine belt systems for powering engine accessories. Drive belt tensioners help maintain the proper tension of the serpentine belt, allowing the efficient functioning of components like the alternator, power steering pump, air compressor, water pump, and more. By ensuring optimal power transmission, drive belt tensioners contribute to the reliable performance and functionality of trucks and commercial vehicles.
A wide range of industrial machinery relies on drive belt tensioners for efficient operation. Industrial equipment such as conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, generators, mills, and agricultural machinery often utilize belt drive systems. Drive belt tensioners in these applications help maintain the proper tension of belts, ensuring efficient power transmission, preventing belt slippage, and maximizing the performance of the machinery. By optimizing belt performance, drive belt tensioners contribute to the productivity, reliability, and longevity of industrial equipment.
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on drive belt tensioners for efficient operation. HVAC systems utilize belt-driven blowers, fans, and pumps to circulate air and control temperatures in buildings, vehicles, and industrial settings. Drive belt tensioners in HVAC applications help maintain the proper tension of belts, ensuring reliable and efficient operation of these components. By optimizing belt performance, drive belt tensioners contribute to energy efficiency, consistent airflow, and comfortable environments in HVAC systems.
Power generation equipment, including generators and turbines, relies on drive belt tensioners for efficient operation. Belt drive systems are commonly used to transfer power from engines or turbines to generators or other auxiliary equipment. Drive belt tensioners help maintain the proper tension of belts, ensuring efficient power transmission, preventing slippage, and maximizing the performance of power generation equipment. By optimizing belt performance, drive belt tensioners contribute to the reliable and efficient generation of electrical power.
Printing presses, packaging machines, and other machinery in the printing and packaging industry rely on drive belt tensioners for efficient operation. Belt drive systems are used to transport materials, control printing mechanisms, and perform various operations in these machines. Drive belt tensioners help maintain the proper tension of belts, ensuring accurate registration, consistent printing quality, and reliable material handling. By optimizing belt performance, drive belt tensioners contribute to the productivity and quality of printing and packaging processes.
In summary, drive belt tensioners are crucial for the efficient operation of vehicles and machinery across different industries. They are found in automobiles, trucks, industrial machinery, HVAC systems, power generation equipment, printing and packaging machinery, and more. By maintaining optimal belt tension, drive belt tensioners ensure efficient power transmission, prevent belt slippage, and maximize the performance and reliability of these vehicles and machinery.
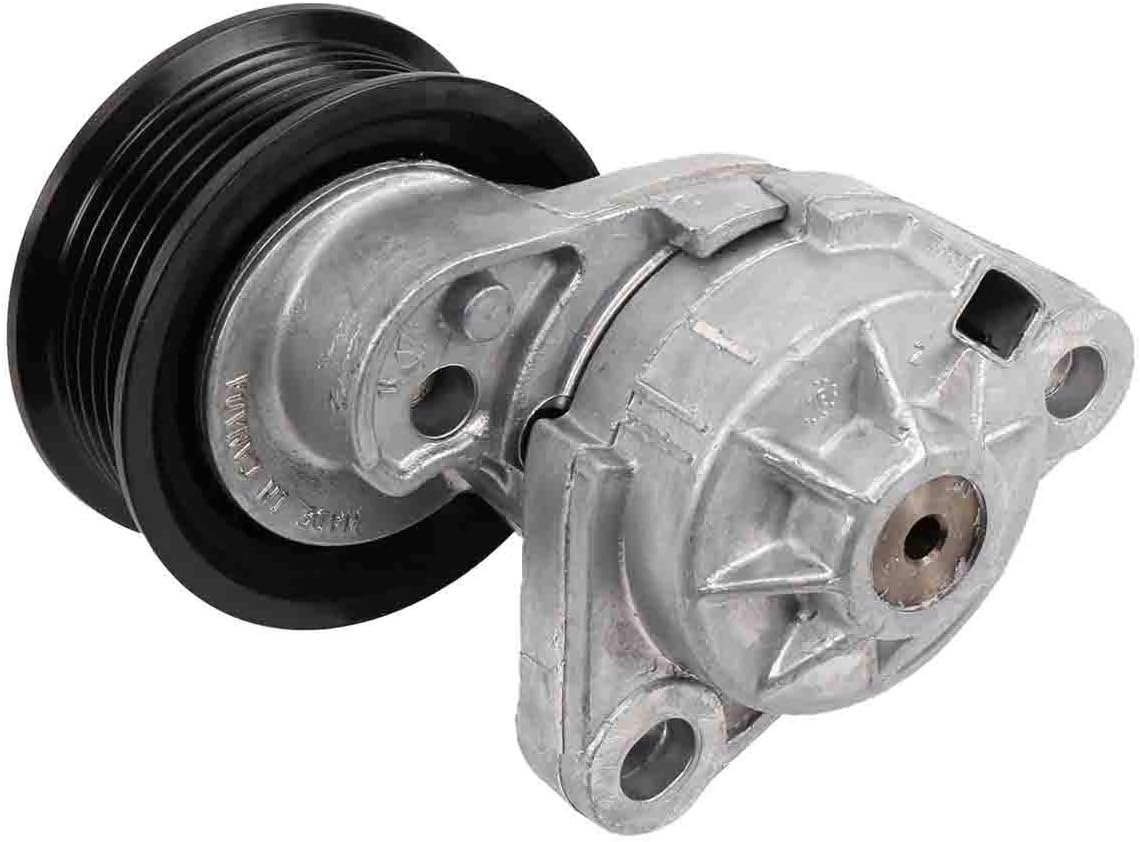

How do drive belt tensioners differ from other types of belt tensioners in terms of design and application?
Drive belt tensioners differ from other types of belt tensioners in terms of their design and application. Their specific features and functions make them suitable for maintaining proper tension in drive belt systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between drive belt tensioners and other types of belt tensioners:
- Design:
- Application:
Drive belt tensioners are typically designed as spring-loaded or hydraulic mechanisms. They consist of a tensioner pulley, an arm or bracket, a spring or hydraulic cylinder, and a pivot point. The tensioner pulley applies tension to the belt, while the arm or bracket holds the pulley in place. The spring or hydraulic cylinder provides the force necessary for tensioning, and the pivot point allows for movement and adjustment. This design allows drive belt tensioners to compensate for belt stretch, wear, and load variations, maintaining constant tension in the drive belt system.
Other types of belt tensioners, such as manual tensioners or automatic tensioners, may have different designs. Manual tensioners typically involve a simple adjustable bracket or arm that allows for manual adjustment of the tension. They often require periodic inspection and adjustment to maintain proper tension. Automatic tensioners, on the other hand, incorporate more complex mechanisms, such as internal springs or hydraulic systems, that automatically adjust the tension based on belt conditions and load variations. These tensioners eliminate the need for manual adjustment and provide continuous tension control.
Drive belt tensioners are primarily used in automotive and industrial applications. In automotive applications, they are commonly found in serpentine belt systems. These systems use a single, long belt to drive multiple engine accessories, such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. Drive belt tensioners in automotive applications ensure that the serpentine belt remains properly tensioned, optimizing power transmission and preventing slippage.
In industrial applications, drive belt tensioners are utilized in various belt drive systems. These systems may involve different types of belts, such as V-belts or timing belts, driving different components in machinery or equipment. Drive belt tensioners in industrial applications maintain proper tension in each belt, ensuring reliable power transmission, preventing slippage, and distributing the load evenly among the belts.
Other types of belt tensioners have different applications based on their design and functionality. Manual tensioners are often used in smaller machinery or equipment where periodic manual adjustment is feasible. They provide a cost-effective solution for maintaining tension in belt drive systems with lower load requirements. Automatic tensioners are commonly employed in applications where continuous tension control is necessary, or where frequent manual adjustment is impractical. They are often found in larger machinery, vehicles, or equipment that experience varying loads and require consistent tensioning.
In summary, drive belt tensioners differ from other types of belt tensioners in terms of their design and application. Drive belt tensioners are designed as spring-loaded or hydraulic mechanisms, incorporating a tensioner pulley, arm or bracket, spring or hydraulic cylinder, and pivot point. They are used in automotive and industrial applications to maintain constant tension in drive belt systems, optimizing power transmission and preventing slippage. Other types of belt tensioners, such as manual tensioners or automatic tensioners, have different designs and applications based on their specific functionality and tensioning requirements.


editor by CX 2024-05-03
China Professional 89480 D11862393 Belt Tensioner, V-Ribbed Belt a wheel and axle simple machine
Product Description
89480 D11862393 Belt Tensioner, v-ribbed belt
OEM:D11862393
REF NO.: 89480
Product Parameters
|
OEM NO. |
89480 D11862393 |
| Application | |
|
Place of Origin |
ZHangZhoug, China |
|
Material |
Aluminium |
| Product Name | Belt tensioner |
|
Reference NO. |
|
|
Packing |
Neutral Packing |
|
SHIPPING TERM |
Sea/Air |
|
Quality |
100%tested |
|
Size |
same as OEM |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | ISO9001, TS16949 |
|---|---|
| Standard Component: | Standard Component |
| Technics: | Casting |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
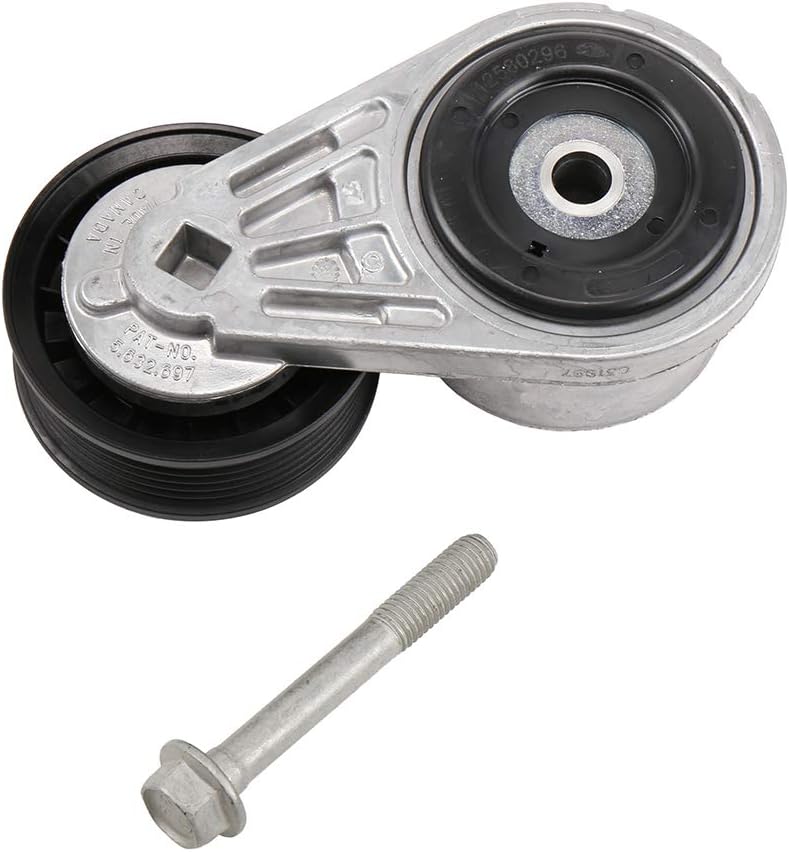

Can you provide guidance on selecting and sizing drive belt tensioners for specific applications?
