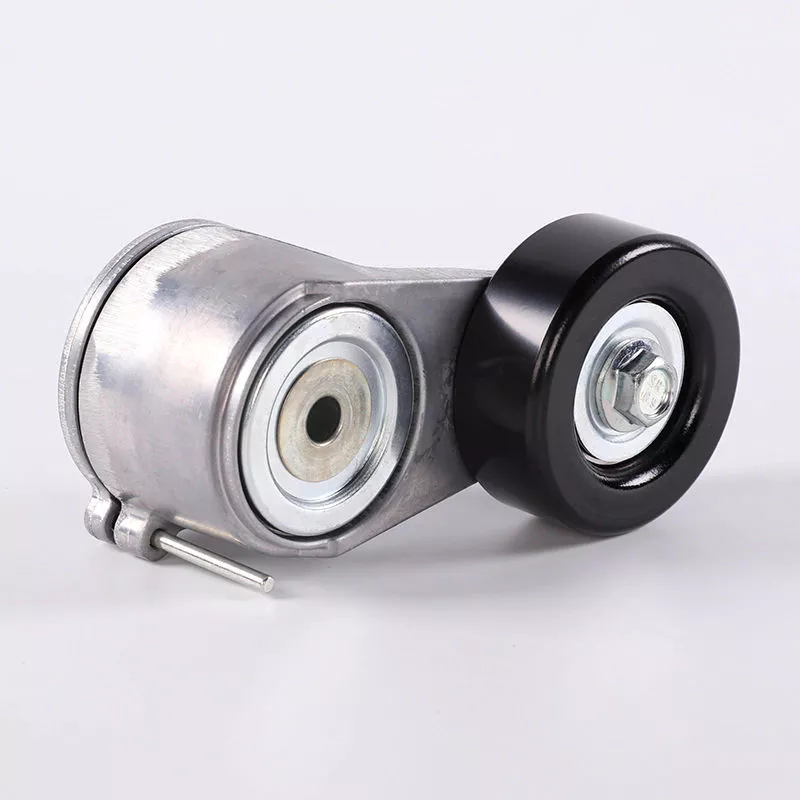
Merchandise Description
CZPT Machinery gives a vast assortment of large top quality Timing Belt Pulleys and Toothed Bars/ Timing Bars. Normal and non-common pulleys in accordance to drawings are offered.
Kinds of substance:
1. AlCuMgPb 6061 6082 Aluminum Timing Pulley
2. C45E 1045 S45C Carbon Metal Timing Pulley
3. GG25 HT250 Solid Iron Timing Pulley
4. SUS303 SUS304 AISI431 Stainless Metal Timing Pulley
5. Other materials on demand from customers, these kinds of as cooper, bronze and plastic
Kinds of surface area treatment method
1. Anodized area -Aluminum Pulleys
2. Hard anodized surface — Aluminum Pulleys
3. Black Oxidized surface — Steel Pulleys
4. Zinc plated floor — Steel Pulleys
5. Chromate area — Steel Pulleys Cast Iron Pulleys
6. Nickel plated area –Metal Pulleys Forged Iron Pulleys
Types of enamel profile
| Teeth Profile | Pitch |
| HTD | 3M,5M,8M,14M,20M |
| AT | AT5,AT10,AT20 |
| T | T2.5,T5,T10 |
| MXL | .08″(2.032MM) |
| XL | one/5″(5.08MM) |
| L | three/8″(9.525MM) |
| H | one/2″(twelve.7MM) |
| XH | seven/8″(22.225MM) |
| XXH | one 1/4″(31.75MM) |
| STS STPD | S2M,S3M,S4.5M,S5M,S8M,S14M |
| RPP | RPP5M,RPP8M,RPP14M,RPP20M |
| PGGT | PGGT 2GT, 3GT and 5GT |
| PCGT | GT8M,GT14M |
Kinds of pitches and measurements
Imperial Inch Timing Belt Pulley,
one. Pilot Bore MXL571 for 6.35mm timing belt teeth quantity from sixteen to seventy two
two. Pilot Bore XL037 for 9.53mm timing belt enamel variety from 10 to 72
3. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore L050 for twelve.7mm timing belt tooth amount from 10 to one hundred twenty
four. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore L075 for 19.05mm timing belt tooth quantity from 10 to a hundred and twenty
5. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore L100 for twenty five.4mm timing belt tooth amount from 10 to a hundred and twenty
6. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H075 for 19.05mm timing belt teeth number from fourteen to 50
seven. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H100 for 25.4mm timing belt teeth variety from fourteen to 156
8. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H150 for 38.1mm timing belt teeth variety from 14 to 156
9. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H200 for 50.8mm timing belt enamel variety from fourteen to 156
10. Pilot Bore, Taper Bore H300 for 76.2mm timing belt tooth number from fourteen to 156
eleven. Taper Bore XH200 for 50.8mm timing belt enamel amount from 18 to a hundred and twenty
12. Taper Bore XH300 for seventy six.2mm timing belt teeth variety from 18 to 120