When selecting and sizing drive belt tensioners for specific applications, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here’s a detailed guidance on selecting and sizing drive belt tensioners:
- Identify the Application Requirements:
- Consult Manufacturer Specifications:
- Consider Tensioner Design and Mounting:
- Calculate Tension and Load Requirements:
- Consider Additional Features and Maintenance:
- Consult with Experts:
Start by identifying the specific requirements of the application. Consider factors such as the type of system being driven by the belt (e.g., alternator, water pump, power steering), the power transmission requirements, the belt width and length, and the operating conditions (e.g., temperature, environment). Understanding these requirements will help determine the appropriate tensioner design, load capacity, and additional features needed for the application.
Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines for the tensioner. Manufacturers typically provide detailed information about the tensioner’s load capacity, belt compatibility, and other relevant technical details. It’s important to ensure that the selected tensioner is compatible with the specific belt type, size, and pulley configuration of the application. Manufacturers may also offer application-specific recommendations or provide technical support to assist with the selection process.
Evaluate the tensioner design and mounting options based on the application’s space constraints, belt path, and alignment requirements. Tensioners are available in various designs such as spring-loaded tensioners, hydraulic tensioners, or automatic tensioners. Consider the advantages and limitations of each design and choose the one that best suits the application’s needs. Additionally, assess the mounting options and ensure that the tensioner can be easily installed and aligned within the system.
Calculate the required tension and load for the drive belt system. The tension should be within the belt manufacturer’s recommended range to prevent slippage or excessive wear. Consider the power requirements of the driven components and the expected operating conditions. If necessary, consult engineering references or software tools that provide tension calculations based on the belt type, pulley size, and power transmission requirements. Ensure that the selected tensioner can handle the calculated tension and load without compromising its performance.
Evaluate any additional features or maintenance requirements that may be beneficial for the application. Some tensioners offer adjustable arms or pulleys, which allow fine-tuning of the belt tension. Others may have built-in dampers to reduce vibrations or diagnostic capabilities for monitoring belt condition. Consider these features based on the application’s specific needs and their potential to enhance performance, reliability, and ease of maintenance.
If you’re unsure about the selection and sizing process, consider consulting with experts or engineers experienced in belt-driven systems. They can provide valuable insights, recommend suitable tensioner options, and ensure that the selected tensioner meets the application’s requirements. Additionally, they can assist with belt tension calculations, system design considerations, and troubleshooting potential issues.
In summary, selecting and sizing drive belt tensioners for specific applications requires a systematic approach. By identifying the application requirements, consulting manufacturer specifications, considering tensioner design and mounting, calculating tension and load requirements, and evaluating additional features and maintenance needs, you can make an informed decision. Consulting with experts can also provide valuable assistance throughout the selection process. Properly selected and sized tensioners will contribute to the overall efficiency, reliability, and longevity of the belt-driven system.
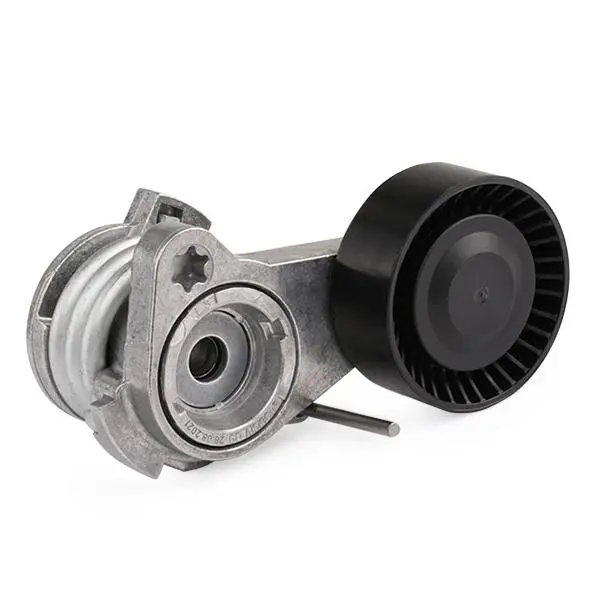

Can drive belt tensioners be customized or modified to suit specific automotive or industrial needs?
Drive belt tensioners can be customized or modified to suit specific automotive or industrial needs. Manufacturers of tensioners offer various options and configurations to accommodate different applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive belt tensioners can be customized or modified:
- Tensioner Design:
- Tensioner Size and Mounting:
- Tensioner Load Capacity:
- Additional Features:
Drive belt tensioners come in different designs to meet specific needs. Manufacturers offer a range of tensioner designs, such as spring-loaded tensioners, hydraulic tensioners, and automatic tensioners. These designs can be customized based on the specific requirements of the automotive or industrial application. For example, some applications may require tensioners with higher load-bearing capacity or increased resistance to environmental factors like dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures. Manufacturers can modify the tensioner design to incorporate features that enhance durability, performance, and reliability in these challenging conditions.
Drive belt tensioners are available in various sizes to accommodate different belt widths and pulley configurations. Manufacturers provide tensioners in different dimensions, allowing customization based on the specific dimensions of the belt and pulley system. Additionally, tensioners can be modified to suit different mounting requirements. Some applications may require tensioners with specific mounting brackets or orientations to fit within the available space or align with other components. Manufacturers can customize the tensioner’s size, shape, and mounting features to ensure compatibility and ease of installation in the target application.
The load capacity of a drive belt tensioner is an essential consideration for certain applications. Industrial or heavy-duty automotive applications may require tensioners with higher load capacity to withstand increased belt tensions or accommodate larger belt-driven systems. Manufacturers can customize tensioners to meet these requirements by using stronger materials, incorporating reinforced components, or optimizing the tensioner’s internal structure to handle higher loads. By customizing the tensioner’s load capacity, it can reliably handle the specific demands of the application and ensure long-term performance.
Drive belt tensioners can be customized with additional features to enhance their functionality or address specific needs. For example, manufacturers may offer tensioners with built-in dampers to reduce vibrations or noise in certain applications. Some tensioners may have adjustable arms or pulleys to provide fine-tuning of the belt tension. Manufacturers can also customize tensioners to incorporate special coatings or materials that improve resistance to corrosion, abrasion, or other environmental factors. These additional features can be tailored to suit the specific automotive or industrial needs, providing enhanced performance and longevity.
In summary, drive belt tensioners can be customized or modified to suit specific automotive or industrial needs. Manufacturers offer various options for tensioner design, size, mounting, load capacity, and additional features. By customizing tensioners, they can be optimized to meet the requirements of different applications, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and enhanced performance. When selecting or modifying drive belt tensioners, it is essential to consider the specific needs of the application and consult with manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable customization options.

Can you explain the importance of proper tensioning for drive belts in various machinery and vehicles?
Proper tensioning of drive belts is of utmost importance in various machinery and vehicles. Maintaining the right level of tension ensures optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the belt drive system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the importance of proper tensioning for drive belts:
- Efficient Power Transmission:
- Preventing Belt Slippage:
- Reducing Wear and Fatigue:
- Optimizing Belt Life and Performance:
- Adapting to Load Variations:
- Enhancing System Reliability:
Proper tensioning is crucial for efficient power transmission in machinery and vehicles. When a drive belt is under-tensioned, it can slip on the pulleys, resulting in power loss and reduced performance. Insufficient tension leads to inadequate friction between the belt and the pulleys, compromising the transfer of power from the driving pulley to the driven pulley. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts remain properly engaged with the pulleys, ensuring maximum power transfer and efficient operation of the machinery or vehicle.
Correct tensioning helps prevent belt slippage, which is a common issue in belt drive systems. Slippage occurs when the belt loses its grip on the pulleys, leading to power loss, decreased efficiency, and potential damage to the belt and pulleys. Proper tension ensures that the belt remains securely in place, creating sufficient friction to prevent slippage even under high loads or sudden changes in speed or torque. By preventing belt slippage, proper tensioning maintains reliable power transmission and protects the integrity of the belt drive system.
Improper tensioning can cause excessive wear and fatigue on drive belts. If a belt is over-tensioned, it experiences increased stress, leading to accelerated wear and potential premature failure. On the other hand, under-tensioning can cause the belt to flex excessively, leading to fatigue and eventual belt failure. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts operate within their design limits, minimizing wear and fatigue. Proper tensioning extends the lifespan of the belts, reducing maintenance costs and downtime associated with belt replacements.
Proper tensioning plays a vital role in optimizing the life and performance of drive belts. When belts are correctly tensioned, they operate in their intended range, minimizing stress and strain. This optimal operating condition reduces the risk of belt damage, such as cracking, stretching, or delamination. Additionally, proper tensioning ensures that the belts track properly on the pulleys, preventing misalignment and excessive side loads. By optimizing belt life and performance, proper tensioning contributes to increased reliability, reduced maintenance, and improved overall efficiency of machinery and vehicles.
Drive belts in machinery and vehicles often experience load variations during operation. Proper tensioning allows the belts to adapt to these load changes effectively. When the load increases, the tensioner compensates by applying additional tension to prevent slippage. Conversely, when the load decreases, the tensioner releases some tension to avoid excessive stress on the belt and pulleys. This adaptability ensures that the belts maintain the optimal tension regardless of the varying load conditions, allowing for consistent power transmission and reliable performance.
The proper tensioning of drive belts enhances the overall reliability of machinery and vehicles. By maintaining optimal tension, belts operate within their designed parameters, reducing the risk of unexpected belt failure and associated downtime. Reliable power transmission ensures that machinery operates as intended, minimizing the chances of equipment damage, production delays, and costly repairs. The use of proper tensioning techniques adds a layer of control and stability to the belt drive system, enhancing its overall reliability and ensuring smooth operation.
In summary, proper tensioning of drive belts is essential for efficient power transmission, preventing belt slippage, reducing wear and fatigue, optimizing belt life and performance, adapting to load variations, and enhancing system reliability in various machinery and vehicles. By maintaining the correct tension, drive belts operate effectively, ensuring reliable performance, extended lifespan, and minimized downtime.


editor by CX 2024-04-30
China manufacturer Volovo 1660001 Truck Tensioner, V-Belt a wheel and axle simple machine
Product Description
Volovo 1660001 Truck tensioner,V-Belt
OEM:1660001
Application:1660001
Product Parameters
|
OEM NO. |
1660001 |
| Application | VOLVO |
|
Place of Origin |
ZHangZhoug, China |
|
Material |
Aluminium |
| Product Name |
Belt Tensioner |
|
Reference NO. |
|
|
Packing |
Neutral Packing |
|
SHIPPING TERM |
Sea/Air |
|
Quality |
100%tested |
|
Size |
same as OEM |
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Certification: | CCC, ISO9001, TS16949 |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
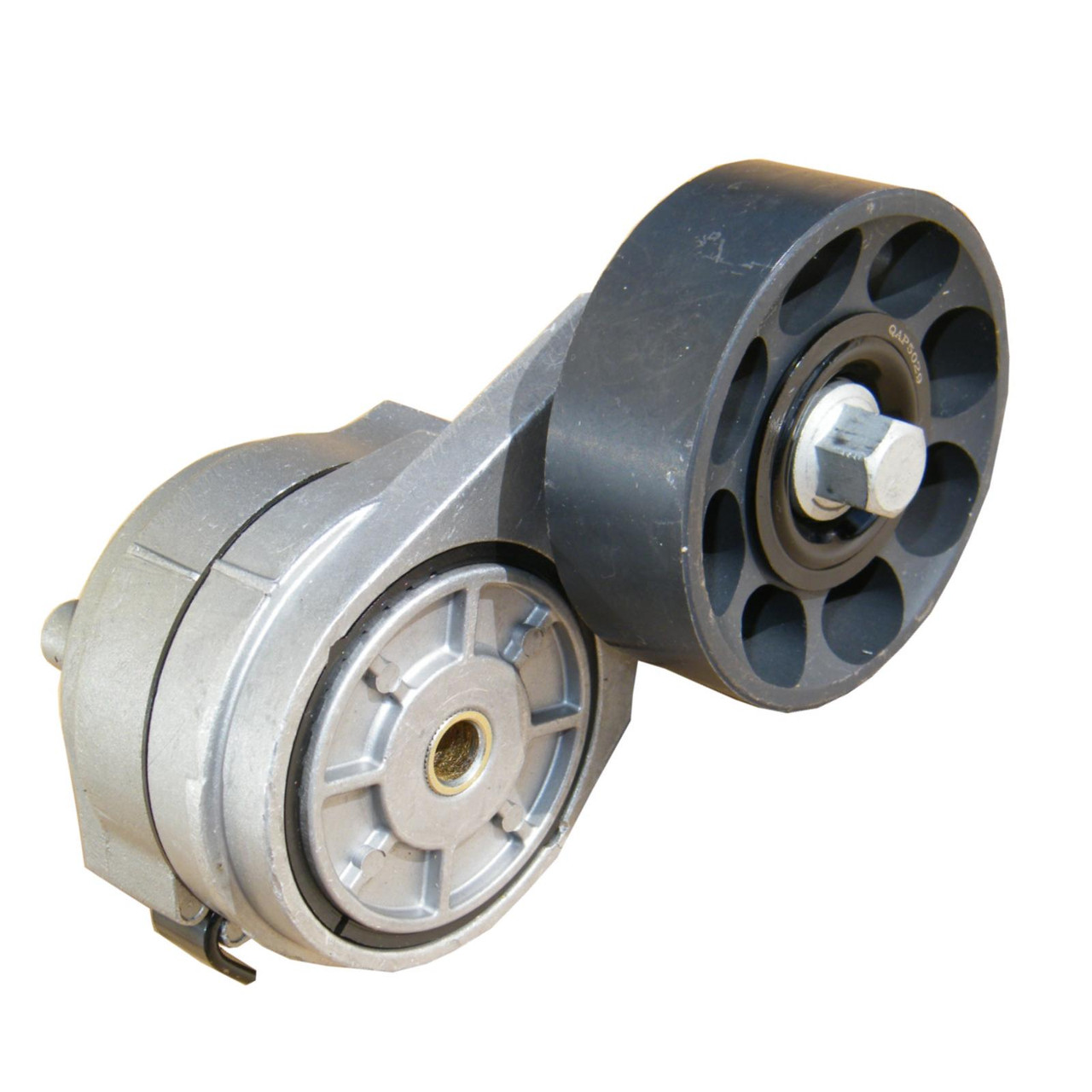

What role do materials and coatings play in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners?
Materials and coatings play a crucial role in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners. The selection of appropriate materials and the use of specialized coatings can significantly impact the tensioner’s durability, resistance to wear, and overall functionality. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role materials and coatings play in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners:
- Strength and Stiffness:
- Wear Resistance:
- Corrosion and Rust Protection:
- Friction Reduction:
- Heat Resistance:
The materials used in drive belt tensioners should exhibit sufficient strength and stiffness to withstand the forces and stresses exerted on them during operation. High-quality materials, such as hardened steel or alloyed metals, are commonly employed in tensioner components like brackets, pulleys, and arms. These materials provide the necessary strength and rigidity to maintain the tensioner’s structural integrity and prevent deformation or failure under load. By using robust materials, tensioners can effectively withstand the demands of the belt drive system, ensuring long-term performance and longevity.
Tensioners are subjected to continuous contact with the belt and other moving components, which can lead to wear over time. The choice of materials with excellent wear resistance properties can significantly extend the tensioner’s lifespan. Hardened steel, cast iron, or materials with specialized surface treatments, such as nitriding or hard chrome plating, are commonly used to enhance wear resistance. These materials and coatings reduce friction, minimize surface degradation, and prevent premature wear of critical tensioner components. By improving wear resistance, tensioners can maintain consistent tension and performance over an extended period.
Drive belt tensioners are often exposed to harsh environments, including high humidity, temperature variations, and chemical contaminants. Corrosion and rust can compromise the performance and longevity of tensioners, leading to premature failure. To mitigate these issues, manufacturers employ materials and coatings that provide corrosion and rust protection. Stainless steel, galvanized steel, or materials with corrosion-resistant coatings, such as zinc or powder coatings, are commonly used. These protective measures prevent the degradation of tensioner components, ensuring their functionality and prolonging their lifespan even in challenging operating conditions.
Reducing friction is essential for optimizing the performance and efficiency of drive belt tensioners. Excessive friction can lead to energy losses, increased wear, and decreased belt life. Materials and coatings that possess low friction characteristics are employed in tensioner components to minimize frictional forces between the belt and the tensioner. For example, self-lubricating materials or coatings with low friction coefficients, such as Teflon or molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), can be utilized. By reducing friction, tensioners operate more efficiently, generate less heat, and experience reduced wear, resulting in improved performance and longevity.
Drive belt tensioners are exposed to elevated temperatures generated by the operating belt drive system. Materials and coatings with excellent heat resistance properties are necessary to ensure the tensioner’s performance and longevity. High-temperature alloys, heat-resistant plastics, or coatings designed to withstand thermal stresses are utilized to prevent deformation, softening, or degradation of tensioner components at elevated temperatures. By using heat-resistant materials and coatings, tensioners can operate reliably and maintain consistent tension without compromising their structural integrity.
In summary, materials and coatings play a vital role in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners. The selection of appropriate materials and the application of specialized coatings help ensure the tensioner’s strength, stiffness, wear resistance, corrosion protection, friction reduction, and heat resistance. By utilizing high-quality materials and employing suitable coatings, tensioners can withstand the demands of the belt drive system, resist wear and corrosion, operate efficiently, and maintain consistent tension over an extended period, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of the belt-driven system.
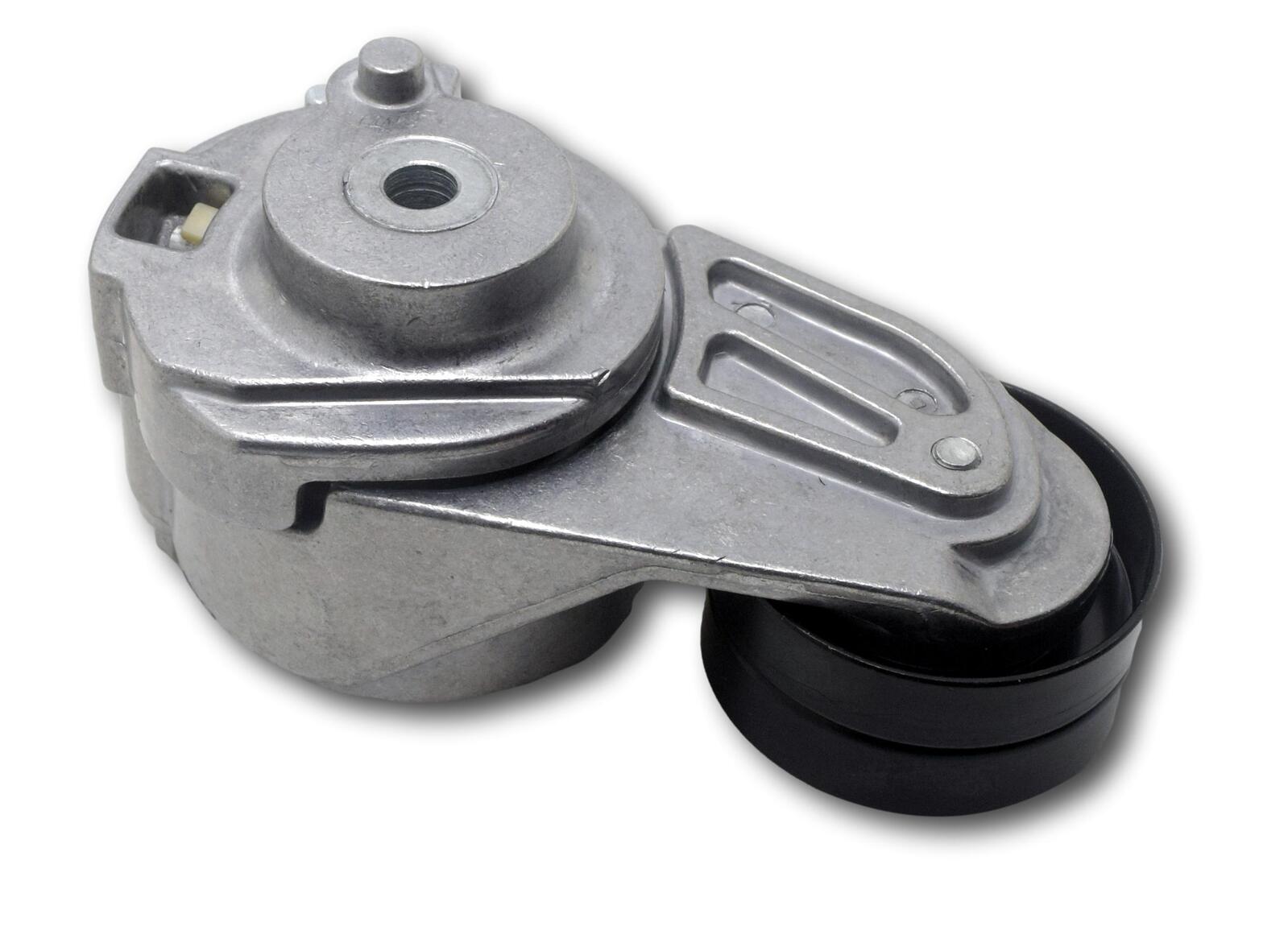

Can you explain the principles behind the operation and adjustment of drive belt tensioners?