thirteen. Taper Bore XH400 for one zero one.6mm timing belt enamel number from 18 to a hundred and twenty
Metric Timing Belt Pulley T and AT
1. Pilot Bore T2.5-16 for 6mm timing belt teeth amount from twelve to 60
2. Pilot Bore T5-21 for 10mm timing belt teeth variety from ten to 60
3. Pilot Bore T5-27 for 16mm timing belt tooth amount from ten to 60
four. Pilot Bore T5-36 for 25mm timing belt tooth quantity from 10 to 60
5. Pilot Bore T10-31 for 16mm timing belt tooth number from twelve to 60
six. Pilot Bore T10-40 for 25mm timing belt tooth number from twelve to 60
7. Pilot Bore T10-47 for 32mm timing belt tooth quantity from eighteen to 60
8. Pilot Bore T10-66 for 50mm timing belt enamel quantity from 18 to sixty
nine. Pilot Bore AT5-21 for 10mm timing belt enamel amount from 12 to 60
ten. Pilot Bore AT5-27 for 16mm timing belt tooth amount from twelve to sixty
11. Pilot Bore AT5-36 for 25mm timing belt tooth amount from 12 to 60
12. Pilot Bore AT10-31 for 16mm timing belt teeth number from fifteen to 60
thirteen. Pilot Bore AT10-40 for 25mm timing belt teeth number from 15 to 60
fourteen. Pilot Bore AT10-47 for 32mm timing belt teeth number from 18 to 60
fifteen. Pilot Bore AT10-66 for 50mm timing belt teeth amount from eighteen to 60
Metric Timing Belt Pulley HTD3M, 5M, 8M, 14M
one. HTD3M-06 3M-09 3M-15 teeth number from ten to 72
2. HTD5M-09 5M-15 5M-twenty five enamel amount from 12 to 72
3. HTD8M-20 8M-thirty 8M-fifty 8M-eighty five enamel number from 22 to 192
4. HTD14M-40 14M-55 14M-eighty five 14M-one hundred fifteen 14M-a hundred and seventy teeth quantity from 28-216
5. Taper Bore HTD5M-15 8M-20 8M-30 8M-fifty 8M-eighty five 14M-40 14M-fifty five 14M-eighty five
14M-115 14M-170
Metric Timing Belt Pulleys for Poly Chain GT2 Belts
1. PCGT8M-twelve PCGT8M-21 PCGT8M-36 PCGT8M-62
2. PCGT14M-twenty PCGT14M-37 PCGT14M-68 PCGT14M-ninety PCGT14M-a hundred twenty five
Energy Grip CZPT Tooth/ PGGT 2GT, 3GT and 5GT
one. 2GT-06, 2GT-09 for timing belt width 6mm and 9mm
two. 3GT-09, 3GT-fifteen for timing belt width 9mm and 15mm
three. 5GT-fifteen, 5GT-25 for timing belt width 15mm and 25mm
OMEGA RPP HTD Timing Pulleys
one. RPP3M-06 3M-09 3M-15 tooth variety from 10 to 72
two. RPP5M-09 5M-15 5M-25 teeth amount from twelve to 72
three. RPP8M-twenty 8M-30 8M-50 8M-eighty five enamel variety from 22 to 192
4. RPP14M-forty 14M-fifty five 14M-eighty five 14M-one hundred fifteen 14M-one hundred seventy tooth number from 28-216
five. Taper Bore RPP5M-fifteen 8M-20 8M-30 8M-50 8M-eighty five 14M-40 14M-fifty five 14M-eighty five