Drive belt tensioners operate based on specific principles to maintain the proper tension in drive belts. Understanding these principles is essential for adjusting and ensuring the optimal operation of drive belt tensioners. Here’s an explanation of the principles behind the operation and adjustment of drive belt tensioners:
- Tensioning Mechanism:
- Automatic Tension Adjustment:
- Idler Pulley:
- Adjustment Mechanism:
- Tensioner Maintenance:
Drive belt tensioners typically employ a spring-loaded mechanism to maintain the desired tension in the belt. The tensioner consists of a pulley or arm that is connected to a spring. The spring applies a specific force to the pulley or arm, which in turn applies tension to the belt. The tensioner is designed to compensate for belt elongation and other factors that can cause the tension to decrease over time. The spring force is carefully calibrated to provide the appropriate tension for the specific belt and application.
Drive belt tensioners are designed to automatically adjust the tension in response to changes in the belt’s length, temperature, and other operating conditions. As the belt stretches or contracts due to temperature fluctuations or normal wear, the tensioner compensates by adjusting the position of the pulley or arm to maintain the desired tension. This automatic adjustment ensures that the belt operates within the optimal tension range, reducing wear and optimizing power transmission efficiency. Automatic tension adjustment also compensates for belt wear over time, extending the belt’s lifespan.
In some drive belt tensioner designs, an idler pulley is incorporated to guide and support the belt. The idler pulley is typically mounted on a movable arm and works in conjunction with the tensioner pulley. The idler pulley helps ensure proper belt alignment and prevents excessive belt deflection. It also assists in maintaining the correct belt tension by applying additional pressure on the belt. The tensioner and idler pulleys work together to ensure optimal belt operation and reduce wear.
Drive belt tensioners often feature an adjustment mechanism that allows for manual tension adjustment when necessary. This mechanism may involve a bolt or other means of altering the position or tension of the tensioner pulley or arm. Manual adjustment is typically required during belt installation or when replacing a worn-out belt. It ensures that the belt is initially tensioned correctly and allows for fine-tuning the tension if needed. Manual adjustment should be performed following the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the appropriate tension for the specific belt and application.
Proper maintenance of drive belt tensioners is crucial for their optimal operation. This includes regular inspection for signs of wear or damage, such as worn pulley bearings or damaged springs. If any issues are identified, the tensioner should be replaced to maintain the desired tension and prevent potential belt failure. Additionally, drive belt tensioners may require periodic lubrication according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure smooth operation and longevity.
In summary, drive belt tensioners operate based on a spring-loaded mechanism that automatically adjusts the tension in response to changes in the belt’s length and operating conditions. They may incorporate an idler pulley to support the belt and an adjustment mechanism for manual tension adjustment. Proper maintenance of tensioners is essential to ensure their optimal operation. By understanding and applying these principles, drive belt tensioners can effectively maintain the desired tension, ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of drive belts in various applications.
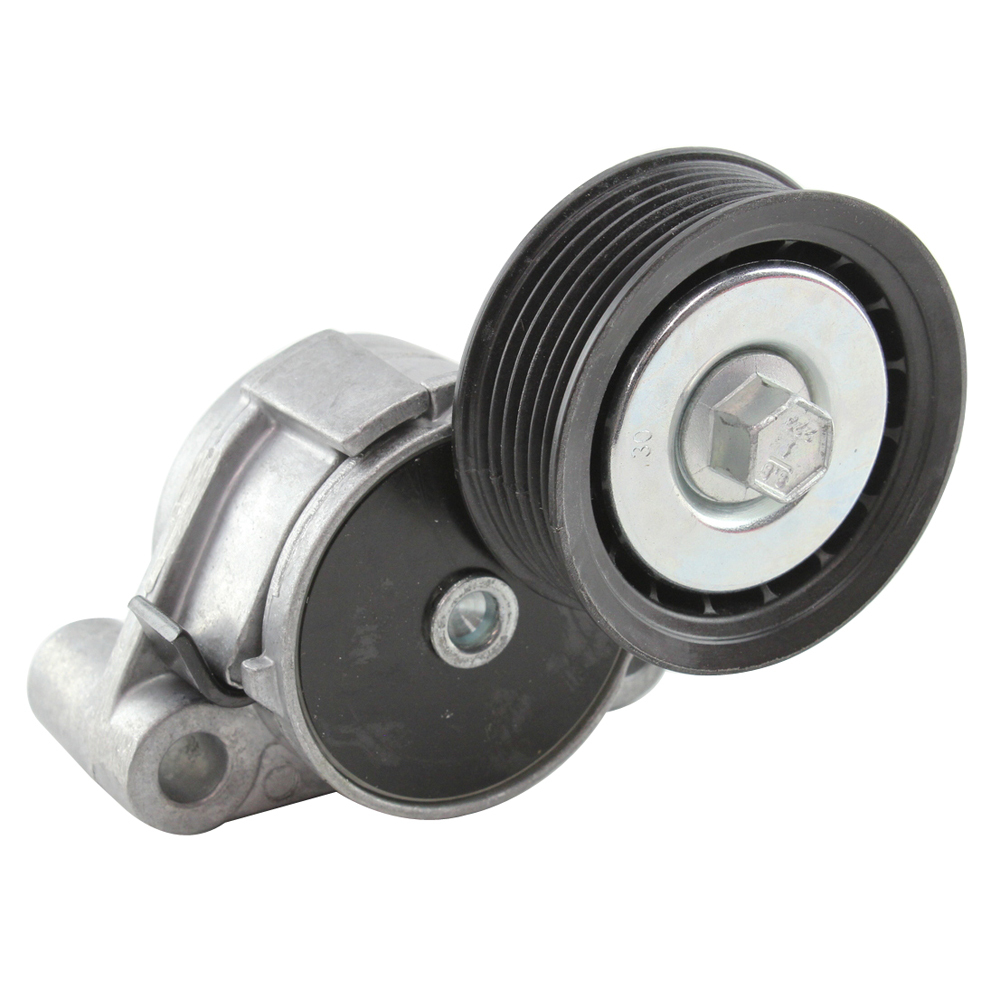

Are there specific designs of drive belt tensioners for different applications, like cars, trucks, or industrial equipment?
Yes, there are specific designs of drive belt tensioners tailored for different applications, such as cars, trucks, and industrial equipment. The design of a drive belt tensioner is influenced by factors like the specific requirements of the application, the type of belt being used, the load conditions, and the space constraints. Here’s a detailed explanation of the specific designs of drive belt tensioners for different applications:
- Automotive Tensioners:
- Truck Tensioners:
- Industrial Equipment Tensioners:
In the automotive industry, drive belt tensioners are designed to meet the specific requirements of different vehicle models and engines. Automotive tensioners are commonly used in serpentine belt systems that power various engine accessories. The design of automotive tensioners includes features like a spring-loaded or hydraulic mechanism for automatic tensioning, a pulley with a smooth or grooved surface for proper belt traction, and a compact and durable construction to fit within the limited space in the engine compartment. These tensioners are engineered to withstand the high operating temperatures and vibrations commonly encountered in automotive applications.
Trucks and other heavy-duty vehicles often have specific drive belt tensioner designs to handle the higher loads and operating conditions associated with these applications. Truck tensioners are typically robust and durable, capable of withstanding heavy loads, vibrations, and harsh environments. They may incorporate features like larger tensioner pulleys, heavy-duty springs or hydraulic systems for increased tensioning force, and reinforced brackets or arms to handle the higher belt tensions. The design of truck tensioners ensures reliable belt performance and longevity in demanding trucking applications.
For industrial equipment, drive belt tensioners are designed to cater to a wide range of applications and load conditions. Industrial tensioners can be found in various belt drive systems, such as those used in manufacturing machinery, mining equipment, construction machinery, and agricultural machinery. The design of industrial tensioners depends on factors like the type and size of the belt, the power transmission requirements, and the specific environmental conditions. These tensioners may feature different mechanisms like spring-loaded, hydraulic, or manual adjustment systems, depending on the application. They are often designed to be robust, resistant to contamination, and capable of withstanding heavy loads and harsh operating conditions.
In summary, drive belt tensioners have specific designs tailored for different applications. Automotive tensioners are designed for use in vehicles and feature compact, temperature-resistant designs. Truck tensioners are built to handle heavy loads and harsh operating conditions associated with trucks and heavy-duty vehicles. Industrial equipment tensioners are designed to meet the diverse requirements of industrial machinery and equipment, with considerations for various belt types, load conditions, and environmental factors. The specific design of a drive belt tensioner is chosen to ensure optimal belt performance, durability, and reliability in the respective application.


editor by CX 2024-01-12
China Hot selling High Quality Htd 5m Industrial Rubber Drive Timing Belt 2m 3m 5m 8m 14m for Wire Stripping Machine Power Transmission with Good quality
Product Description
High quality HTD 5M Industrial Rubber Drive Timing belt 2M 3M 5M 8M 14M for Wire stripping machine power transmission
|
Color : |
Red ,green,brown,grey,Blue etc |
||
|
Size (length * width * height) |
400mm-1500mm*20-35mm*4-12mm(SIZE 0F SINK HOLE is Customizable) |
||
|
Material: |
Vulcanized rubber |
||
|
Tooth shape: |
2M/S2M/3M/S3M/5M/8M/14M/20M/ |
||
|
Whether standard parts: |
Standard |
||
|
Process (construction) |
Vulcanized rubber belt punching ,Single row hole, multi – emptying evenly distributed |
||
|
Performance: |
Excellent strong friction wear resistance, oil and corrosion resistance, no lamination, long service life |
||
|
Processing: |
punch/ slot / pattern / block / CZPT bar / profile |
||
|
Use (for machines): |
Used for pulling plastic film in packaging machine, Printing industry, packaging industry, paste box machine belt, vertical |
||
Note: This product is all customized products, common specifications can be made, and the thickness of the glue is customized, usually 6mm or 8mm. The glue colors are white glue, red glue, green glue and grey glue.
similar product
The surface color of the belt can be red, green, white, gray, etc.
Various specifications can be customized, such as length, width and thickness of glue.
The tooth surface can be ground, punched, etc.
Drawings are required for grinding teeth, slotting and drilling.
Consult customer service for specific specifications and specific quotations
Suitable for positioning system, wood industry, textile machine, glass industry, CZPT and marble industry, packaging industry, tobacco industry, paper and carton industry, chemist and pharmaceutical industry.
Certifications
FAQ
Q1. Can I have a sample order for Rubber Timing Belt?
A: Yes, we welcome sample order to test and check quality. Mixed samples are acceptable.
Q2. What about the lead time?
A:Sample needs 3-5 days, mass production time needs 1-2 weeks for order quantity.
Q3. Do you have any MOQ limit for order?
A: Low MOQ, 1-10 pcs for sample checking is available.
Q4. How do you ship the goods and how long does it take to arrive?
A: We usually ship by DHL, UPS, FedEx or TNT. It usually takes 3-5 days to arrive. Airline and sea shipping also optional.
Q5: What are the payment terms?
Western Union, Paypal, Ali Secure Pay or T/T (company account and personal account)
Q6.What are your company major products?
Our main products are Sausage Timing Belt ,film pull belt ,rubber belt, transmission belt,triangle V belt etc.
Q7.What about the price?
We try our best to give the competitive price with the high quality.
How to Fix a Faulty Drive Belt Tensioner
If you’re experiencing grinding, squeaking, or other unusual sounds from your car, your drive belt tensioner may be the culprit. In this article, we’ll discuss why a failed drive belt tensioner may need to be replaced and how to fix it. Once you have determined that your belt tensioner is faulty, you can use a Wrench to remove it and replace it with a new one. After you replace the belt tensioner, it will no longer be making noises.
Problems with timing belt tensioner
Whenever your engine is making strange noises, it is likely that the timing belt tensioner is causing the problem. A bad timing belt tensioner is a big cause of such sounds, as the timing of the engine is critical. When the belt is moving properly, the camshaft and crankshaft are perfectly synchronized, and the valves work in perfect sync during the intake and exhaust strokes of each cylinder.
Other signs of a worn tensioner include rust bleeding and dripping. Usually, rust will appear at the mounting bolts and “stops” on the tensioner. Other symptoms of a worn timing belt tensioner are noise, resistance, and roughness. If any of these symptoms are present, it’s important to get the car fixed as soon as possible. Troubleshooting problems with timing belt tensioner is an easy process if you know the symptoms.
If your car starts making squeaking or grinding noises when you drive, it’s probably the timing belt tensioner. The timing belt can also cause problems with your engine’s valves. When the timing belt is too loose, the valves cannot fully combust the fuel-air mixture. If this problem is left undiagnosed, it could result in severe engine damage. To solve the problem, you must replace the timing belt tensioner.
The repair of the timing belt tensioner is not a difficult job if you’re experienced and comfortable with DIY car repairs. If you have a good knowledge of car repair, you can try to replace it yourself – but don’t forget that it is a complex repair job that requires a lot of skill. So, it’s best to hire a professional mechanic. And if you don’t have the necessary tools and training, you can always try the DIY method.
Other symptoms of a bad timing belt tensioner include an abnormal chirping noise, misfiring, and check engine light malfunction. If you notice any of these symptoms, you should replace the timing belt tensioner as soon as possible. Often, the belt is wearing out and can’t spin freely. You may have to replace the timing belt tensioner to avoid major damage to your engine. The best way to tell if the timing belt tensioner is failing is to check it regularly.
Cost of a new drive belt tensioner
A new drive belt can be expensive. Replacing 1 is usually a straightforward task that requires little knowledge, but some cars are more difficult than others. Replacing a drive belt by yourself may result in the replacement of parts you do not know. You may also encounter problems that cannot be resolved unless you have a mechanic check all the affected parts. You can save money by taking the car to a mechanic before trying to fix the problem yourself.
A drive belt tensioner should last at least 125,000 miles, but can break sooner. Most car mechanics will replace the tensioner after you notice the belt is slipping. It takes about 15 minutes to an hour to replace 1 of these parts, and you can do it yourself with the proper tools. You can also ask about the replacement of pulleys or sprockets. The price of a new drive belt tensioner depends on the make and model of your car.
The average cost to replace a drive belt tensioner is between $235 and $267. This cost includes labor and parts, but doesn’t include taxes or fees. Some vehicles may need related repairs as well, such as serpentine belts or tensioner housing. For a detailed estimate, use the RepairPal Fair Price Estimator. You can compare labor costs and shop for the best price. There are many options available online, and you can choose the most convenient 1 for your needs.
In addition to replacing the drive belt, you should also check the idler pulleys, which do not drive anything. If they have excessive movement, replace them. A failed drive belt tensioner can cause the belt to slip and affect other components of the car. You may also notice warning lights that indicate a problem with the alternator, water pump, or power steering. You should also check your vehicle’s air conditioning.
Replacing the tensioner pulley can be done yourself for about $50. Depending on the type of pulley and belt, you may need to replace other parts of the engine as well. You can save money by replacing a tensioner pulley yourself if you have the time and skills. It’s easy to replace a new drive belt tensioner if you’re a mechanically inclined individual.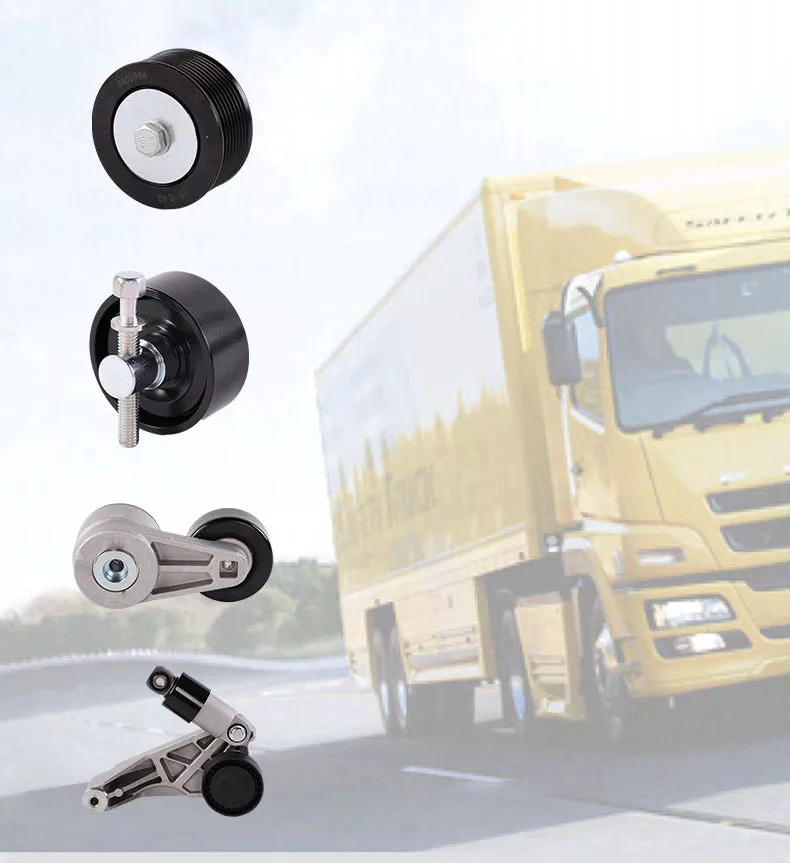
Repair options for a failed drive belt tensioner
A failed drive belt tensioner may have several symptoms. For instance, it can make a grinding or squealing sound, and it may emit a burning smell. The battery light on your car may also stay on. These are all signs that your drive belt has failed. However, these symptoms are not always indicative of the failure of the drive belt tensioner. Listed below are some common problems that can be caused by a failed drive belt tensioner.
To check for a failed drive belt tensioner, turn off the engine and examine the arm. If it doesn’t move, it’s time to replace the drive belt. A manual drive belt tensioner is easy to replace. A hydraulic or bad spring drive belt tensioner, however, will not be able to be fixed. If you can’t find a repair shop in your area, visit 1 of NAPA AutoCare locations, or a NAPA online store. They will be able to diagnose the failure and provide solutions for your car.
A spring tensioner is a type of drive belt tensioner that uses a spring-loaded pulley to apply the proper tension to the drive belt. However, spring tensioners can fail and seize if not properly maintained. A hydraulic tensioner uses hydraulic oil under pressure and can malfunction. In some cases, the tensioner can leak oil or lose its ability to tension the drive belt. It can also be damaged by excessive wear, which will cause the belt to break.
A failed drive belt tensioner can affect your car’s performance and functionality. In addition to making your car squeaky and jerky, a failed drive belt tensioner can cause the serpentine or v-belt to slip and wear out prematurely. Repairing a failed drive belt tensioner can also prevent your car from experiencing the same problems in the future. So, what do you do if you find your drive belt is slipping?