14M-one hundred fifteen 14M-a hundred and seventy
|
US $0.5-50 / Piece | |
10 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Certification: | ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | Timing |
| Manufacturing Process: | Sawing |
| Material: | Aluminum 6082 |
| Surface Treatment: | Phosphating |
| Application: | Chemical Industry, Grain Transport, Mining Transport, Power Plant |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 3/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Teeth Profile | Pitch |
| HTD | 3M,5M,8M,14M,20M |
| AT | AT5,AT10,AT20 |
| T | T2.5,T5,T10 |
| MXL | 0.08"(2.032MM) |
| XL | 1/5"(5.08MM) |
| L | 3/8"(9.525MM) |
| H | 1/2"(12.7MM) |
| XH | 7/8"(22.225MM) |
| XXH | 1 1/4"(31.75MM) |
| STS STPD | S2M,S3M,S4.5M,S5M,S8M,S14M |
| RPP | RPP5M,RPP8M,RPP14M,RPP20M |
| PGGT | PGGT 2GT, 3GT and 5GT |
| PCGT | GT8M,GT14M |
|
US $0.5-50 / Piece | |
10 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Certification: | ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | Timing |
| Manufacturing Process: | Sawing |
| Material: | Aluminum 6082 |
| Surface Treatment: | Phosphating |
| Application: | Chemical Industry, Grain Transport, Mining Transport, Power Plant |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 3/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Teeth Profile | Pitch |
| HTD | 3M,5M,8M,14M,20M |
| AT | AT5,AT10,AT20 |
| T | T2.5,T5,T10 |
| MXL | 0.08"(2.032MM) |
| XL | 1/5"(5.08MM) |
| L | 3/8"(9.525MM) |
| H | 1/2"(12.7MM) |
| XH | 7/8"(22.225MM) |
| XXH | 1 1/4"(31.75MM) |
| STS STPD | S2M,S3M,S4.5M,S5M,S8M,S14M |
| RPP | RPP5M,RPP8M,RPP14M,RPP20M |
| PGGT | PGGT 2GT, 3GT and 5GT |
| PCGT | GT8M,GT14M |
Calculate the ideal mechanical advantage of pulleys
The basic equations for pulleys can be found in this article. It will also cover the different types of pulleys, the ideal mechanical advantages of pulleys, and some common uses of pulley systems. Read on to learn more! After all, a pulley is a simple mechanical device that changes the direction of a force. Learn more about pulleys and their common uses in engineering.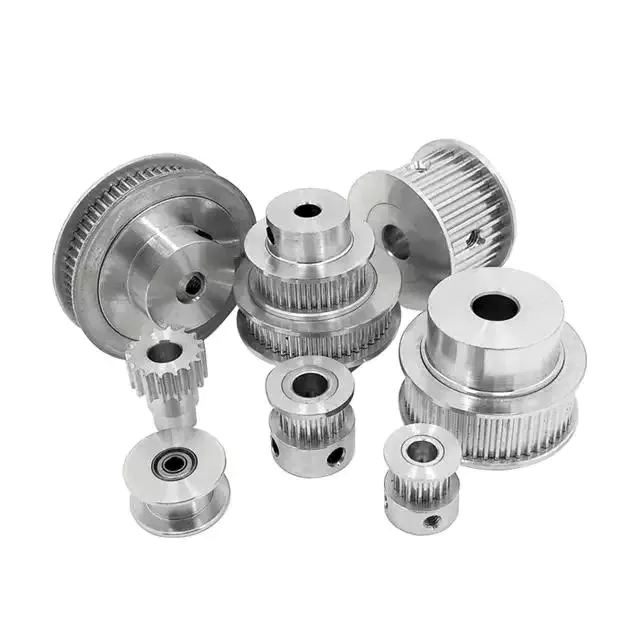
pulley basic equation
Pulleys work the same way as gravity, so they should withstand similar forces. Newton’s laws of motion can be used to calculate the forces in a pulley system. The second law of motion applies to forces and accelerations. Similar to this is Newton’s third law, which states that the directions of forces are equal and opposite. The fourth law dictates the direction of force. The Fifth Law states that tension is in equilibrium with gravity.
A pulley is a simple mechanism that transmits force by changing direction. They are generally considered to have negligible mass and friction, but this is only an approximation. Pulleys have different uses, from sailboats to farms and large construction cranes. In fact, they are the most versatile mechanisms in any system. Some of their most common applications and equations are listed below.
For example, consider two masses m. Those of mass m will be connected by pulleys. The static friction coefficient of the left stop is ms1, and the static friction coefficient of the right stop is ms2. A no-slip equation will contain multiple inequalities. If the two blocks are considered to be connected by a pulley, the coefficient of kinetic friction is mk. In other words, the weight of each block carries the same mass, but in the opposite direction.
Types of pulleys
A pulley is a device used to pull and push objects. Pulley systems are ropes, cables, belts or chains. The “drive pulley” is attached to the shaft and moves the driven pulley. They are available in a variety of sizes, and the larger they are, the higher the speed of power transmission. Alternatively, use small pulleys for smaller applications.
Two-wheel pulleys have two mechanical advantages. The greater the mechanical advantage, the less force is required to move the object. More wheels lift more weight, but smaller pulleys require less force. In a two-wheel pulley system, the rope is wound around two axles and a fixed surface. As you pull on the rope, the shafts above slowly come together.
Compound pulleys have two or more rope segments that are pulled up on the load. The mechanical advantage of compound pulleys depends on the number of rope segments and how they are arranged. This type of pulley can increase the force by changing the direction of the rope segment. There are two main types of pulleys. Composite pulleys are most commonly used in construction. The ideal mechanical advantage of pulleys is 2 or more.
Construction pulleys are a basic type. They are usually attached to wheel rails and can be lifted to great heights. Combinations of axes are also common. Construction pulleys can be raised to great heights to access materials or equipment. When used in construction, these pulleys are usually made of heavy materials such as wood or metal. They are secured with ropes or chains.
The ideal mechanical advantage of pulleys
The pulley system is a highly complex system with high mechanical advantages. Use a single pulley system to reduce the force required to lift an object by cutting it in half. The mechanical advantage increases as you add more pulleys, such as six or seven. To calculate the mechanical advantage of a pulley system, you need to count the number of rope segments between the pulleys. If the free end of the rope is facing down, don’t count it. If it’s facing up, count. Once you have your number, add it up.
The required mechanical advantage of a pulley is the number of rope segments it has to pull the load. The more rope segments, the lower the force. Therefore, the more rope segments the pulley has, the lower the force. If the rope segments are four, then the ideal mechanical advantage is four. In this case, the composite pulley quadrupled the load force.