If your drive belt tensioner isn’t the problem, you’ll have to replace it. In some cases, a loose tensioner arm can lead to cracks in the tensioner housing. In the worst case scenario, the damaged tensioner can also lead to an overheated engine. Ultimately, a failed drive belt tensioner can cause your car to experience overheating, weak battery charging, and even a weakened power steering system.
Maintenance requirements for a drive belt tensioner
Drive belt tensioner maintenance begins with proper alignment of the pulleys. Misaligned pulleys or drives can wear a belt out too fast. Misalignment can occur if the component was recently replaced. A set of shims can restore the pulleys to the proper alignment. It is important to regularly check the tensioner to ensure proper function. Also, check the belt for cracks or wear.
Before performing any maintenance work, always turn off the drive to protect the motor. The belt should be in a safe position so that it will not fall on the workers. Lock down any moving parts and ensure the fans do not freewheel. When inspecting the drive belt tensioner, examine the belt guard for wear and debris. If the belt is damaged or has excessive heat, it is necessary to clean it or replace it.
It is important to maintain a proper fit between the belt and the drive belt tensioner. An incorrectly-sized drive belt will be difficult to install and adjust. An incorrect-rib count drive belt will fit, but will not last as long. Likewise, drive belts with too many ribs will not last as long. For these reasons, drive belt tensioners should be replaced when they are over 50,000 miles.
A drive belt tensioner is a pulley that rides on the outside surface of the serpentine belt. Its purpose is to maintain constant pressure on the pulleys that power car components. It is typically mounted on the front of the engine, bolted to the crankshaft, and rests against the serpentine belt. If the drive belt is cracked, it needs to be replaced immediately. If the arm is loose or bent, the bearings in the tensioner are probably worn.
The drive belt tensioner is an important part of the drive system, which is essential for smooth operation of the vehicle. However, it does wear out prematurely and should be replaced at a certain mileage. It should also be inspected for normal wear and tear as a result of road dirt, excessive heat, and oil leaks. However, it is important to remember that drive belts are highly sensitive to excessive heat, road dirt, and oil leaks.


China Good quality V Belt Alternator Chain Double Pulley Block Timing Crankshaft Machine Manufacturer Price Vee Sheave SPA Spb Spc Spz China Manufacturer wholesaler
Product Description
V Belt Alternator Chain Double Pulley Block Timing Crankshaft Machine Manufacturer Price Vee Sheave SPA Spb Spc Spz China Manufacturer
pulley machine
1) V-Belt pulleys for taper bushes
SPZ
|
SPA
|
SPB
|
SPC
|
2)V-belt pulleys with solid hub
SPZ
|
SPA
|
SPB
|
SPC
|
3) Adjustable Speed V-belt pulleys prebored and for taper bushes
| Type | Profile |
| 5VS092-1 | 10X6 SPZ |
| 5VS093-1 | 10X6 13X8 |
| 5VS108-1 | 10X6 13X8 SPZ SPA |
| 5VS120-1 | 10X6 13X8 SPZ SPA |
| 5VS138-1 | 10X6 13X8 SPZ SPA |
| 5VS159-1 | 10X8 SPA |
| 5VS180-1 | 10X8 17X11 SPA SPB |
| 5VS120-2 | 10X6 13 X8 SPZ SPA |
| 5VS138-2 | 10X6 13 X8 SPZ SPA |
| 5VS159-2 | 13X8 SPA |
| 5VS180-2 | 13X8 17X11 SPA SPB |
| 5VS200-2 | 13X8 17X11 SPA SPB |
| 5VS250-2 | 13X8 17X11 SPA SPB SPC |
Tips For Replacing a Belt Tensioner
When replacing a serpentine belt or automatic tensioner, you will need a special tool. This tool has a long, flat extension handle that allows you to place a socket onto the bolt and flats on the tensioner arm. The following are some tips to follow when replacing the belt or tensioner on your vehicle. To replace your belt or tensioner, you should start by checking the tensioner’s lubrication.
Serpentine belt
If you notice that the power steering or air conditioning are not working, you should check the serpentine belt tensioner. A malfunctioning serpentine belt tensioner can lead to a host of other issues. The belt may stretch, which can be caused by several factors. Over time, serpentine belt tensioners can also get worn down. Additionally, they can have a variety of other problems, including rust or dirt in the housing.
You can replace your serpentine belt by following the instructions found on your vehicle’s manual. Some tensioners attach to the engine via a single bolt. To remove and replace the belt, remove the old unit and the retaining bolt. Locate the locking pin in the engine and place the new tensioner over it. Use a torque wrench or hand tool to tighten the bolts. When installing the new tensioner, be sure to line up the mounting bolt holes with the mounting bolts. Once the tensioner is installed, test the tension by ensuring that the gauge is above the ribs. If it slides down, it is time to replace the tensioner.
Before you begin the process of replacing your serpentine belt, be sure to park your vehicle in a level area. Turn off the engine and chock both rear wheels before starting the process. Using a diagram from your vehicle’s repair manual can make the process easier, especially if you are a beginner. You can draw it in your hand, or refer to a repair manual to find out the exact location of the tensioner pulley.
If you notice that the belt is slipping or squealing while driving, it may be time to replace the serpentine belt tensioner. A worn-out belt can cause the belt to slip and can cause power steering, air conditioning, and alternator malfunctions. You should also check the belt tensioner regularly. The motor may stall or make a loud noise. These are all signs of worn-out serpentine belt.
A serpentine belt uses less space in the engine than a V-belt. It also provides more tension for the serpentine belt, which prevents it from running hot and squealing. Serpentine belts are manufactured to last for several hundred thousand miles. They are a must-have item for your car! So be sure to keep it maintained and properly adjusted! Then, you can be sure to have your car running smoothly and safely.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should replace your serpentine belt tensioner. A serpentine belt tensioner is a simple self-10sioning device that is mounted on the front of the engine. These devices are usually easy to replace and are not complicated to install. You can find 1 at any parts store or online. When the time comes to replace your serpentine belt, don’t hesitate to get the parts you need from a local auto part store.
Idler pulley
The idler pulley and the belt tensioner are essential components of your car’s drivetrain. If any 1 of them fails, all of them must be replaced. This is because they were manufactured at the same time and most likely have the same number of miles on them. As a result, they can all fail within a few thousand miles of each other. Here are some of the symptoms that you should look for when inspecting your idler pulley or belt tensioner.
Idler pulleys are a common part of most cars. They play a vital role in the operation of the belt system by directing the belt’s path and providing additional contact with the pulley. The idler pulley is also responsible for turning the cooling fan in an air-cooled Corvair engine. Because of these functions, idler pulleys are often replaced with idlers that differ in size.
Idler pulleys are small, 2 to 4 inches in diameter and mounted on the front of the engine block. Their purpose is to create a constant amount of tension on the drive belt. When the idler pulley is worn out, the accessory drive belt may experience excessive vibration and squealing noises. You may wish to replace it as soon as possible. You can do so at AutoZone.
A worn or damaged idler pulley will require a replacement. The belt itself will not fall off the car unless the idler pulley is damaged. A squealing sound can be a sign of a broken spring. Alternatively, a mechanic can recommend a replacement based on the condition of the idler pulley. In most cases, idler pulleys are more durable than the belts and are therefore recommended for replacement.
You can also notice that the idler pulley is slipping or causing excessive noise. Its constant rotation wears the idler pulley and reduces the tension of the belt. This causes the belt to slip and may even tear off the engine. Ultimately, this could result in stalling. And if you notice the engine belt squealing or making excessive noises, you should consider replacing it.
An idler pulley for a belt tensioner are often confused. Though both of them are used in the same application, they differ in many ways. The tensioner is the 1 that receives pressure from the belts and moves them. The idler pulley is not attached to an adjustable bolt, and it can cause unusual noises. It might even make squealing or odd noises.
Spring tensioner
A spring belt tensioner is a solution to a loose belt. It features a strong torsion spring that reduces slack. These devices are designed to fit up to 6mm wide belts. They are highly reliable and durable. They are also suitable for applications where the engine speed is often fluctuating. Here’s how you can choose the best 1 for your vehicle. The spring in the tensioner should be in the proper position to keep the belt taut and free of slippage.
The RunRight tensioner is a durable, high-quality product that uses aluminum alloy. Its elastomeric inserts rely on highly elastic natural rubber for good shape memory and durability. Spring tensioners are easy to install and maintain. They are designed for both axial and helical drives. They feature detailed technical drawings and 3-D models to help you determine the best 1 for your application. To choose a spring tensioner, visit our website.
A worn bushing in the tensioner pulley or a loose pivot arm can result in excessive noise, vibration, and premature belt failure. In addition, worn springs cannot maintain proper tension. Over time, they lose tension. The pulley arm itself can also become damaged, preventing it from rotating properly. If these problems occur, you’ll need to replace the spring tensioner. If you don’t see any signs of wear, check your mounting bracket and tensioner.
A worn pivot bushing can cause the tensioner arm to misalign, leading to excessive back and forth sway. It may also cause the tensioner to jam, which means the belt is too long or too short. If you notice excessive wobble, you should replace the spring tensioner. A faulty tensioner may also be causing excessive oscillation in the pulley. To determine if the spring tensioner is too weak or jammed, check the belt’s length by using a breaker bar or socket with a long handle ratchet.
When it’s time to replace your serpentine belt, don’t forget to replace the belt tensioner. The tensioner protects other components from premature failure. It is a relatively inexpensive repair. It should be replaced as part of a larger multi-ribbed belt. It also provides protection for other components of the drive system. In addition to its protection and performance, the tensioner is inexpensive and relatively easy to replace.
It’s vital to check the tensioner and idler pulleys to make sure the system is aligned properly. If they don’t align, the belt will slip and cause premature wear. Alternatively, the tensioner may have too much tension, overloading the shaft bearings and causing premature failure in other parts. You should also check the idler pulleys for noise as well, since these are engine-driven accessories.