The ideal mechanical advantage of a pulley system is the sum of the mechanical force and the force required to lift the load at its output. Typically, a single pulley system uses two ropes, and the mechanical force required to lift the load is multiplied by the two ropes. For a multi-pulley system, the number of ropes will vary, but the total energy requirement will remain the same. The friction between the rope and pulley increases the force and energy required to lift the load, so the mechanical advantage diminishes over time.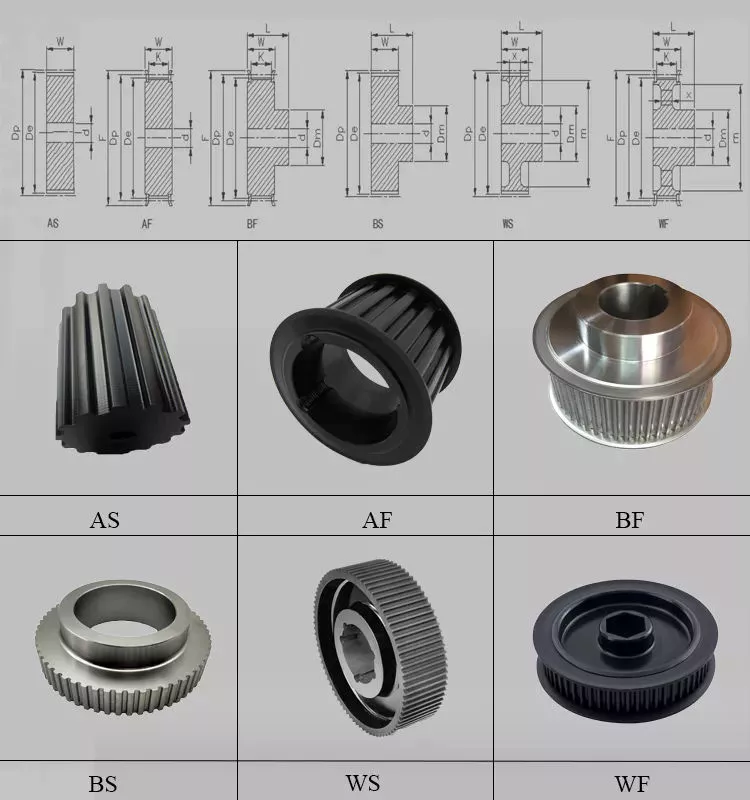
Common uses of pulley systems
A pulley system is a simple mechanical device typically used to lift heavy objects. It consists of a rotating wheel attached to a fixed shaft and a rope attached to it. When the wheel moves, the force applied by the operator is multiplied by the speed of the pulley, and the force is multiplied by the weight of the object being lifted. Common uses for pulley systems include pulling, lifting, and moving heavy objects.
The oil and petroleum industries use pulley systems in a variety of applications. Most commonly, pulleys are used in drilling operations and they are installed on top of the rig to guide the cable. The cable itself is attached to two pulleys suspended in the derrick, where they provide mechanical energy to the cable. Using a pulley system in this application provides the force needed to move the cable safely and smoothly.
The main advantage of the pulley system is that it minimizes the force required to lift an object. The force used to lift the object is multiplied by the desired mechanical advantage. The more rope segments, the lower the force required. On the other hand, a compound pulley system can have many segments. Therefore, a compound pulley system can increase the force a worker can exert on an object.
Safety Precautions to Take When Working on Pulley Systems
There are many safety precautions that should be observed when working on a pulley system. The first is to wear proper protective gear. This includes hard hats that protect you from falling objects. Also, gloves may be required. You should limit the amount of movement in the penalty area, and you should also keep the area free of unnecessary people and objects. Also, remember to wear a hard hat when working on the pulley system.
Another important safety precaution when working on a pulley system is to check the Safe Working Load (SWL) of the pulley before attaching anything. This will help you understand the maximum weight the pulley can hold. Also, consider the angle and height of the pulley system. Always use safety anchors and always remember to wear a hat when working on a pulley system.
Safe use of chain hoists requires training and experience. It is important to read the manufacturer’s manual and follow all safety precautions. If you’re not sure, you can actually inspect the hoist and look for signs of damage or tampering. Look for certifications for sprocket sets and other lifting accessories. Look for the Safe Working Load (SWL) marking on the chain hoist.
Example of a pulley system
Pulley systems are often used to lift items. It allows you to reduce the effort to lift and move the load by applying force in one direction. Pulley systems can be built and modeled to fit any type of project. This resource focuses on pulley systems and is designed to support the new GCSEs in Engineering, Design and Technology. There are also many examples of pulley systems suitable for various applications.
In the study, participants who read easy text took longer to manipulate the pulley system than those who read challenging text. In general, this suggests that participants with prior scientific experience used their cognitive abilities more effectively. Additionally, students who read simple texts spent less time planning the pulley system and more time on other tasks. However, the study did show that the time required to plan the pulley system was similar between the two groups.
In everyday life, pulley systems are used to lift various objects. Flagpoles are one of many pulley systems used to raise and lower flagpoles. They can also be used to raise and lower garage doors. Likewise, rock climbers use pulleys to help them ascend and descend. The pulley system can also be used to extend the ladder.


editor by czh 2022-12-21