China supplier PU/Rubber Timing Belt for Industrial Machine near me factory
Product Description
CZPT Industrial Equipment Co.;,;Ltd,; was founded in 2007,; and located in a coastal cosmopolis—HangZhou,; with its convenient transportation facilities.; CZPT specializes in producing synchronous belts and synchronous pulley,; and we have devoted ourselves to the research and development of Chinese transmission products,; we spare no effort to promote the progress of the transmission technology,; integrated design,; research,; production,; sales and after-sales service.; We have become a professional manufacturer in domestic market due to our large-scale production ability,; great variety,; efficient delivery and excellent quality.;
As 1 of the most excellent synchronous belts suppliers of Asia,; CZPT can provide you all sorts of belts,; industrial synchronous belts,; transmission belt,; rubber synchronous belts,; PU synchronous belts,; double-sided synchronous belts,; special synchronous belts (blocks,; Sponge,; PU glue,; PVC decorative pattern,; rubber and all sorts of material can be added on the surface of belt);,; automotive belt,; ribbed V-belts,; and matching aluminum synchronous pulley,; steel synchronous pulley,; copper synchronous pulley,; locking assembles,; taper bushing series.; Also we are CZPT to process according to customer’s blueprint.;
Our products are widely applied to security,; glass ceramic,; wood,; metal plastic,; printing,; packaging,; textile,; food,; tobacco,; instrument,; communication and cable,; electronics,; automobile,; sports and other industries of mechanical transmission.;
Products name:; Timing Belts
Material:; Polyurethane
Main type:; MXL/XL/L/H/XH/XXH/T2.;5/T5/T10/T20/AT5/AT10/AT20/HTD2M/3M/5M/8M/14M/STD2M/S3M/S5M/S8M/S14M/RPP3M/RPP5M/RPP8M/RPP14M
Brand name:; Jbosun
Place of origin:; HangZhou,; China (mainland);
Packing method:; Export Carton
Delivery Detail:; About 7 days after receiving 30% T/T payment in advance.;
Application
1.; Office automation equipments
2.; Medical equipment
3.; Packaging machinery.;
4.; Swimming pool cleaning robots
5.; Plotters
6.; Money changers
7.; Optical instruments
8.; Robotic arms
9.; Electric appliances
10.; Vacuum systems
11.; Vending machines
12.; Food machinery
13.; Textile machinery
14.; DIY equipments
Any question or need,; please kindly contact us.; Will reply ASAP!
| Timing Belt | ||||
| Type | Pitch | Tooth height | Belt thickness | |
| pb(mm); | ht(mm); | hs(mm); | ||
| T-type |
MXL | 2.;032 | 0.;51 | 1.;14 |
| XL | 5.;08 | 1.;27 | 2.;3 | |
| XXL | 3.;175 | 0.;76 | 1.;52 | |
| L | 9.;525 | 1.;91 | 3.;6 | |
| H | 12.;7 | 2.;29 | 4.;3 | |
| XH | 22.;225 | 6.;35 | 11.;2 | |
| XXH | 31.;75 | 9.;53 | 15.;7 | |
| T2.;5 | 2.;5 | 0.;7 | 1.;3 | |
| T5 | 5 | 1.;2 | 2.;2 | |
| T10 | 10 | 2.;5 | 4.;5 | |
| T20 | 20 | 5 | 8 | |
| AT5 | 5 | 1.;2 | 2.;7 | |
| AT10 | 10 | 2.;5 | 5 | |
| AT20 | 20 | 5 | 8 | |
| Arc toothHTD | 2M | 2 | 0.;75 | 1.;36 |
| 3M | 3 | 1.;22 | 2.;4 | |
| 5M | 5 | 2.;06 | 3.;8 | |
| 8M | 8 | 3.;36 | 6 | |
| 14M | 14 | 6.;02 | 10 | |
| 20M | 20 | 8.;4 | 13.;2 | |
| Arc tooth STD | S2M | 2 | 0.;76 | 1.;36 |
| S3M | 3 | 1.;14 | 2.;2 | |
| S5M | 5 | 1.;91 | 3.;4 | |
| S8M | 8 | 3.;05 | 5.;3 | |
| S14M | 14 | 5.;3 | 10.;2 | |
| Arc tooth RPP | RPP3M | 3 | 1.;15 | 1.;9 |
| RPP5M | 5 | 1.;95 | 3.;5 | |
| RPP8M | 8 | 3.;2 | 5.;5 | |
| RPP14M | 14 | 6 | 10 | |
Types of V-Belts and Their Properties
A v-belt’s inside length and pitch are determined by measuring along the bottom side. The included angle of a v-belt is measured from its flanks when it is extended. Most v-belt sections are 40 degrees. There are different types of v-belts, and the dimensions of each are standardized by different organizations. This article will introduce the different types of v-belts and their properties.
Notched v-belts reduce bending stress
Notched V-belts reduce bending stress by reducing the axial length of the belt by 2 or more notches. These notches are characterized by different profiles, which differ in the pitch angle and the inside length. ISO and DIN standards are followed by the manufacturers of these belts. Notched v-belts are used on industrial machinery in countries other than the US.
Compared to the standard V-belts, notched ones are designed to resist bending stress better and offer better heat dissipation. They also last longer and run cooler than standard V-belts. Furthermore, they are about 2 percent more energy efficient than their standard counterparts. Therefore, notched V-belts are a viable replacement for standard V-belts.
Notched V-belts are commonly used in industrial applications because of their low price, ease of installation, and availability of many sizes. Another advantage of notched V-belts is that they provide more wedging force and higher load capacity. Notched V-belts have a wider v-groove than flat ones, which makes them more effective for heavy-duty applications.
Notched V-belts also provide better traction. They reduce bending stress, which is beneficial for preventing fatigue and tearing of v-belts. Additionally, v-belts can be installed in an existing equipment to add more performance. And with proper maintenance and installation, notched V-belts will provide trouble-free service for many years to come.
Ribbed v-belts reduce heat dissipation
Various kinds of v-belts are available for varying applications. The more popular types are the fractional horsepower and the double-V. Fractional horsepower v-belts are designed for light-duty applications, such as machine shop equipment and household appliances. The common sectional names are 2L, 3L, 4L, and 5L. The L in each of these belts refers to the top width of the belt, multiplied by 1 eighth inch.
Unlike conventional belts, ribbed v-belts are flexible, making them ideal for use in vibrating loads. They reduce heat dissipation and can be ordered in single or multiple sets to match your application. However, ribbed v-belts should not be mounted on deep-groove sheaves, as this can cause the belt to turn over. If you use deep-groove sheaves, the risk of rupture is very high. Deep-groove sheaves can also cut banded belts. Extremely worn sheaves can also cause the belt to rip.
The 2 types of ribbed v-belts differ in their construction and application. While both types have trapezium cross-sections, they are similar in that they are made of polyurethane or other durable materials. Ribbed v-belts have an additional layer of fabric on the elastomer core for reduced noise and better heat dissipation.
Ribbed v-belts are available in a variety of sizes, including trough v-belts. Their cross-sections are categorized by their top and bottom widths and depths. The included angle of most v-belt sections is approximately 40 degrees. Different types of v-belts have different cross-sections, and these cross-sections are standardized by various organizations.
As the load increases, a ribbed v-belt will wedge into the groove and decrease the amount of friction needed to maintain the correct torque. Flat belts can track off the pulleys due to friction. However, V-belts are more stable and require less width than flat belts. The main advantage of ribbed v-belts is their increased efficiency.
The global-local finite-element model is also used to calculate the maximum and minimum J-integrals during a belt’s running cycle. The data is then used to evaluate the durability of ribbed v-belts in various applications. The numerical models used for the calculations involve a ribbed V-belt with 5 full ribs.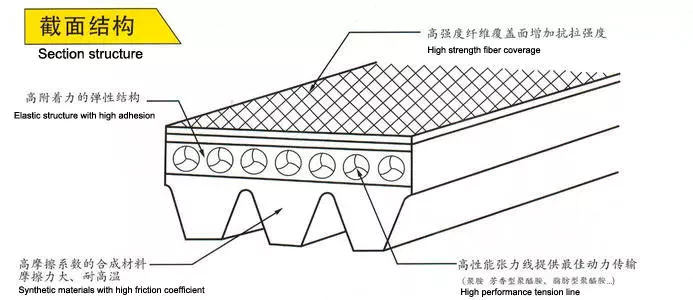
Cogged v-belts increase lateral rigidity to reduce belt whip
Cogged v-belts are designed for maximum performance and durability on even the harshest drive systems. These belts are made from high-modulus polyester cords that resist hardening and stretch and provide superior balance and strength. They also feature raw-edge sidewalls to reduce slip and drive vibration. In addition, they have specially-formulated rubber compounds for oil resistance. CZPT Cog-Belt offers substantial savings in downtime, energy consumption and horsepower.
A double cogged v-belt combines the benefits of cogged and double vee-belts. Its bonded reinforced tie band offers enhanced flexibility and reduces belt whipping in multiple-belt drives. Double cogged v-belt dimensions vary depending on the standards of the manufacturer. Regardless of the type, you’ll want to use a belt that is aligned correctly.
Standard v-belts are also known as wrapped or raw edge v-belts. Wrapped V-belts feature fabric covers above and beneath the cord to increase lateral rigidity and reduce belt whip. Cogged V-belts also have fabric covers to prevent wear on the core and increase the belt’s operating temperature. They’re ideally suited for applications that require high-temperature operation.
Cogged V-belts can significantly decrease energy consumption and improve power transmission capabilities. They also have a bias-cut cover stock that provides axial and lateral stability while preserving the cord integrity. A fiber loaded cogged construction offers optimum flexibility while minimizing heat buildup. It can be installed on any type of drive, including chain conveyors and industrial-grade machines.
The two-layer tie-band permanently bonds multiple belts together. This provides maximum cord support, heavy shock absorption, and stability. The belts are also engineered with patented banding processes that eliminate belt turnover and distribute load evenly across the drive. CZPT Cog-Band Belts minimize belt whip and provide stability. They also minimize belt turnover and rollover in heavy-duty industrial applications.
A classic v-belt is the most common and economical belt. Its nominal dimensions are 1/2″ to 1-11/2″ wide and 16″ to 400 inches long. The width is usually 40 degrees. Different organizations use different cross-sections to classify v-belts. The following table provides a general comparison of the 2 types. The Cogged V-Belt is designed to reduce belt whip by increasing the lateral rigidity of the belt.
Cogged v-belts provide superior environmental resistance
The patented design of the Dayco V-Belt provides maximum power transmission while combining the benefits of a cogged belt and raw-edge construction. The belt’s top cogged design helps increase air flow around it, preventing deterioration and extending its useful life. The belt’s three-ply design features neoprene impregnated fabric for superior durability and a specially-formulated polyester cord for increased strength and stability.
A variety of v-belts are available, with cogged and notched versions presenting unique characteristics. Cogged V-belts are more flexible than uncogged versions and feature ‘X’-shaped grooves for enhanced heat dissipation. Cogged V-belts are interchangeable with conventional v-belts, although their ‘X’ design is most common. Hexagonal v-belts are a popular option for applications where traction is needed.
Another type of Cogged V-belt is designed specifically for outdoor power equipment. This v-belt is brown, with smooth clutching covers. Its aramid cord is very strong and provides superior durability in adverse conditions. Cogged V-belts can withstand severe shock loads and are therefore ideal for outdoor power equipment. Furthermore, they offer superior environmental resistance, minimal stretch, and a long service life.
A Cogged V-belt is composed of tensile cords that are supported by a rubber stock. Different manufacturers use different synthetic rubber stocks for this purpose. These materials help to extend the belt’s operating temperature range and resist premature failure. In addition to tensile cords, the belt’s body is covered with a fabric cover. The fabric is treated to form a chemical bond with the core materials, which allows it to withstand constant bending.


China supplier Pneumatic Steel Combo Strapping Tensioning and Cutting Machine near me factory
Product Description
Product Description
Easy to operate
Put on the buckles
First,pass the steel opening through the steel belt,then wrap the steel strip around the bound object,then insert it into the steel opening and bend it about 50mm away from the steel buckle.
Tighten the strap
Rotate the take up machine clockwise,and the tension wheel turns to make the steel belt tighten until it reaches the saturation state,and the tension wheel will stop rotating.
Lock the packing buckle
Place the locking machine on the steel buckle and press the switch handle to complete the locking.
Cut the strap
After completing the locking action,tilt the tensioning machine to the vertical position until the syeel strip breaks,and then turn the rotating ring to the stop position.
Note.
This packer is a steel belt packer,please be careful in the use process!To prevent the steel sheet from hurting people!Take up the tension machine until the upper steel belt needs to be clamped,and the double layer steel strip is not required to be clamped into the tension wheel.
Product Parameters
| Model | FLT/S19-25-32 |
| Air pressure | 0.49-0.63Mpa |
| Steel strip tension speed | 85mm/sec |
| Tension force | 8.5KN |
| Tensioner weight | 4.1kg |
| Sealer weight | 3.1kg |
| Straps specification | Width:19-32mm,thickness:0.8-1.2mm |
| Strength of extension | 15KN |
Company Profile
ZheJiang Ditu Import and Export Co., Ltd. is a company specializing in the development and sales of TIJ inkjet printers, strapping tools, continuous band sealing machines, carton sealing machines, vacuum machines and other packaging equipment, and provides comprehensive services for various related products . Ditu Import and Export Company has a registered capital of 5 million yuan. Established in 2011, it is located in HangZhou, ZheJiang , an innovative highland/big lake city. We have many years of experience in the coding and packaging equipment industry, and have accumulated strong R&D and production capabilities. Ditu Import and Export has professional R&D personnel and cooperates with many high-tech companies to develop, design and customize product molds according to customer requirements. Main business: TIJ inkjet printer, CIJ inkjet printer, laser marking machine, pneumatic strapping tool, electric battery strapping tool, vacuum machine, continuous band sealing machine, carton case sealer machine, accessories and consumables. Products are widely used in printing, electronics, plastics, hardware, food and beverage, medicine, cosmetics, wood, auto parts, cables and building materials and other fields. So far, we have more than 50 distributors in 30 countries/regions including India, Bangladesh, Russia, Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, and Malaysia. Ditu Import and Export always takes customer needs as the benchmark, and constantly integrates and upgrades while pursuing innovation, and strives to provide personalized services for all products, and strive to become the most intimate and reliable supplier.
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
Exhibition
Payment Options
FAQ
Why You Should Get a New Timing Belt
A timing belt is a rubber belt with teeth that transfer rotary motion from the central motor to the drive pulley. It prevents the piston from striking the valves at a critical level. Unfortunately, these belts cost a lot to replace. Here are some reasons why you should consider getting a new one. If you’re not sure whether a new timing belt is necessary, read on. You can also save money by avoiding unnecessary repairs and replacements by choosing an aftermarket timing belt.
Timing belts are rubber belts with hard teeth
While it’s true that timing belts are commonly known as “drive belts,” there are several different types of belts that are used in engines. Despite their commonity, timing belts are made of different materials. The material used to make them is important because it can either negatively impact performance or negatively affect its life span. Whether it’s a car, truck, or motorcycle, timing belts are an essential part of your engine.
Among their many advantages, timing and drive belts are designed to reduce friction, increase speed, and transmit torque more efficiently. In fact, the design of timing belts is similar to that of a cam belt. Both belts work in conjunction with each other to increase the torque and speed of a vehicle. In both types, the teeth of the belt are aligned at the same angle. In a small-scale drive system, this elongation is minimal, but if the load is too high, the teeth of the belt will begin to jump or cog over the pulley’s teeth, causing the noise.
Timing belts are used to synchronize the movement of the crankshaft and camshaft. Timing belts have hard teeth on the inner side of the belt and interlock with the cogwheels on the crankshaft and camshafts. Because of this, they make it easier for the exhaust and intake valves to open and close at the proper time. Timing belts are made of high-10sile rubber, but they may also be polyurethane, welded urethane, or moulded polyurethane.
When a timing belt is worn, it may degrade. The teeth will gradually lose their shape over time and the belt will begin to slip. If the teeth become rounded, the belt may still work, but its timing will be off. Hence, it is vital to replace the timing belt if you notice these signs. If you find any damage, contact a qualified mechanic for repair. If the teeth are worn or damaged, consider replacing the entire belt.
When it comes to a car’s engine, timing is vital. Timing belts connect the internal moving parts of the engine. In addition to timing, they can also power water, oil, and injection pumps. And it’s vital to make sure your timing belt doesn’t get damaged because it will not function properly. So don’t neglect timing belts unless you’re certain they’re damaged.
They transfer rotary motion from the central motor to the drive pulley
A timing belt is a mechanical device that transfers rotary motion from a central motor to a drive pulley through a chain. The belt must be wide enough to accommodate the torque that will be produced by the design. The belt must be wider than the size selected for the drive pulley. In order to determine the correct belt width, the center-to-center distance between the drive pulley and the central motor is measured.
Unlike the elastic belt, which tends to stretch when pressed against a large load, the timing belt does not suffer from this problem. Instead, it exhibits low torsional stiffness, which allows it to transfer rotary motion efficiently. The timing belt also reduces the likelihood of slippage. This is because the cord material is very strong compared to the loads that it must handle.
The most common type of timing belt pulley is made of nylon. The advantage of nylon is that it has a natural lubrication surface and is relatively low-maintenance. It is also durable, malleable, and low-melting point. It is also highly resistant to wear and tear and is suitable for applications that are exposed to high temperatures. However, the belt must be cleaned and maintained on a regular basis.
A Timing belt can be used in a variety of applications. For instance, the timing belt is used in automotive engines. However, the timing belt is also found in stationary power generators, marine engines, and aviation engines. Additionally, it is used in conveyors, winches, treadmills, and washing machines. It also plays a crucial role in the curtain at a theater hall.
The timing belt can be flat, V-shaped, or trapezoidal. The latter is usually made of rubber. The distance between the 2 pulleys is between 5 and 10 meters. The flat belts transmit power through friction between the belt and the pulley. The efficiency of flat belts is approximately 98% and it makes very little noise. However, it must be used in conjunction with the appropriate motor drive. Ultimately, the engineers must choose the best 1 that can deliver the torque that the drive pulley needs to generate.
They prevent pistons from striking the valves on a critical level
In an interference engine, the valves and pistons share the same space in the cylinder, but they move at different rates. While 1 or more of the valves may open into the piston’s travel area, the other is closed and never makes contact with the piston. Timing belts prevent this critical collision from occurring and prevent the piston from damaging the engine. Most timing belts fail at start-up and shutdown. Check the car owner’s manual for recommended replacement intervals.
The timing belt synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft. The timing belt allows the piston to move without striking the valves, allowing the engine to perform its essential functions. The camshaft is used to push fuel and air into the cylinder. The valves close and open as the engine moves forward. When the engine is running, the timing belt prevents the piston from striking the valves on a critical level.
Because of their critical role in the engine, timing belts are often an overlooked component. Without proper timing, an engine will not work properly, and valve damage can be costly. If timing fails, the piston will strike the valves on a critical level, which will damage the engine. Timing belts are a vital automotive component, so make sure yours is in good condition.
A timing belt is a necessary part of your Subaru’s engine. It synchronizes the crankshaft and camshaft to prevent problems with the engine. If a timing belt breaks, the pistons will strike the open valves and cause massive engine damage. Timing belts must be replaced when recommended in your owner’s manual. If it breaks, the engine will shut down.
They cost a lot to replace
Timing belts are expensive to replace, with the average car owner paying $1,200 to have them replaced. Most cars have transverse engines, where the cam cover rests against the driver’s side of the engine. These specialty cars are notoriously difficult to service and require the services of a specialist mechanic. Timing belts are a complex system with a series of idler bearings and tensioner bushes to guide and drive the belt. These components are often replaced at the same time as other routine maintenance work, and they may cost you a bundle.
If you have a car that’s been in the shop for a while, timing belt replacement may be the only option. A timing belt that’s popped isn’t going to make the car run, so you’ll need to get it replaced. If you need the belt replaced, you can use a car service, or you can try to replace the timing belt yourself. It’s a good idea to get several quotes before making the decision to replace the belt.
Depending on the make and model of your car, timing belt replacement costs may range from $250 to more than $1,000. Prices will vary according to vehicle type, labor hours, and the brand of parts and labor. If you don’t have a mechanic handy, you can always use a free online tool like CZPT to get an estimate for timing belt replacement and find a mechanic near you. This will help you save money and avoid the hassle of spending a lot of money on an unnecessary repair.
While timing belts typically last between 60,000 and 100 thousand miles, you may only need to replace them once in your car’s lifetime. Timing belts may seem cheap at first, but if you’re planning on selling your car, you’ll want to avoid the expense of replacing your timing belt. If you don’t, your car’s engine may run poorly and cause your car to use more fuel than it should.

